Generality
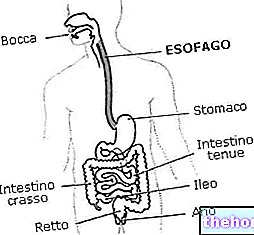
Esophagitis is a fairly common condition, characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to excessive rise of acidic juices from the stomach.
In addition to these episodes of gastroesophageal reflux, infectious diseases (in immunocompromised patients), ionizing radiation, allergies (eosinophilic esophagitis) and the ingestion of particular drugs or corrosive substances can be included among the less frequent causes of esophagitis.

Insights:
Symptoms of esophagitisMain causes of esophagitis
Risk factors
Complications of esophagitis
Diagnosis of esophagitis
Treatment
Symptoms
For further information: Symptoms of esophagitis
Difficulty and pain in swallowing (dysphagia and odynophagia), feeling that food is struggling to go down the esophagus, episodes of retrosternal chest pain, nausea, vomiting, stomach pains, regurgitation of saliva and loss of appetite.
Contact your doctor promptly if these symptoms become particularly severe, do not resolve with common over-the-counter antacids (such as sodium bicarbonate) or are associated with those typical of a flu (fever, headache and muscle aches).
Causes
Reflux esophagitis
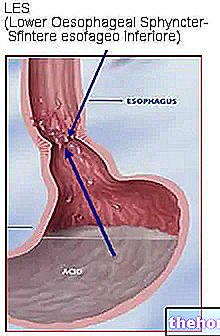
At the junction of the stomach and esophagus, there is a narrowing called the gastroesophageal sphincter. Normally ajar, this special valve opens during chewing to allow the passage of the swallowed bolus and, obviously, during belching and vomiting. The incontinence of the gastroesophageal sphincter and its opening at inopportune moments, determine the ascent into the esophagus of the gastric content which, by virtue of the marked acidity, ends up strongly irritating the mucosa. When similar episodes are repeated with an abnormal frequency, we speak of gastroesophageal reflux disease, whose chronicity sees in esophagitis one of the most important complications.
Eosinophilic esophagitis
The name recalls that of the white blood cell population responsible for controlling the inflammatory and allergic reaction. High concentrations of these cells in the esophageal tissues, together with the inevitable inflammatory state they cause, are generally the consequence of one or more food allergies (to milk, soy, wheat, peanuts, etc.); eosinophilic esophagitis can however appear in response to non-food allergies, such as those from pollen inhalation.
Drug-induced esophagitis
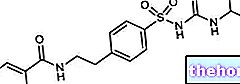
The problem occurs when a pill - taken with insufficient quantities of water - or its residues, remain in contact with the esophageal mucosa for a long time. Among the drugs potentially implicated in this type of esophagitis, we mention NSAIDs (aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, etc.), some antibiotics (tetracycline and doxycycline), potassium chloride and bisphosphonates (used in the treatment of osteoporosis).
Infectious Esophagitis
It affects immunocompromised individuals, such as HIV positive patients for many years or with cancer, and is caused by infectious agents of bacterial, fungal or viral origin. Common is Candida albicans esophagitis, a fungus normally present in the intestine, oral cavity and vagina (in concentrations that are not pathogenic); in addition to the weakening of the immune system, this type of esophagitis is favored by the prolonged use of antibiotics and by chronic hyperglycemia (diabetes).
Esophagitis - Video: Causes, Symptoms, Cures
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to Wellness Destination
- Watch the video on youtube
Risk factors
- REFLUX EXOPHAGITATES: obesity, smoking, fatty foods, alcohol and coffee, pregnancy, hiatal hernia, clothing that is too tight, eating before bedtime. For further information: nutrition and gastroesophageal reflux.
- EOSYOPHILIC EXOPHAGITES: familiarity with the pathology.
- IATROGEN EXOPHAGITATES: swallowing oddly or excessively shaped pills; ingest them with insufficient quantities of water or even without drinking; take them before bedtime.
- INFECTIOUS ESOPHAGITES: AIDS / HIV, certain types of cancer or chemotherapy treatments, use of immunosuppressive drugs (eg after organ transplantation), various diseases of the immune system.
Other articles on "Esophagitis"
- Esophagitis: diagnosis and treatment
- Medicines for the treatment of esophagitis
- Barrett's esophagus
- Medicines for the treatment of Barret's esophagus
- Diet for esophagitis