
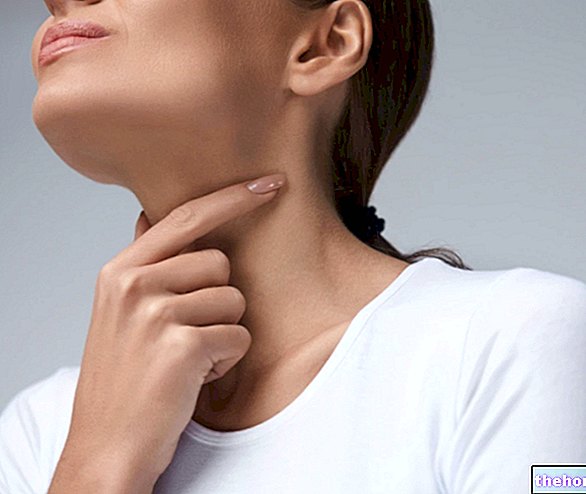
Basically, the swollen lymph nodes on the neck may be a response of the human body to the presence of infectious states, tumors, trauma and autoimmune diseases.
Characterized by one or more painful swellings, swollen lymph nodes on the neck are easy to diagnose; their identification, in fact, requires a simple palpatory examination of the region between the head and the clavicles.
Brief review of what lymph nodes are
The lymph nodes are small ovoid organs of the lymphatic system, having a very important immune role; in fact, they act as collection points for part of the B and T lymphocytes (cells of the immune system), in order to intercept and destroy any germs, foreign substances and / or neoplastic cells circulating in the lymph (the lymph is the fluid similar to the plasma, which flows along the lymphatic vessels and receives waste substances present in the tissues).
Acting in a similar way to purifiers, lymph nodes are often referred to as biological filters.
Since in medicine the enlargement of the lymph nodes is more properly called lymphadenopathy, the enlarged lymph nodes on the neck can be defined with the expression "lymphadenopathy of the neck".
Brief clarification on terminology
Before continuing with the reading, two terminological notes are required:
- Lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes and enlarged lymph nodes are synonymous.
- The "adjective" lymph node "indicates" all that is attributable to the lymph nodes ".
Outline of anatomy relating to the lymph nodes of the neck
According to a more generic classification, under the heading "neck lymph nodes" belong the lymph nodes that reside:
- Behind the ears (posterior auricular lymph nodes);
- In correspondence of the occipital bone of the skull (occipital lymph nodes);
- Under the ear and next to where the mandible engages with the temporal bone of the skull, forming the temporomandibular joint (jugulo-digastric lymph node);
- Under the mandible (submandibular lymph nodes);
- Just above the collarbone (supraclavicular lymph nodes);
- On the actual neck (superficial cervical lymph nodes, deep cervical lymph nodes and posterior cervical lymph nodes).

According to a more specific classification, on the other hand, the definition "lymph nodes of the neck" only includes the lymph nodes located in the anatomical region called the neck (ie the actual neck mentioned above "indeed). Therefore, based on this classification, the lymph nodes of the neck are only the superficial cervical lymph nodes, the deep cervical lymph nodes and the posterior cervical lymph nodes.
In this article, the term "swollen lymph nodes on the neck" refers to lymphadenopathy of the lymph nodes of the neck falling within the first classification, the most generic and with the most extensive meaning.
Did you know that ...
When the enlarged lymph nodes on the neck are exclusively the cervical ones, doctors speak of cervical lymphadenopathy.
, palatine tonsils and larynx;Pharyngitis
Inflammation of the pharynx (ie the back of the mouth) is the condition commonly known as a sore throat.
Viruses (including Rhinoviruses, Coronaviruses and Adenoviruses), bacteria (including Streptococcus group A beta hemolytic, Streptococcus pneumoniae And Haemophilus influenzae) and non-infectious agents (such as, for example, allergies, gastroesophageal reflux and inhalation of irritants).
In a context of pharyngitis, the presence of swollen lymph nodes on the neck mainly involves the superficial, deep and posterior cervical lymph nodes, and the submandibular lymph nodes.

Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis recognizes its main causes in viruses, such as Rhinoviruses, Coronaviruses, Adenoviruses and Epstein Barr viruses, and in bacteria, such as Streptococcus beta hemolytic group A e Streptococcus pyogenes.
In the presence of tonsillitis, the phenomenon of enlarged lymph nodes on the neck usually has the superficial and deep cervical lymph nodes, the submandibular lymph nodes and the jugulo-digastric lymph node as main actors.
Laryngitis
Inflammation of the larynx and vocal cords contained in the larynx is attributable to various factors, including viruses (eg: Rhinovirus, influenza virus, varicella virus, Coronavirus and Adenovirus), bacteria (eg: Bordetella pertussis), mushrooms (ex: Candida albicans And Aspergillus) and excessive use of the voice.
When there is laryngitis, the presence of swollen lymph nodes on the neck tends to have the upper and deep cervical lymph nodes as protagonists.
Gingivitis, dental abscesses and pericoronitis
Gingivitis, dental abscesses and pericoronitis are inflammations in which bacteria play a fundamental causal / favoring role.
In their presence, the phenomenon of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck sees the participation above all of the submandibular lymph nodes and deep cervical lymph nodes.
Ear infection
Otitis media is almost always a consequence of bacterial infections, sustained by pathogens such as Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis And Streptococcus pneumoniae; otitis externa, on the other hand, is more often the result of mycosis (fungal infections) or, in any case, pathogens with a preference for humid environments.
When there is an otitis, the presence of swollen lymph nodes on the neck recognizes, above all, in the posterior auricular lymph nodes and in the upper cervical lymph nodes its most important actors.
Rubella, chicken pox, flu and mononucleosis
The viral pathogens responsible for rubella, chicken pox, influenza and mononucleosis are, respectively, rubella virus, varicella-zoster virus, influenza virus and Epstein-Barr virus.
On the occasion of these known viral diseases, the presence of enlarged lymph nodes on the neck usually gives a prominent role to the superficial, deep and posterior cervical lymph nodes.
AIDS
In AIDS, swollen lymph nodes on the neck, together with swollen lymph nodes in the armpit and in the retro-nuchal compartment, are a characteristic sign of the early stage of infection, an early stage which is equivalent to the stage following the so-called latency stage of AIDS. .
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas
In non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, swollen lymph nodes on the neck represent one of the effects of indiscriminate and unregulated reproduction of B and T lymphocytes in the lymph nodes (ie in the lymph nodes).
Did you know that ...
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas are related to cervical lymphadenopathy, axillary lymphadenopathy, and inguinal lymphadenopathy.
Tumors of the mouth-throat compartment
In cancers of the mouth, throat, tongue and the like, the enlarged lymph nodes on the neck are the result of the large accumulation of neoplastic cells in the lymph node.
Usually, oral cavity tumors affect the deep cervical lymph nodes; however, in some circumstances, they also affect the other cervical lymph nodes (superficial and posterior) as well as the submandibular.
Rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
In rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, swollen lymph nodes on the neck are the result of abnormal immune cell behavior when an autoimmune disease is ongoing.
Autoimmune diseases, in fact, are particular clinical conditions, the symptoms and signs of which are due to a malfunction of the immune system: the immune cells, instead of merely carrying out their normal action against external threats (viruses, bacteria, etc.), are aggressive towards the organism they should protect.
Insect bites
Insect stings or bites on or near the neck cause swollen lymph nodes on the neck, when an infection arises, which produces an inflammatory response and draws immune cells to the lymph node.
- Histoplasmosis (fungal infection)
- Brucellosis (bacterial infection)
- Toxoplasmosis (parasitic infection)
- Secondary syphilis (bacterial infection)
- Herpes virus infections
- Cytomegalovirus infections
- Leukemia (blood cancers)
- Sinusitis
- Tuberculosis
- Laryngeal cancer
- Malignant chest tumor
- Reactions to drugs or vaccines
Acute or gradual enlargement: what can this mean?
Swollen lymph nodes on the neck can result from an "acute enlargement process - where acute s" means quick to occur - or from a gradual enlargement process.
Generally, the process of swollen lymph nodes in the neck is acute when the underlying cause is an infection or trauma, while it is gradual when the underlying cause is a tumor or autoimmune disease.
Associated symptoms
The symptoms and signs that may accompany the presence of swollen lymph nodes on the neck are numerous and depend on the condition triggering the enlarged lymph node.
Going more specifically, among the symptoms and signs in question, they certainly deserve a mention:
- Pain in the throat
- Runny nose (runny nose)
- Red throat;
- Dry throat;
- Itching in the throat
- Fever;
- Ear pain (ear pain);
- Stuffed nose and consequent breathing difficulties;
- Hoarseness;
- Drop in voice
- Cough;
- Difficulty chewing
- Difficulty chewing
- Pain in the jaw
- Generalized fatigue;
- Toothache.
Complications
In the presence of swollen lymph nodes on the neck, the possible occurrence of complications depends on the severity of the cause triggering the enlarged lymph node and the remaining symptoms. In other words, swollen lymph nodes on the neck can be associated with complications if the underlying condition is clinically relevant.
Examples of conditions that cause lymphadenopathy of the neck and from which, given their severity, complications can arise are: throat cancer, mouth cancer, tongue cancer, AIDS and cases of infections not treated properly.
When to see a doctor?
Swollen lymph nodes on the neck are a sign that should not be underestimated but, indeed, should be brought to the attention of the attending physician, when:
- They are persistent;
- They are accompanied by the enlargement of other lymph nodes (eg axillary lymph nodes, inguinal lymph nodes, etc.);
- They are accompanied by a rich and / or severe symptomatology (eg: high fever, severe difficulty in swallowing and chewing, intense pain in the throat, etc.);
- They are accompanied by toothache.
- Blood tests;
- A throat swab
- Diagnostic imaging tests (X-rays, magnetic resonance, CT scan, etc.) with particular reference to the oral cavity and neck;
- An "endoscopy of the upper aero-digestive tracts and of the larynx.




















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




