Generality
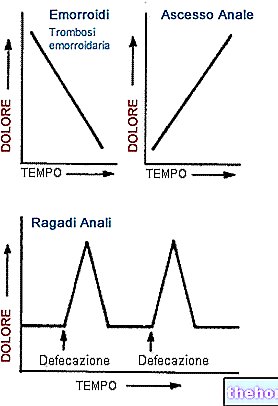
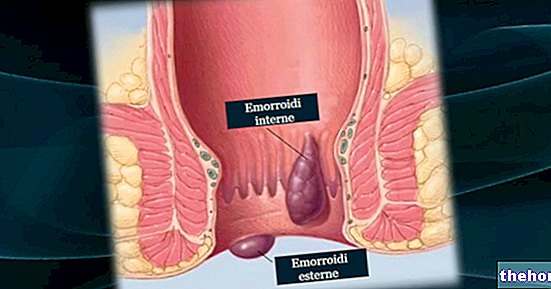
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis is one of the most common complications of hemorrhoids (understood as a medical condition, more properly defined as hemorrhoidal disease).
Thrombosis consists in the formation of a thrombus inside a blood vessel, specifically in one of the vessels that supply the hemorrhoids intended as an anatomical part.

Hemorrhoidal thrombosis is a very painful circumstance, which also involves intense itching, anal bleeding and the formation of a bluish-red swelling, always at the anal level.
Diagnosing hemorrhoidal thrombosis is simple; almost always, in fact, a physical examination and anamnesis are sufficient.
To treat hemorrhoidal thrombosis, there are three therapeutic approaches: conservative treatment, representing first-line therapy, hemorrhoidal thrombectomy, implemented when first-line therapy fails, and "hemorrhoidectomy, practiced only in cases where the two previous approaches are are proven ineffective.