Constipation or constipation is defined as a symptom characterized by the alteration in fecal consistency and the frequency of evacuation.
Constipation causes:
- Reduction of defecations (
- Hard stools (including goat or ribbon-like)
- Sense of incomplete emptying and constipation
- Difficulty, pain and slowness during expulsion.

It is defined constipation when the symptoms remain for at least 3 months. It mainly affects young males and adult females, in addition to the elderly.
It is not a real disease but it creates a very intense discomfort to those who suffer from it.
It can be triggered by: various anatomical pathologies, hormonal imbalances, dietary factors, alteration of the bacterial flora, modification of circadian rhythms or habits, dehydration, nervous factors, lifestyle, etc.
Constipation is related to the onset of various more or less serious pathologies, which is why it is essential to try to identify its origin and treat it.
Also, don't forget that constipation can cause or aggravate:
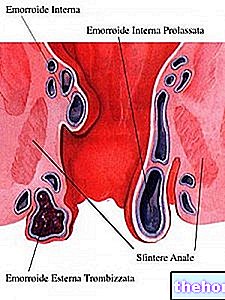
- Hemorrhoids.
- Anal fissures.
- Rectocele.
- Rectal prolapse.
- Tumors.
- Diverticulitis.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Constipation or Constipation; such indications must in no way substitute the opinion of the attending physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
What to do
- Finding one or more of the discomforts related to constipation, it is necessary to contact a doctor immediately. This is especially important if constipation:
- It arises quickly.
- It has been going on for a long time.
- It goes with:
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Bleeding.
- Asthenia.
- Colon cancer familiarity.
- Fever.
- The diagnostic path, in addition to the anamnesis and the analysis of symptoms and clinical signs, should include one or more of the following analyzes:
- Colonoscopy.
- Double contrast opaque enema.
- Study of intestinal transit times.
- Anorectal manometry.
- Diagnosis has the function of looking for the triggering cause of constipation, without which it is difficult to prevent and cure it. Among the morbid conditions most often responsible for constipation we mention:
- Anatomical alterations and stenosis.
- Diabetes and hypothyroidism.
- Pregnancy.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS, is the most frequent).
- Tumors.
- Excess of diarrhea medications.
- If the search for these factors is negative, it is necessary to carefully analyze the other elements such as:
- Diet (at least 30g of fiber per day).
- State of hydration (at least 1ml / kcal introduced, therefore 1.8-2.2 liters per day for an adult).
- Trophism of the intestinal bacterial flora
- Sleep wake rhythms (especially in shift workers).
- Degree of general psychological stress.
- Motor physical activity level.
- Treatment of constipation primarily involves treating the triggering cause. However, when it is of idiopathic origin or caused by IBS, it becomes necessary to follow some guidelines:
- Improve the composition of the diet, increasing the beneficial nutritional components (especially fiber and other prebiotics) and reducing the counterproductive ones (astringents).
- Increase general hydration status and prevent dehydration.
- Optimize the composition and density of the physiological bacterial flora in the intestine using probiotics.
- Set aside a moment of the day to devote to evacuation. Often people become constipated from neglect.
- Reduce the level of psychological stress and promote relaxation.
What NOT to do
- Ignore constipation and other related symptoms.
- Not respecting the diagnostic path.
- Not treating the disease that causes constipation.
- Follow an inadequate diet, rich in astringent products and low in fiber, prebiotics and laxatives.
- Staying dehydrated:
- Eating foods or drinks that promote dehydration (alcohol, coffee, thermogenic, etc.).
- Follow a ketogenic diet: it tends to increase kidney filtration by dehydrating the body.
- Drink little, especially in case of intense sweating.
- Do not follow probiotic therapy if advised by your doctor or nutritionist
- Having a lifestyle that is not regulated, discontinuous and devoid of rhythms.
- Suffering from deep and constant stress.
