Generality
Nortriptyline is a drug belonging to the class of tricyclic antidepressants, but which has also been shown to be useful in smoking cessation therapy.

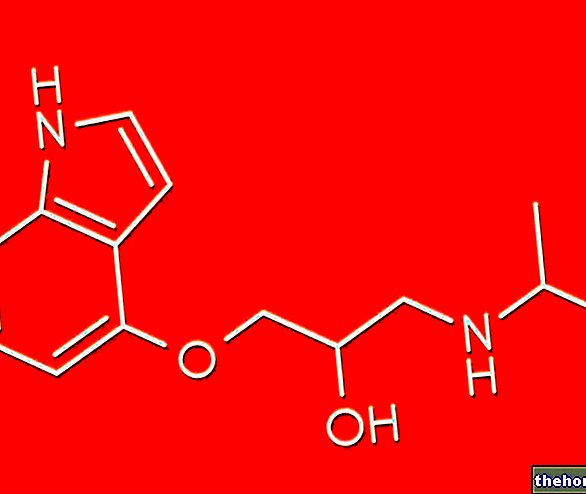
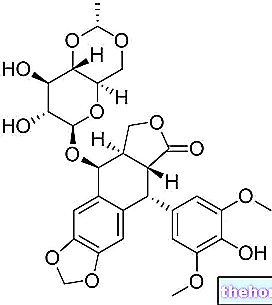
Nortriptyline - Chemical Structure
In reality, nortriptyline is marketed in Italy only with indications for the treatment of major depressive disorder, but many studies have shown that this drug can be of great help in the process of smoking cessation.
Mechanism of action
As mentioned above, nortriptyline is a drug belonging to the class of tricyclic antidepressants and, as such, is able to inhibit noradrenaline reuptake and to a lesser extent also serotonin reuptake. Furthermore, nortriptyline is endowed with antihistamine, anticholinergic and adrenolytic activity.
The exact mechanism by which nortriptyline acts to counteract addiction to smoking is not entirely clear, but it is thought that the aforementioned actions that this drug performs are implicated in the cessation mechanism. However, nortriptyline is capable of decreasing smoking. an urgent desire to smoke and to reduce secondary symptoms resulting from nicotine withdrawal syndrome, including depression.
Furthermore, a recent study has shown how behavioral support for smokers in addition to drug treatment (including nortriptyline-based treatment) can increase the likelihood of success of smoking cessation therapy.
Side effects
Nortriptyline therapy can cause the characteristic side effects of tricyclic antidepressants, although not all patients experience them.
Among the main side effects that can occur, we remember:
- Dry mouth
- Sedation;
- Nausea;
- Difficulty urinating
- Constipation;
- Blurred vision
- Tremors
- Headache
- Palpitations and tachycardia.
Dosage
Nortriptyline is available in tablet form to be taken orally.
Generally, in smoking cessation therapy, 10 mg of nortriptyline per day is given during the first week of treatment. In the following weeks, the dose of the drug is increased to 25-75 mg per day.
After about twelve weeks of therapy, the dose of nortriptyline administered is gradually reduced, until the therapy itself is discontinued.
The amount of drug to be used will be determined by the physician on an individual basis for each patient. In this regard, it is essential to always follow the instructions provided by the doctor, both as regards the quantity of drug to be taken and as regards the duration of the treatment.
Use in pregnancy and during lactation
Nortriptyline should not be used by pregnant women unless the doctor deems it absolutely necessary.
Nortriptyline is excreted in breast milk, albeit in rather low amounts. In any case, mothers who are breastfeeding should seek medical advice as to whether they can continue breastfeeding while taking the drug.
Contraindications
The use of nortriptyline is contraindicated in the following cases:
- In patients with known hypersensitivity to the same nortriptyline;
- In patients who have recently suffered from myocardial infarction;
- In patients with heart disease, including arrhythmias;
- In patients suffering from hepatic insufficiency;
- In patients with thyroid disease;
- In patients with pheochromocytoma;
- In patients with narrow-angle glaucoma;
- In patients with acute alcohol and / or barbiturate poisoning;
- In patients with urinary retention;
- In patients already on therapy with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (or MAOIs), drugs used to treat depression and Parkinson's disease.
In truth - in addition to MAOIs - nortriptyline can also establish drug interactions with other types of drugs. Therefore, it is vital that you tell your doctor if you are taking - or have recently been taking - any kind of medication, including non-prescription medicines and herbal products.