Very common in sports and among road hauliers and forklift drivers, patellar tendon inflammation is a pathology caused by functional overload, which arises from the exasperated repetition, with the knee, of an explosive extension movement.
Inflammation of the patellar tendon is typically responsible for local symptoms (ie at the knee level), such as: pain, achiness, joint stiffness and swelling.
In general, for the diagnosis of inflammation of the patellar tendon, a physical examination and anamnesis are sufficient; however, tests of imaging.
The treatment of patellar tendon inflammation is generally conservative; surgery, in fact, is indicated only in extreme cases.
Patellar tendon inflammation is a type of knee tendonitis, just like quadriceps tendonitis and popliteal tendonitis.
Patellar tendon inflammation is by far the most common type of hamstring.
Patellar Tendon: A Brief Review of Anatomy and Physiology

To fully understand the information contained in this article on patellar tendon inflammation, it is essential to know, at least in broad terms, the anatomy and physiology of the patellar tendon.
The patellar tendon, or patellar ligament, is the band of fibrous connective tissue, which joins the lower part of the patella to the characteristic prominence on the anterior aspect of the distal end of the tibia and called the tibial tuberosity.
A fundamental structural component of the knee joint, the patellar tendon has the particularity of being in continuity with the tendon complex, which connects the quadriceps femoris muscle to the upper part of the patella.
Flat, wide and approximately 4.5 cm long, the patellar tendon has the task of keeping the patella in the correct position and supporting the quadriceps femoris muscle in the knee extension action.
; it takes on the characteristics of explosive movement during motor activities such as running and, above all, jumps and leaps.
Who suffers most from Patellar Tendon Inflammation?

Patellar tendon inflammation can affect anyone; however, statistics in the hand, this annoying knee tendonitis is particularly common among:
- Those who play sports in which sudden changes of direction during running, leaps and jumps are expected (eg: volleyball, basketball, football, athletics, etc.). The particular incidence of patellar tendon inflammation in this category of people explains why patellar tendonitis is also called jumper's knee.
- Those who work as a hauler / lorry driver or forklift driver. Individuals assigned to these jobs subject the patellar tendon to stress every time it acts on the pedals in charge of controlling the vehicle.
Risk Factors for Patellar Tendon Inflammation

Knee tendonitis risk factors include:
- The practice of sports in which there are running with changes of direction and sudden braking, jumps, jumps and bending on the legs;
- The practice of jobs that involve movements that stress the patellar tendon (eg: hauler or forklift driver);
- The use of inadequate footwear;
- A lack of firmness on the part of the thigh muscles;
- Lack of flexibility on the part of the joint (this factor may depend on advanced age or sedentary lifestyle);
- The absence of physiological alignment between the patella, leg, ankle and foot (eg valgus);
- The dysmetria of the lower limbs;
- Overweight / obesity;
- The presence of chronic diseases that affect the health of the tendons (eg: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, renal failure and diabetes);
- Repeated corticosteroid injections (when used improperly, these drugs weaken the tendons).
Inflammation of the Patellar Tendon in the Young
For growth-dependent reasons, young people can suffer from two particular forms of patellar tendon inflammation: so-called Osgood-Schlatter disease and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease.
Osgood-Schlatter disease is due to an anomalous mechanism of traction of the patellar tendon against the tibial tuberosity, associated with an "immaturity of the latter"; this condition is characterized by a suffering not only of the patellar tendon, but also (and above all) of the tibial tuberosity (as it is subjected to continuous "tugging" by the patellar tendon).
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease, on the other hand, is associated with stressful phenomena that act on the portion of the patellar tendon connected to the lower part of the patella.
Osgood-Schlatter disease and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease are both the consequence of an imbalance between skeletal growth (faster) and muscle-ligament growth (slower).
.Stages of Inflammation of the Patellar Tendon