- Neglecting the perception of the urge to defecate and postpone the episodes (often happens in the presence of severe pain and / or bleeding attributable to hemorrhoids and fissures).
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Excess with astringent products in case of diarrhea. Sometimes constipation is the result of a "rebound effect" in the drug therapy of diarrhea.
- Excess with natural remedies and medications for constipation. They can be addictive and create a dangerous rebound effect.
What to eat
The nutritional regimen for constipation is called a "high residue diet", which means rich in fiber.
- Foods rich in fiber. Soluble ones are more recommended, but foods usually contain both. Furthermore, the percentage of insoluble ones is generally higher.
- Cereals: wholemeal ones are preferred. The fibrous portion of these foods is mostly insoluble, but it is still advisable to include them in the diet.
- Legumes: those with peel are preferred. Many think that the side effect of the intake of legumes, that is flatulence, derives above all from the fibrous component; It is not so. This is the effect of certain anti-nutritional molecules that remain in excessive quantities in undercooked legumes. NB. Soaking dry ones (eliminating the water) is a factor that helps their expulsion.
- Vegetables and fruits: these are the foods that contain the most soluble fiber.
- Oil seeds: the so-called dried fruit is very rich in fiber; however, they are also high in fat and can have an excessive caloric impact. In the daily diet they should be included in the amount of a few grams.
- Algae: they are a predominantly oriental food that boasts numerous positive characteristics; among these, the richness in soluble fibers.
Additionally, we recommend that you:
- Guarantee the supply of fats: 25-30% of the energy in fats favors the lubrication of the faeces and the consequent sliding in the intestine. It is advisable to prefer:
- Oils of vegetable origin, preferably cold pressed: they soften the stool, are liquid at room temperature and provide many healthy nutrients.
- Eating strongly hydrated foods: as anticipated, the cause of fecal hardening is dehydration. We recommend foods and recipes rich in water such as:
- Fresh and raw foods: especially fruit and vegetables.
- Minestroni in broth.
- Soups of cereals or legumes in broth.
- Milk and yogurt.
- Fish and meat soups.
- Drink plenty of water both between meals and with meals.
- Insert probiotic foods: they enrich the intestinal bacterial flora and can improve intestinal health: yogurt, buttermilk, kefir, tofu, tempeh, miso, kombucha, sauerkraut, gherkins, etc. On the other hand, it must be remembered that the acid barrier of the stomach it eliminates most of the microorganisms.
- Insert prebiotic foods: these are foods containing nourishment molecules for the intestinal bacterial flora. These are the so-called unavailable carbohydrates and fiber. The fibers subjected to cooking have an extremely prebiotic function; the heat treatment tends to partially hydrolyze them, facilitating bacterial nutrition.
- Laxative foods: this category is generic and includes all products capable of exerting a laxative effect. They are laxatives: rehydrated dried plums (also drinking the soaking water), milk (especially hot), yogurt, broth, honey, beer (especially raw), blackberries, grapes, peaches, licorice, figs, kiwis, sugoli, etc.
NB. Some people are very sensitive to nerve intake. A cup of coffee in the morning could reduce the symptom of constipation.
What NOT to Eat
- Among the foods that contain fiber, it is not advisable to prefer:
- Refined cereals and equally purified flours (for example type 00 wheat flour, cornstarch, rice starch, tapioca, white pasta and bread, sugar, etc.).
- Hulled legumes.
- Vegetables and fruits peeled, pureed, centrifuged or naturally low in fiber (for example bananas, potatoes, etc.).
- It is not advisable to follow low-fat diets, ie with a quantity of fat lower than 25% of the energy.
- Eating dehydrated foods:
- Seasoned cheeses and cured meats.
- Dried meat and fish.
- Meat and fish in salt or in oil.
- Condensed milk.
- Dehydrated fruit not found, concentrated, cooked and squeezed vegetables (e.g. spinach), etc.
- Crackers, bread sticks, croutons etc. instead of fresh bread.
