Generality
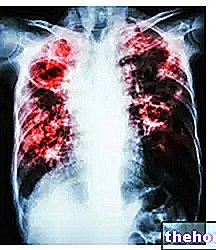
Pulmonary edema consists in the leakage of fluids from the capillary system of the lungs, with consequent accumulation of water and other plasma components in the extravascular space. This is a very serious pathological condition; in fact, the unusual presence of fluids compromises the function performed by the alveoli during breathing, in particular the gas exchanges of oxygen are compromised

The causes of pulmonary edema are different: it can occur as a result of an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary capillaries (heart failure, mitral stenosis), it can result from a lesion of the vascular wall of the pulmonary capillaries or it can arise for particular causes, classified as causes "of another nature".
The symptoms of pulmonary edema are numerous and the most evident is dyspnea, that is, difficulty in breathing.
Pulmonary edema, due to its severity, requires a timely diagnosis, also useful to shed light on the causes. Chest radiography, echocardiography, electrocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, pulmonary catheterization and blood gas analysis are the recommended investigation methods. Finding out the causes is of fundamental importance in planning drug therapy and evaluating the surgical option.