What and what they are
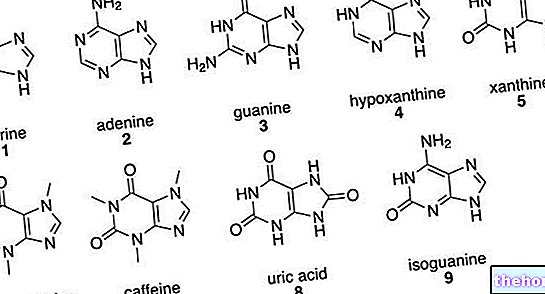
In the category of nerve foods, tea, coffee, cocoa and food products that contain them in significant quantities are traditionally included. The list can also be extended to alcoholic beverages and to those based on cola, guarana, matè and nervine substances in general (caffeine, theobromine, theine, ephedrine, ioimbine, synephrine ...).
Effects and Properties

Regardless of their tonic and invigorating characteristics, nerve foods, if consumed rationally, are precious allies for health. The polyphenols in tea, for example, have a strong antioxidant action, as do those of cocoa, dark chocolate and red wine, while a coffee at the end of a meal, preferably unsweetened, facilitates digestion. Furthermore, we must not forget their anorectic (suppress appetite) and thermogenic (enhance the body's energy consumption) properties; it is no coincidence, therefore, that nervine drugs (guarana, coffee, tea extracts, cola, ephedra, matè, bitter orange yohimbe ...) are widely used in the dietary field for the preparation of energy and slimming products. Their use is however not recommended during pregnancy, lactation, children under 12 years and people particularly sensitive to their action.
Note: tea and coffee provide no calories (unless taken with milk or sugar). Alcohol or ethanol provides a lot of energy, but is considered an "empty food" [food, because it provides calories, empty because it lacks the basic nutritional principles (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins)]. Ethanol itself is a toxic substance and as such devoid of any health benefit, which is instead ascribed to moderately alcoholic beverages, such as red wine and beer, due to the presence of useful micronutrients which have nothing to do with alcohol.