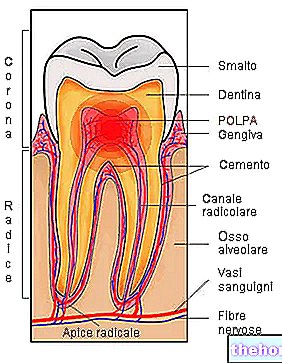
support, root cement and ligaments (elastic connecting fibers). Typical of patients suffering from periodontitis (or pyorrhea if you prefer) and sensitive to gum disease, periodontal dental abscess can also be caused by a "purulent infection" inside a periodontal pocket.

- Multiple dental interventions that are not perfectly successful, such as devitalization, implantation, filling;
- Presence of some types of pathologies, such as:
- Diabetes;
- Bacterial cellulitis;
- Gastroesophageal reflux diseases;
- Diseases that weaken the immune system (for example, AIDS).
- Dry mouth
- Addiction to smoking;
- Alcoholism;
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy of the head and neck;
- Long-term therapy with corticosteroid, antihistamine and antihypertensive drugs.
In addition to the throbbing and acute pain, other symptoms complete the clinical picture triggered by the dental abscess:
- Swollen, red, sometimes bloody gums
- Swelling of the face: the skin overlying the abscess is particularly painful, red and swollen and the intensity of the pain increases on palpation;
- Dentinal hypersensitivity: toothache is accentuated by thermal (cold / hot food or drinks) and mechanical (chewing) stimuli;
- Halitosis;
- Tendency to fall out of the tooth;
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Fever;
- General malaise;
- Muscle spasm of the jaw (in severe cases).
How long does a dental abscess last and how long do the symptoms persist?
The duration of a dental abscess and related symptoms substantially depends on the speed of intervention and the type of therapy that is implemented. It is therefore clear that it is essential to go to the dentist immediately as soon as the first suspicious symptoms appear. If the infection progresses, in fact, the healing times could be protracted, not to mention that more or less serious complications may develop.
however, it is essential since the infection must be completely eradicated.PLEASE NOTE
In no case and for no reason should "do it yourself" methods be attempted to break the abscess. Such a practice is dangerous both for the risk of creating lesions and for the risk of spreading / worsening the existing infection. It is ALWAYS necessary to contact the dentist.
- The periapical abscess does not rupture spontaneously and is not treated: the collection of pus tends to progressively enlarge and the cavity containing the abscess expands enormously to form a fistula or a cyst. In such situations, the infection can spread further, invading some areas of the neck and head.
- Dental abscess affects diabetics, immunocompromised subjects, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatments, etc.: If not treated, the risk of complications such as osteomyelitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, infection of the floor of the mouth and septicemia (sepsis) is very high. In severe cases, an untreated tooth abscess can cause death; however, to date, in our country, this is a "rather rare occurrence.
Main classification
- Periodontal dental abscess: caused by an "infection of the tooth support system" (gum, alveolar bone and ligaments).
- Periapical dental abscess: due to an "infection of the dental pulp.
Causes
A tooth abscess forms due to a bacterial infection of the teeth or gums. Among the risk factors, we remember: bad interventions on the teeth, bad oral hygiene, diabetes, gastroesophageal reflux diseases, AIDS, dry mouth, smoking, alcoholism, long-term therapy with corticosteroids.
Symptoms
In addition to the main symptom of dental abscess - the intense and relentless toothache - the patient often accuses swollen gums, swelling of the face on the side where the abscess is present, halitosis, dentinal hypersensitivity, fever and swollen lymph nodes in the neck .
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of dental abscess is quite simple: it makes use of the anamnestic examination (collection of the symptoms reported by the patient) and of the physical one (the doctor touches the tooth to test the extent of the pain), supported by the aspiration and analysis of a pus sample and x-ray of the tooth to assess damage.
For more information: Dental Abscess: Diagnosis, Therapy and PrognosisWhat to do and Therapies
Being an "infection," the dental abscess requires antibiotic treatment, possibly supported by the administration of pain relievers to mask the pain. Drainage of pus is also essential for healing.
For more information on what to do in case of tooth abscess, read also: Remedies for Dental Abscess