The characteristics of the pain just below the patella represent the parameter with which experts classify the severity of the inflammation of the patellar tendon; going into more detail:
- When pain under the patella appears only at the end of physical exercise, the inflammation of the patellar tendon is in its early stages; in these situations, we also speak of patellar tendonitis in stage I.
- When pain under the patella is present during and at the end of physical exercise, but is not an obstacle to the latter, the inflammation of the patellar tendon is at an intermediate stage; in these circumstances, we also speak of patellar tendonitis. II stage.
- When the pain under the kneecap is such as to prevent physical exercise from taking place and making the most trivial daily activities difficult (eg: climbing stairs, driving a vehicle, etc.), the inflammation of the patellar tendon is at an advanced stage; in such situations, it is also referred to as stage III patellar tendonitis.
In addition to "stage III patellar tendon inflammation, there is laceration of the tendon structure, the most serious and feared complication of patellar tendonitis."
When to see a doctor?
In the presence of pain, discomfort and / or suspicion under the patella, it is good to immediately stop any physical activity at risk of inflammation of the patellar tendon and immediately consult a doctor, to undergo a control examination.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatments and if the patient continues to exercise in spite of the pain, the inflammation of the patellar tendon gives rise to complications; in particular, in the aforementioned circumstances, it happens that the inflammatory state worsens to the point of damaging the patellar tendon, if not even cause it to tear.
When patellar tendon inflammation leads to complications, it is more difficult to treat and may require surgery.
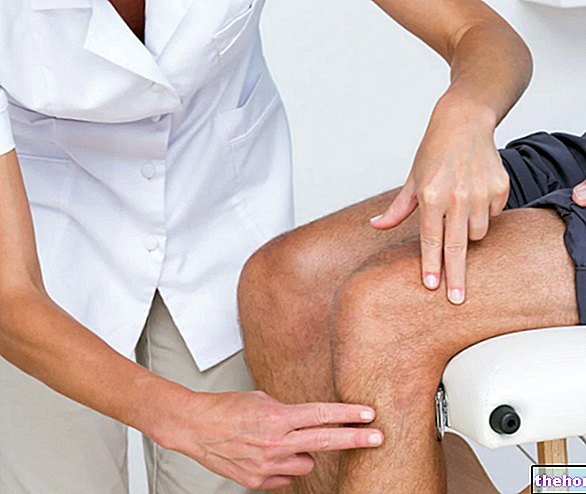
muscle-tendon. It allows to analyze the state of health of the suffering patellar tendon;Physical examination

During the physical examination which serves to identify the inflammation of the patellar tendon, the doctor palpates the patient's knee in significant points at the diagnosis; moreover, he asks the patient to perform, with the suffering knee, specific movements which, in case of patellar tendonitis, they would evoke pain (the presence of pain when performing these movements is, therefore, an alarm bell).
Anamnesis
In the path leading to the diagnosis of inflammation of the patellar tendon, the anamnesis allows to establish the causes and factors that favored the onset of the inflammation.
Knowledge of the causes and risk factors of patellar tendonitis is important when planning therapy.
Generally, the indications for its use are: 4-5 compresses per day on the painful area (under the patella, in the case in question) for 15-20 minutes each (shorter or longer applications are ineffective);
Among the NSAIDs, the most commonly used by those suffering from inflammation of the patellar tendon is ibuprofen;
The use of corticosteroids in the therapeutic management of inflammation of the patellar tendon is rare, due to the possible side effects related to the use of the drugs in question.
Remember that corticosteroids must be taken with a medical prescription;
To know exactly what these exercises consist of, it is good to contact an expert in the field, with experience in problems with the patellar tendon and, more generally, the knee.
Sometimes, to these conservative treatments, the attending physician could add instrumental therapies such as: ultrasound, tecartherapy, iontophoresis and / or TENS (English acronym for Transcutaneous Electrical Nervous Stimulation).
Surgery: when can it be useful?
Typically, patellar tendon inflammation does not require surgery.
However, if the symptoms persist for months in spite of the conservative treatment described above or if the condition has evolved into damage to the patellar tendon or worse still its rupture, surgery becomes a viable therapeutic option.
For episodes of patellar tendon inflammation that require surgery, the operative technique currently used is arthroscopy.
For further information: Knee Arthroscopy: What is in the details before starting any sporting activity related to patellar tendonitis;- Observe breaks during work activities or hobbies that place great strain on the lower limbs;
- To equip oneself, for the practice of high-risk sports activities, with "quality equipment;
- Avoid resorting to corticosteroids unless strictly necessary and in the absence of a medical prescription;
- Wear comfortable shoes.
In sports, the prevention of inflammation of the patellar tendon is based on: the planned rest, the dosage of the workload and the variation of the training.
How to avoid the aggravation of inflammation of the patellar tendon
To prevent the inflammation of the patellar tendon from worsening, it is essential to immediately stop any activity that evokes pain, even if the latter is bearable or controllable with an NSAID.