Sometimes associated with the removal of the fallopian tubes and uterus, ovariectomy is indicated in the presence of: severe endometriosis, ovarian cancer, large ovarian cysts, chronic pelvic pain resistant to conservative therapy, advanced ovarian torsion and ovarian ectopic pregnancy resistant to drug therapy.
Oophorectomy requires specific preparation and involves an anesthetic practice between general anesthesia, epidural anesthesia and spinal anesthesia (the type of anesthesia adopted depends on the surgical approach).
After the ovariectomy, there is a period of hospitalization, which must be followed by an adequate recovery program.
In women of childbearing age, bilateral oophorectomy makes it impossible to have children and triggers the phenomenon of premature menopause.
Oophorectomy is also known as an oophorectomy.
For further information: Salpingectomy: What is it and Why is it performed? For further information: Hysterectomy: What is it and Why is it performed
What are the Ovaries: a quick review

The ovaries (in the singular ovary, but also ovary or ovary) are the female gonads, i.e. the endocrine glands which, in women, have the task of producing gametes (the so-called egg cell) and sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
Given their function, therefore, the ovaries are two fundamental organs in decreeing a woman's fertility.
Equivalent to the testicles in man, the ovaries are two and reside at the pelvic level, in an area called the ovarian fossa, arranged one to the left and one to the right of the uterus.
of the ovary);Oophorectomy can also have preventive purposes and, in these guises, find use in women with a congenital predisposition to ovarian or breast cancer, a congenital predisposition due to the presence of a mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are two tumor suppressor genes whose mutation increases the risk of developing cancers such as breast and / or ovarian cancer in women and prostate cancer in men.
linked, or bilateral, if it affects both ovaries and both fallopian tubes.
Salpingo-Ovariectomy with Hysterectomy: what it is
Oophorectomy performed in combination with salpingectomy and hysterectomy is more properly called salpingo-oophorectomy with hysterectomy (or hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy).
Generally, salpingo-oophorectomy with hysterectomy involves both ovaries and fallopian tubes, therefore there is no distinction between unilateral and bilateral for the intervention in question.
How to prepare for ovariectomy: pre-operative instructions
The pre-operative instructions are those indications that a patient must have the foresight to follow in the days preceding a certain surgical procedure.
In the case of an oophorectomy, the pre-operative instructions consist of:
- Quitting smoking (this clearly makes sense if the patient is a smoker). Cigarette smoking makes surgical incisions more susceptible to infection and slows the healing process.
According to industry experts, smoking patients should initiate smoking cessation at least 2 weeks before surgery and implement it up to at least 2 weeks after the operation. - Temporarily interrupt, starting a few days before the ovariectomy, any drug therapy that alters the normal blood clotting process (therefore, suspend any treatments based on aspirin, warfarin, heparin, etc.).
- Present yourself, on the day of the procedure, on a complete fast for at least 8 hours. This means that, if the oophorectomy is scheduled in the morning, the last meal given to the patient is the dinner the day before the operation.
Fasting is part of the pre-operative instructions of any surgical procedure which, like ovariectomy, involves anesthetic practice between general anesthesia, epidural anesthesia and spinal anesthesia. - One day after the operation, take a product for intestinal cleansing. Generally, it is the doctor who will perform the operation who indicates the exact preparation to use and the best time to take it.
- Prepare a suitcase or bag containing all those personal items (clothes, linen, personal hygiene items, etc.) useful for facing a hospital stay of a few days. As will be seen in detail below, the ovariectomy requires the patient admission to hospital, the duration of which in terms of days varies in relation to the surgical technique used for the operation.
- Ask a relative or close friend for their support on the day of the procedure, especially with regards to returning home once the operation is complete.
The choice of the surgical technique used for the realization of an oophorectomy is not accidental, but depends on factors such as: the purpose of the intervention, the condition to be treated and the state of health of the patient.
The medical figure specifically trained to carry out the crucial phase of the ovariectomy is the gynecologist.
For further information: Gynecologist: Who is he? When to contact him?If necessary, the three surgical techniques mentioned above also allow the removal of the fallopian tubes and the uterus.

