How does it work
Penile Doppler ultrasound is an imaging technique widely used in the diagnosis of erectile dysfunction, thanks to its ability to analyze penile blood flow and highlight its main alterations.
The penile echocolordoppler uses high frequency ultrasound probes (7.5-13 MHz) equipped with digital software and a color-Doppler module, which allow to analyze the waves reflected by the corpuscular part of the blood flowing into the vessels of the penis. therefore the sound waves are exploited, without administering any kind of dangerous radiation.
Dynamic Echocolordoppler
In addition to ultrasound probes and related instrumentation, the "penile ecocolordoppler, dressed in the" dynamic "adjective, involves the use of vasoactive drugs, such as papaverine and / or prostaglandin PGE1 (Alprostadil - Caverject) - injected directly into the corpora cavernosa of the penis to induce a "pharmacological erection.
In this way, by carrying out the penile echocolordoppler in basal conditions and repeating it at pre-established intervals after the injection of drugs (fic-test), it is possible to study the size and dilatation of the cavernous arteries, the speed of blood flow to the "internal vessels of the penis, and the structure of the corpora cavernosa at rest and in erection. The examination is also able to study the morphology of the penis, highlighting any ecostructural alterations such as fibrosis or calcified plaques.
In addition to the injection of drugs that cause penile vasodilation, during the examination some doctors make an erotic film available to the patient; this approach is dictated by the attempt to minimize the emotional component, with blocks of a psychic nature that could alter the results of the examination. Although - unlike the classic PDE5 inhibitors tadalafil, vardenafil, sildenafil, avanafil - the drugs injected into the cavernous bodies do not have need for a "psychic arousal to induce an erection," the patient's anxiety could still lead to a reduced response to the drug.
When you do
Penile Doppler ultrasound is generally the first-line test in case of clinical suspicion of vascular-based erectile dysfunction, for example in patients with atherosclerosis, diabetes, hypertension or other cardiovascular risk factors. The doctor may prescribe the test even after testing the therapeutic ineffectiveness of oral therapies for erectile dysfunction.
In case of positive results, to identify the presence and the exact location of an arterial problem or a venous leak highlighted by the penile echocolordoppler, it is necessary to resort to more invasive diagnostic investigations, such as cavernosometry, dynamic cavernography and selective arteriography dynamics of the penile arteries.
How it takes place
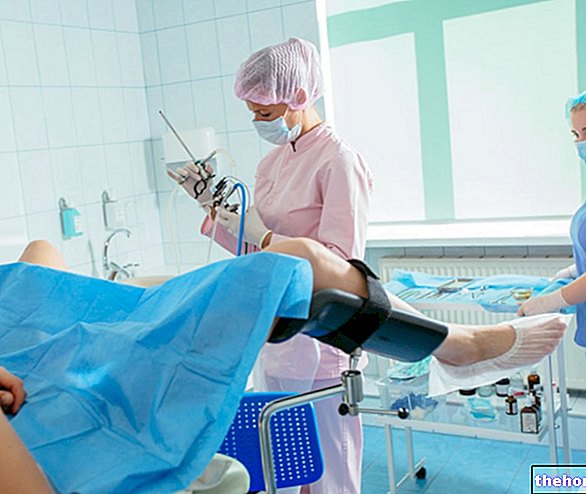
During the penile echocolordoppler the patient is normally studied in supine decubitus (lying on his stomach) with the penis resting on the anterior wall of the abdomen. The examination - which takes about 30 minutes - is not painful and the intra-canvernous injection of the drugs, if carried out according to the correct technique, well known to the doctor, besides being almost painless, does not cause any harm to the patient.
Risks
The only possible complication of penile echocolordoppler resides in the appearance of priapism: an erection that lasts beyond the effective time of the drug (about 1 hour) and which can become painful. If it occurs, priapism can be easily treated by means of appropriate local drug therapies, such as the intracavernous administration of ethylephrine, and only in rare cases requires surgical detumescence.


















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




