Generality
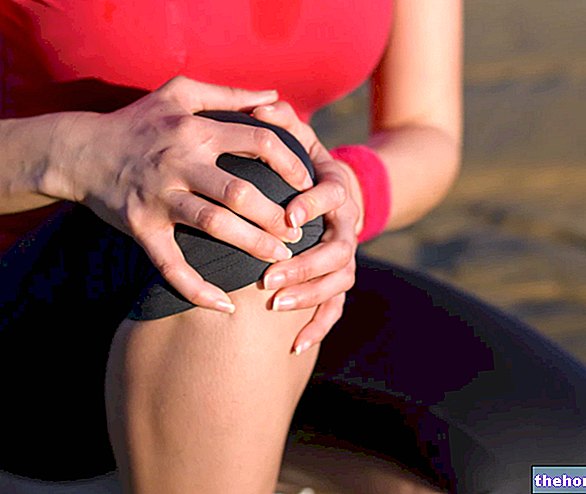
The sprain is an injury of the musculoskeletal system, characterized by the temporary alteration of the anatomical relationships that exist between the elements of the affected joint. Such an event involves damage to one or more components of the affected joint.

The main risk factors for sprain include: physical-sporting activity, insufficient muscle tone and a sedentary lifestyle.
A joint that has been sprained is painful, swollen and stiff, has lost some of its characteristic mobility, is unstable and noisy, and finally has a more or less extensive hematoma around it.
For an accurate diagnosis of sprain, physical examination, medical history, X-rays, and nuclear magnetic resonance are essential.
The treatment adopted in the event of a sprain depends on the extent of the joint damage that has occurred. For mild or moderate damage, the therapy tends to be conservative; for severe damage, on the other hand, surgery is required.