Generality
Acuminate warts are the typical expression of a sexually transmitted disease, rather contagious and widespread, especially in immunosuppressed and defected by other pathologies. The responsible biological agent is a virus known as HPV (human papilloma virus, normally belonging to type 6 or type 11).
Symptoms
For further information: Acuminate Condyloma Symptoms

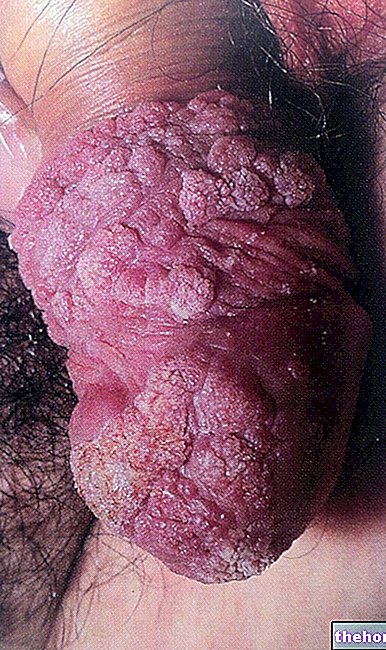
Severe cases of anal, vulvar and penile condylomatosis. From wikipedia.org.
See More Photos Acuminate Condyloma
Acuminate warts are warty neoformations with an appearance similar to a rooster's comb, which tend to flow together until they resemble a cauliflower in the most florid forms; these growths - called sharp condylomas or genital warts - are localized on the mucous and skin surfaces of the anogenital area.
They affect both the man - with typical localization on the glans, on the balano-preputial sulcus, on the urethral meatus and along the frenulum and the shaft of the penis - and the woman, where they frequently affect the vulva, the lower third of the vagina and the neck of the "uterus; warts in the perivulvar and perianal regions are also common.
In addition to the immunosuppressed, warts can reach considerable size during pregnancy.
The incubation period is normally between one and six months, at the end of which the accuminate warts make their onset.
Complications
In itself, the presence of these lesions is not particularly debilitating: while causing itching and irritation at times intense, condylomas generally do not pain, are sometimes asymptomatic and can even regress spontaneously.
Lately, however, the interest in the disease has grown significantly, both for its considerable spread and for the existence of a correlation between HPV infection, warts and some types of cancer, in particular that of the uterine cervix.
The probability of a "cancerous evolution depends on the subtype of papilloma virus responsible for the disease; the viral types normally involved have a low degree of association with malignant lesions, while the types 16 and 18 present a high risk of neoplastic evolution; in general, such danger is more concrete in debilitated subjects, such as HIV-positive, transplant patients and cancer patients.Furthermore, the psychological repercussions of the disease should not be underestimated.
Therapeutic difficulties, often ineffective in preventing the occurrence of relapses, contribute to further complicating the problem of acute condyloma.
Risk factors
Since the disease is particularly contagious, hygienic prevention is essential; since it is a sexually transmitted disease, there is a direct correlation between the number of sexual partners and the frequency of genital warts. In addition to sexual promiscuity, an important risk factor for the disease naturally concerns the failure to use a condom during intercourse (many subjects are contagious even without knowing it).
Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
Diagnosis and Treatment
For further information: Medicines for the treatment of acute warts
The diagnosis, sometimes occasional in the asymptomatic patient, is essentially clinical, but histological confirmation is generally required.
The therapy is based on the treatment of acute condylomas, which can take place according to different methods.
In general, destructive therapy is preferred to pharmacological therapy (based on the administration of interferon, podophylline, trichloroacetic acid or 5-fluorouracil).
- Cryosurgery, for example, uses a swab soaked in liquid nitrogen to freeze the warts and remove them later without the need for anesthesia and without causing bleeding.
- Laser therapy, to be performed under local or general anesthesia in the most serious cases, causes cell lysis and death of the viruses contained therein. The laser beam can be directed with extreme precision on the warts, minimizing the extension of post-treatment scars.
- The same result can be achieved through electrocoagulation, while in other cases surgical excision of the warts is preferred; in these cases the scars are more conspicuous and disfiguring.
As far as pharmacological treatment is concerned, the local application of podophyllin-based preparations causes the whitening of the lesion and the subsequent fall within a few days; however, it is a "medical operation" (important is washing a few hours later of the application site), absolutely to be avoided during pregnancy, as well as on bleeding lesions or more than two cm; trichloroacetic acid guarantees the same result with fewer contraindications and toxicity.
Given the relationship between warts and cervical cancer, women affected by warts must undergo specific tests (pap smear and colposcopy), which allow to detect any cancer even in its initial stage.
Considering the important risk of relapse, the patient is followed even after the removal of the warts, by means of an "adequate monitoring of his condition in the months to come. All this must be integrated with the rigorous use of condoms during the entire duration. of the therapy and with the control and eventual treatment of the sexual partner (s) (even if they do not have warts visible to the naked eye).