Information on Carnosine G1F - Keforma
CARNOSINE G1F - KEFORMA
Food supplement based on L-carnosine
FORMAT
Pack of 50grams
COMPOSITION
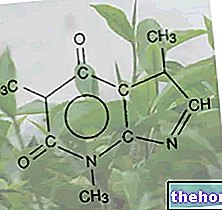
L-carnosine
Glucose 1 phosphate
Product features Carnosine G1F - Keforma
NUTRITIONAL INFORMATION
100 g
dose
Energy value
Kcal / Kj
Proteins
Fat
Carbohydrates
Glucose 1 phosphate
L-Carnosine
160/680
absent
absent
20 g
60 g
20 g
4/17
absent
absent
0.5 g
1.5 g
0.5 g
L-Carnosine- also known as beta-alanin L-histidine, is partly synthesized by the liver and partly introduced through foods of animal origin. It is estimated that the quantity of carnosine introduced daily, in a "diet that includes at least one course of animal origin, is between 50 mg and 250 mg, considering that 100 grams of beef provide about 124 mg of carnosine. This dipeptide is absorbed intact in the intestine, through a specific transporter, and from there distributed to the various tissues, in which it can be metabolized by enzymes known as carnosinase, or accumulated and used for its biological properties, which are carried out above all at the level of skeletal muscle and the brain.
Experimental evidence suggests a key role of this molecule in the control of the body's acid / base homeostasis and in the control of oxidative damage, so much so that it has been identified as an anti-aging agent. Today it is used in different clinical trials, for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, for neuropathies associated with diabetic disease, for the prevention of pathologies induced by ROS (oxygen free radicals) and to reduce cardiovascular risk. . However, there is no lack of studies, still in the experimental phase, which test the potential anti-neoplastic role.

Glucose 1 phosphate: central is the role of glucose in energy metabolism, representing one of the main sources of sustenance of the organism.

Rationale for use Carnosine G1F - Keforma
Numerous studies have highlighted a series of benefits deriving from the use of carnosine in sports. In most cases, these are benefits in ergogenic terms, with an increase in maximum strength, average strength and aerobic capacity. studies in which an increase in muscle mass was also recorded.
The molecular mechanism of action has not yet been clarified, but it is thought to be due to the buffering action on the one hand, which by preventing acidosis, supports muscle contraction, and to the glucogenic effect on the other, which definitely improves the properties. muscle energetics It is worth mentioning a study in which it was observed that the administration of carnosine for 3 days ensured an increase in 2.3 diphosphoglycerate, with a general improvement in aerobic capacity.
The presence of glucose 1 phosphate should support the restoration and accumulation of muscle glycogen, thus allowing an increase in energy capacity and support of athletic performance.
Method of use recommended by the company - Carnosine G1F - Keforma
Dissolve a measuring cup (2.5 g) of product in 200 ml of water.
Directions for use in sports Carnosine G1F - Keforma
For some time now, the use of this supplement in sports has been supplanted by beta alanine, which is cheaper and in any case effective in restoring muscle carnosine stores. However, currently quite varied dosages are used, ranging from 500mg to several grams per day.
Generally it is advisable to divide the intake into small doses, in order to avoid blood hydrolysis and renal excretion, making the product more available for accumulation. The presence of glucose 1 phosphate also suggests the assumption with simple sugars, in order to use the relative insulin peak to increase the muscle uptake of carnosine, and of the same glucose 1 phosphate, promoting glycogen synthesis.
Given the powdered form of this supplement, it may be useful to split the 500mg into two 250mg intakes diluted in fruit juice. Protocols are described in which 3 days of performance you can use higher dosages, even up to 1500mg.
How to optimize your business - Carnosine G1F - Keforma
As described for beta alanine supplements, the synergy with creatine has been shown to be particularly useful both in improving the ergogenic and anabolic properties, recording a significant increase in muscle mass in several studies. Furthermore, creatine has been shown to be useful in increasing muscle carnosine stores, albeit temporarily.
Particularly effective could also be the synergy with antioxidants such as vitamin E, glutathione, selenium and lipoic acid, in counteracting the damage induced by intense physical exercise with an improvement in the recovery phase.
Carnosine G1F side effects - Keforma
There does not appear to be any toxic effects associated with carnosine, especially when it is consumed at doses comparable to those that would be obtained with a healthy diet.
Doses higher than 500mg, used in anticancer trials, have proved equally safe.
In experimental models, even at doses of 50mg / kg, no side effects were recorded.
However, there is a lack of long-term clinical trials.
Precautions for use Carnosine G1F - Keforma
The product is contraindicated in cases of renal or hepatic pathology, cardiovascular disease and / or hypertension, during pregnancy, during lactation and under 14 years.
This article, elaborated on the critical rereading of scientific articles, university texts and common practice, is for information purposes only and therefore has no medical prescription value. It is therefore always required to consult your doctor, nutritionist or pharmacist before undertaking the use of any supplement.. Learn more about the critical analysis of Carnosine G1F - Keforma.
Safety evaluation of chicken breast extract containing carnosine and anserine.
Sato M, Karasawa N, Shimizu M, Morimatsu F, Yamada R.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Feb; 46: 480-9. Epub 2007 Aug 23
Carnosine supplementation protects rat brain tissue against ethanol-induced oxidative stress.
Ozel Turkcu U, Bilgihan A, Biberoglu G, Mertoglu Caglar O.
Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan 3.
Rejuvenation Res. 2008 Jun; 11: 641-7.
Derave W, Jones G, Hespel P, Harris RC.
Research Center for Exercise and Health, Department of Biomedical Kinesiology, Faculty of Kinesiology and Rehabilitation Sciences, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium. [email protected]
[The significance of free radicals and antioxidants due to the load induced by sport activity]
Holecek V, Liska J, Racek J, Rokyta R.
Cesk Fysiol. 2004; 53: 76-9. Review. Czech.
Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of L-carnosine supplementation in children with autistic spectrum disorders.
Chez MG, Buchanan CP, Aimonovitch MC, Becker M, Schaefer K, Black C, Komen J.
J Child Neurol. 2002 Nov; 17: 833-7.
[Using carnosine and natural antioxidants for the prophylaxis of acute post-loading oxidative stress]
Rozhkova EA, Ordzhonikidze ZG, Druzhinin AE, Seĭfulla NR, Paniushkin VV, Kuznetsov IuM.
Eksp Klin Farmakol. 2007 Sep-Oct; 70: 44-6. Russian.
The carnosine content of vastus lateralis is elevated in resistance-trained bodybuilders.
Tallon MJ, Harris RC, Boobis LH, Fallowfield JL, Wise JA.
J Strength Cond Res. 2005 Nov; 19: 725-9.
Jpn J Physiol. 2002 Apr; 52: 199-205.
Suzuki Y, Ito O, Mukai N, Takahashi H, Takamatsu K.
J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jun 15; 53: 4736-9.
Int J Sport Nutr. 1995 Dec; 5: 300-14.
Effects of multibuffer supplementation on acid-base balance and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate following repetitive anaerobic exercise.Kraemer WJ, Gordon SE, Lynch JM, Pop ME, Clark KL.
Center for Sports Medicine, Pennsylvania State University, University Park 16802, USA.
J Physiol. 1991 Aug; 439: 411-22.
Gardner ML, Illingworth KM, Kelleher J, Wood D.
Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Bradford.
Hormonal Responses to Resistance Exercise after Ingestion of Carnosine and Anserine.
Goto K, Maemura H, Takamatsu K, Ishii N.
J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Mar 10. [Epub ahead of print]
Carnosine and anserine ingestion enhances contribution of nonbicarbonate buffering.
Suzuki Y, Nakao T, Maemura H, Sato M, Kamahara K, Morimatsu F, Takamatsu K.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006 Feb; 38: 334-8.
Physiological role of carnosine in contracting muscle.
Begum G, Cunliffe A, Leveritt M.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2005 Oct; 15: 493-514. Review.
Muscle carnosine metabolism and beta-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training.
Derave W, Everaert I, Beeckman S, Baguet A.
Sports Med. 2010 Mar 1; 40: 247-63
The Role of beta-alanine Supplementation on Muscle Carnosine and Exercise Performance.
Giannini Artioli G, Gualano B, Smith A, Stout J, Herbert Lancha A Junior.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009
Beta-alanine improves sprint performance in endurance cycling.
Van Thienen R, Van Proeyen K, Vanden Eynde B, Puype J, Lefere T, Hespel P.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009 Ap
The effect of 4 weeks beta-alanine supplementation and isokinetic training on carnosine concentrations in type I and II human skeletal muscle fibers.
Kendrick IP, Kim HJ, Harris RC, Kim CK, Dang VH, Lam TQ, Bui TT, Wise JA.
Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009 May; 106: 131-8. Epub 2009 Feb 12.
Effects of beta-alanine supplementation and high-intensity interval training on endurance performance and body composition in men; a double-blind trial.
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009
Carnosine loading and washout in human skeletal muscles.
Baguet A, Reyngoudt H, Pottier A, Everaert I, Callens S, Achten E, Derave W.
J Appl Physiol. 2009 Mar; 106: 837-42. Epub 2009 Jan 8.
Beta-alanine and the hormonal response to exercise.
Hoffman J, Ratamess NA, Ross R, Kang J, Magrelli J, Neese K, Faigenbaum AD, Wise JA.
Int J Sports Med. 2008 Dec; 29: 952-8. Epub 2008 Jun 11.
Effects of twenty-eight days of beta-alanine and creatine monohydrate supplementation on the physical working capacity at neuromuscular fatigue threshold.
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Mielke M, O "Kroy J, Torok DJ, Zoeller RF.
J Strength Cond Res. 2006 Nov; 20: 928-31.
Effect of creatine and beta-alanine supplementation on performance and endocrine responses in strength / power athletes.
Hoffman J, Ratamess N, Kang J, Mangine G, Faigenbaum A, Stout J.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2006 Aug; 16: 430-46.
Effects of 28 days of beta-alanine and creatine monohydrate supplementation on aerobic power, ventilatory and lactate thresholds, and time to exhaustion.
Zoeller RF, Stout JR, O "kroy JA, Torok DJ, Mielke M.
Amino Acids. 2007 Sep; 33: 505-10. Epub 2006 Sep 5.
Amino Acids. 2006 May; 30: 279-89. Epub 2006 Mar 24.
The absorption of orally supplied beta-alanine and its effect on muscle carnosine synthesis in human vastus lateralis.
Harris RC, Tallon MJ, Dunnett M, Boobis L, Coakley J, Kim HJ, Fallowfield JL, Hill CA, Sale C, Wise JA.