- Dry snacks (fried corn, peanuts, nachos etc).
- Astringent foods: the astringent action has a rather subjective effect. Some are: tea, lemon juice, banana, boiled white rice, carob and flour, etc.
- Diuretic supplements.
Natural Cures and Remedies
Natural remedies for constipation are mainly of type: behavioral hygiene, food supplements and herbal products.
- Correction of habits:
- Schedule a time of day to go to the bathroom.
- Respect the stimuli: also make use of public toilets. Don't put it off for fear of exertion or pain; the following act will certainly be worse.
- Don't over-strain: Fatigue can lead to several complications.
- Train the muscles of the abdominal girdle and pelvic floor: they are responsible for defecation and greater efficiency can only be positive.
- Practicing motor activity: in addition to the previous reason, mechanical stress (vibrations, rebounds, etc.) stimulates the progress of stool in the colon.
- Laxative plants; it is advisable to use it only when strictly necessary:
- Anthraquinone drugs: senna, cascara, buckthorn, aloe juice, rhubarb.
- Oils: castor, olive, etc.
- Products rich in fiber or extracted fibers: bran, psyllium seeds, various mucilages (for example agar agar), various gums (guar, karaya, etc.).
- Amorphophallus konjac and glucomannans extracts.
- Foods and plants: tamarind, honey, cassia, senna, dried plums (also drink the water).
- Laxative herbal teas: they are infusions or decoctions that reduce constipation. Example:
- Buckthorn bark, linseed, star anise and licorice. Pour a soup spoon of the mixture into 200ml of boiling water. Cool down and filter. Take a cup in the evening.
- Inorganic salts.
- Mineral oils.
Pharmacological treatment
They are very effective but also have several side effects. Some are addictive, others violent diarrhea. Some irritate the intestine to the point of causing mucus to be expelled.
- Phenophthalein.
- Bisacodyl.
- Picosulfate.
- Sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate.
- Sorbitol.
- Lactulose.
- Methylcellulose.
- Polyethylene glycol.
Extraction drugs made from certain natural products also belong to this category. Eg:
- Anthraquinones:
- Bisacodyl (for example Dulcolax, Stixenil, Alaxa).
- Senna (e.g. Xprep, Agiolax, Pursennid, Falquilax).
- Sodium docusate (e.g. Macrolax, Sorbiclis).
- Volume laxatives:
- Methylcellulose.
- Sterculia gum (e.g. Normacol).
- Psyllium seeds (e.g. Fuibrolax).
- Emollients / lubricants:
- Liquid paraffin (e.g. Lacrilube, Paraf L BIN).
- Peanut oil in enemas.
- Glycerin in enemas.
- Osmotic laxatives:
- Lactulose (for example Duphalac, Epalfen, Normase).
- Macrogol (e.g. Movicol, Isocolan, Selg Esse, Moviprep, Paxabel).
- Anticholinesterases:
- Bethanechol (for example Myocholine).
- Neostigmine (for example Prostigmine).
- Saline laxatives:
- Phosphates (e.g. Sod Fos Sof Enema, Sod Fos Zet Enema).
- Magnesium hydroxide (e.g. Magnesia, Maalox).
- Sodium Citrate (e.g. Biochetase, Novilax).
Prevention
The prevention of constipation can be implemented in a few simple steps:
- By following a balanced diet rich in: fiber, water, probiotics, prebiotics, etc.
- Following a diet low in: astringents, alcohol, caffeine and other nerves.
- Avoiding dehydration: compensating for sweating, limiting dehydrating products etc.
- Dedicating attention and time to evacuation.
- Performing motor activity.
- If necessary, taking a few natural remedies such as herbal teas, supplemental fibers etc.
- Treating any primary pathologies that trigger constipation.
Medical Treatments
There are no medical treatments for constipation other than supplements and medications.
The only exception is the treatment for the primary ailments that trigger constipation.