Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
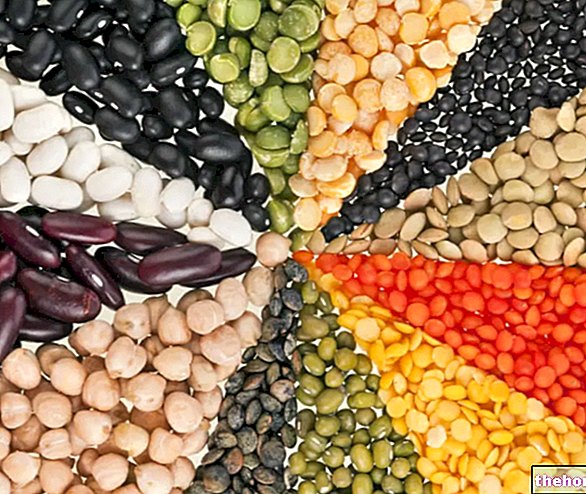
Fresh legumes are immature seeds, with a high water content, whose nutritional characteristics make them fall into the group of vegetables.

Dried legumes are an "excellent source of protein, in fact they contain more than twice as many cereals and more than the same meats, but of lower quality.
The legume-cereal association improves the protein quality, this is the reason why man all over the world has learned to prepare dishes such as: pasta and beans, rice and peas, etc.
Peanuts and soy also belong to the legume family, from whose seeds peanut and soybean oils are extracted, for which they are referred to as oilseeds.
Currently, the consumption of dried legumes is extremely low, 4.5 kg / inhabitant / year.
The reasons for these low consumption are to be found in the long soaking and cooking times, but probably also in the fact that someone has defined them as the meat of the poor.
The low consumption of dried legumes represent a negative fact from the nutritional point of view, but also from the point of view of health, as these foods are able to lower cholesterolemia, thanks to the good content of lecithin.
g / 100
carbohydrates
g / 100
vitamins
minerals
Beans
293
22
1÷2
47÷51
B1 and PP
Fe, Ca
Lentils
291
23
1
51
B1 and PP
Fe, Ca
Soy
407
37
19
23
B1 and PP
Fe, Ca
Peanuts
600
29
49
9
B1 and PP
Fe, Ca
* the content in proteins, fats and carbohydrates of dry legumes is about double compared to fresh ones (lower% of water) which are however richer in vitamins and mineral salts
the weight of dried legumes increases about 3 times with cooking
The high carbohydrate content gives the legumes a good energetic power.
With the exception of soy (rich in precious polyunsaturates), legumes are low in fat and particularly suitable for low-fat diets.
The high fiber content makes them satiating foods and helps prevent conditions bordering on the pathology such as mild dyslipidemias, diverticulosis of the colon, constipation, overweight or other pathological situations, such as coronary artery disease, "atherosclerosis, diabetes," obesity and other metabolic diseases, malignant tumors of the large intestine and gallbladder stones.
Legumes are among the most calcium-rich plant foods.
Legumes are plastic foods with a protein content comparable to that of meat (even if the biological value is lower overall)
The content of vitamin B1, iron and potassium is certainly appreciable; however a certain amount of minerals is neutralized by the "abundant presence of phytates," anti-nutritional "substances that reduce their absorption
Legumes are cheap and "solidarity" foods since they can be used instead of meat, saving natural and economic resources. In fact, to produce one kilo of beef, 16 kilos of wheat and soy are needed; the energy consumed to produce it is ten times higher than that required to produce vegetable proteins.
Legumes and proteins Other Foods - Legumes Peanuts Chickpeas and Chickpea Flour Cicerchie Beans Azuki Beans Green Beans Broad Beans Falafel Chickpea Flour Bean Flour Bean Flour Lentil Flour Pea Flour Soy Flour Legumes Lentils Lupins Peas Soy Jackdaws Tempeh Tofu Yogurt ARTICLES Soy OTHER Categories Alcoholics Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and derivatives Legumes Oils and fats Fish and fishery products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Second courses Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice creams and sorbets Syrups, Liqueurs and grappas Basic Preparations ---- In the Kitchen with Leftovers Carnival Recipes Christmas Recipes Diet Recipes Light Recipes Women's Day, Mum, Dad Functional Recipes International Recipes Easter Recipes Recipes for Celiacs Recipes for Diabetics Recipes for Holidays Recipes for San Valentino Recipes for Vegetarians Recipes p roteiche Regional Recipes Vegan Recipes