Breathing difficulties can be attributed:
- The discrepancy between the organism's demand for oxygen and the ability to respond to this input;
- Attempting to overcome an obstacle to regular lung ventilation.
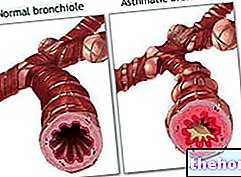
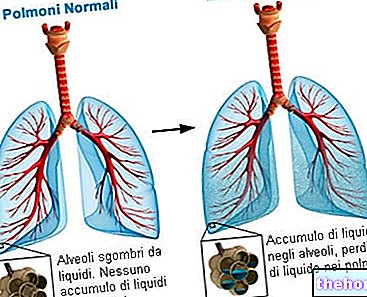
Therefore, breathing difficulties may depend primarily on dysfunctions of the lungs and / or the heart, ie the organs that supply the body with oxygen respectively through gas exchange and blood circulation.
Breathing with difficulty can derive from multiple causes: some are purely physiological, such as, for example, during or after "intense physical activity or in the last trimester of pregnancy"; in other cases, the respiratory difficulties have a pathological origin and are often observed in the context of diseases of the respiratory system and heart disease. There are, however, other conditions associated with this manifestation, such as neurological, musculoskeletal, endocrine, haematological and psychiatric conditions.
which function independently of the control of the will of the subject; these are located, in a structure of the central nervous system, below the hemispheres of the brain (brain stem). When the function of these neurons is compromised, breathing can be affected. The onset of breathing difficulties can therefore be , the consequence of: inflammation, infections, trauma (especially from road accidents), toxic substances (drugs or opium-based drugs, barbiturates), hypoxia, hypercapnia (accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood) and tumors.Furthermore, breathing difficulties can be functional in nature; in this case, it is a compensatory phenomenon implemented for:
- Overcoming an obstacle to regular lung ventilation;
- Satisfy the organism's increased oxygen demand.
Difficulty in breathing can occur in an acute form, ie suddenly or, as happens in chronic diseases of various origins, gradually.




















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