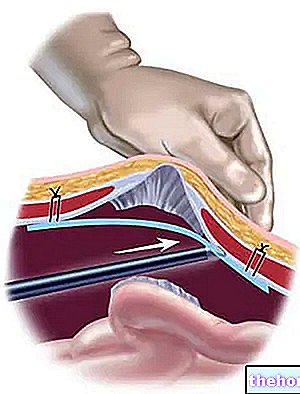
Abdominal OVARIECTOMY
During abdominal oophorectomy operations, the gynecologist removes one or both ovaries through an "incision a few centimeters long in the abdominal area that he himself made.
The removal of one or both ovaries is followed, in order, by the repair of the abdominal muscles, the closure of the incision with sutures and the bandaging of the operated area.
Due to the size of the surgical incision, abdominal oophorectomy is not only the most invasive surgical technique (of the three possible), but also the one with the highest risk of adverse effects.
Being an invasive operation, abdominal oophorectomy requires the practice of general anesthesia.
Vaginal ovariectomy
During vaginal oophorectomy operations, the gynecologist removes one or both ovaries, through an "incision at the level of the upper surface of the vaginal canal that he himself has made.
The removal of one or both female gonads is followed by the stitching of the surgical wound, through the application of special sutures, and the application of an internal bandage.
Vaginal oophorectomy can be performed both under general anesthesia and spinal or epidural anesthesia. It is less invasive than abdominal oophorectomy, but more invasive than laparoscopic oophorectomy.
Laparoscopic OVARIECTOMY
During laparoscopic oophorectomy operations, the gynecologist accesses the organs to be removed through 3 small one-centimeter incisions made in the abdominal area and through the use of surgical instruments (clearly, of the size of the aforementioned incisions), including the so-called laparoscope.
The removal of the organs is followed, as in the previous cases, by the closure of the incisions by means of sutures and the bandaging of the wounds.
Usually performed under general anesthesia, laparoscopic oophorectomy is a minimally invasive solution: in fact, it allows one or both ovaries to be removed without resorting to large incisions.
The minimal invasiveness of laparoscopic ovariectomy leads to a significant reduction in hospitalization and post-operative recovery times.
Unfortunately, laparoscopic oophorectomy has a limitation: it cannot be performed on all patients who require the removal of one or both ovaries.
Did you know that ...
Today, for laparoscopic oophorectomy operations, the most advanced hospitals provide their medical staff with a robot, which guarantees greater precision and a further less invasiveness (robotic oophorectomy).
Duration of ovariectomy
Oophorectomy can last from 1 to 4 hours.
The surgical technique used and the possible execution of other operations, such as the removal of the fallopian tubes and the uterus, affect the duration of the ovariectomy.
Is ovariectomy painful?
Since the anesthesia begins to take effect, the patient undergoing an oophorectomy no longer feels any kind of pain.
Spinal anesthesia and epidural anesthesia can be slightly annoying when inserting the needle for administering the anesthetic.
, lack of balance, slow reflexes and headaches; these are temporary sensations, which vanish within 24 hours following the anesthetic practice mentioned above.Hospitalization: Duration and other details
- After the interventions by abdominal oophorectomy, the expected hospitalization has a canonical duration of 2-4 days.
- After a "vaginal ovariectomy, the expected hospital stay usually lasts 1-3 days.
- After the operations of laparoscopic ovariectomy, the expected hospitalization usually lasts 1-2 days.
It should be noted that hospitalization following the "ovariectomy involves the installation of a bladder catheter, the connection to a drip, the administration of painkillers (if the patient complains of pain)" and, exclusively in the case of abdominal oophorectomy, the further connection to an abdominal drainage tube (the latter serves to prevent the accumulation of blood where the gynecologist made the incision).
Ovariectomy: when to remove the stitches
Except in special cases, the removal of the sutures applied during the ovariectomy takes place 5-7 days after the operation.
Ovariectomy: recovery times
Recovery times from an "oophorectomy vary according to the surgical technique used.
In general, the more invasive the surgical technique is, the longer the recovery times are:
- For full recovery from a "abdominal oophorectomy, it takes at least 6 weeks;
- For full recovery from a "vaginal ovariectomy, it takes from 2 to 4 weeks;
- Finally, for full recovery from a "laparoscopic ovariectomy, 2 weeks may be enough.
Ovariectomy: Do's and Don'ts During Recovery?
While recovering from an oophorectomy, the patient must:
- Be at rest, but not overdo it. From the first moments following the intervention, the patient should stand up and walk, even for a few minutes; this measure serves to prevent the dangerous vascular complications connected to excessive immobility (deep vein thrombosis).
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for at least 4 weeks. The resumption of all those activities that require a certain effort must take place gradually.
- Avoid driving as long as you are in pain.
- Avoid traveling before 3 weeks have passed since the operation.
- Avoid sporting activity in the first 4-6 weeks following the operation.
- Avoid having sexual intercourse for 6 weeks following the ovariectomy.
To this, it should be added that the patient can resume her normal diet immediately and take a bath, as long as she takes care to gently wash the operated area (NB: in the case of vaginal ovariectomy it is absolutely necessary to avoid internal washing vagina).
to anesthetic, nerve damage and death);Did you know that ...
Death due to the practice of general anesthesia is a phenomenon that affects 1 individual every 100,000-200,000 people; therefore it is very rare.
Consequences of Bilateral Ovariectomy

In women of childbearing age, bilateral oophorectomy makes it impossible to have children and triggers the phenomenon of premature menopause.
For further information: Treatments for Premature Menopause