
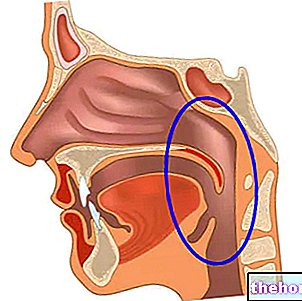
Responsible exclusively for the passage of air, the nasopharynx begins at the same level as the base of the skull, where it borders with the nasal cavities, and ends at the same height as the upper surface of the soft palate, where it borders the oropharynx and the cavity. oral.
Lined with a typical respiratory tract epithelium, the nasopharynx hosts the adenoid tonsils (or pharyngeal tonsils) and the oral openings of the Eustachian tube.
By channeling the air coming from the nasal cavities and introduced with breathing towards the larynx, the nasopharynx plays a decisive role in the respiratory function; moreover, it is responsible for promoting swallowing, maintaining the right pressure at the level of the eardrum, protecting the human body from any pathogens.
The nasopharynx can be the subject of various medical conditions, including: nasopharyngitis, nasopharyngeal (or nasopharyngeal) carcinoma and enlargement of the adenoids.
In anatomy, the nasopharynx is also known as the nasopharynx.





.jpg)


















