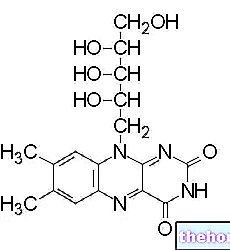
It has a mainly coenzymatic function and, in its metabolically active forms (FMN and FAD), constitutes the prosthetic group of redox enzymes called flavoenzymes or flavoproteins - necessary for cellular respiration and the metabolic pathways of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids.
It is found both in plant and animal foods, but abundantly only in milk and its derivatives, in eggs and offal, such as liver, heart and intestine - mainly used in traditional recipes (stigliola, pajata, etc.).
It is absorbed in the intestine - a process hindered by alcohol and other nutritional factors such as methylxanthines - and metabolized largely inside the intestinal cells; in the blood it is carried by globulins. The primary route of excretion is renal via urine.
Deficiency manifests itself first with nonspecific symptoms and signs, then with other rather specific ones - affecting the dermis, eyes and tongue. Toxicity is almost impossible to achieve, due to limited absorption and poor solubility.
The recommended intake is about 0.6 mg / 1000 kcal / day. However, it is recommended not to go below 1.2 mg / day.
in the form of coenzyme. Only thanks to gastric acidity and intestinal digestive enzymes it is possible to detach FAD and FMN from enzymatic proteins, releasing the vitamin in free form.
Riboflavin is absorbed by ATP-dependent specific active transport but this process is saturable. This means that while assuming very high nutritional concentrations, the difference between the total and the one that can be used by specific carriers is inexorably lost with the faeces.
The absorption of riboflavin is inhibited by the presence of ethyl alcohol - as occurs for thiamine or vitamin B1 - while caffeine, theophylline, saccharin, tryptophan, vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and urea decrease its bioavailability.
, enterocytes:
Riboflavin + ATP → FMN + ADP FMN + ATP → FAD + Ppi
In the blood, riboflavin is present both in free form and as FMN, and is transported bound to different classes of globulins, mainly IgA, IgG, IgM; it seems that various proteins capable of binding flavins are synthesized during pregnancy.