Types of tracheostomy?
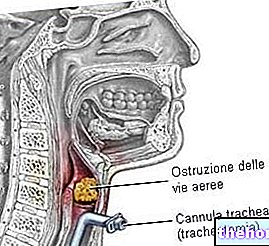
The tracheotomy is a delicate surgical maneuver performed to build a direct (and reversible) respiratory communication between the external environment and the tracheal lumen. This passage, created by making an "incision of the skin and tracheal wall, is made possible through the insertion of a special tracheal cannula.
Similar interventions are performed on all occasions in which the patient complains of severe breathing difficulties, caused for example by inflammation, neoplasms, accumulations of mucus in the trachea, chronic respiratory failure or other.
There are essentially two types of tracheostomy:
- Emergency intervention, which must be performed immediately to safeguard the patient's life. To reduce the execution time, the emergency tracheostomy can also be performed in the ward.
- Elective operation, which requires longer intervention times and is almost always performed in the operating room.
Emergency tracheotomy and elective tracheotomy
EMERGENCY TRACHEOTOMY (or cricothyrotomy)
It requires extremely rapid execution times to save the patient's life: the "time" factor therefore strongly conditions this type of tracheotomy.
In such circumstances, doctors sever the trachea by making a longitudinal incision through the cricothyroid membrane (for this reason, emergency tracheostomy is also called cricothyrotomy). We then proceed by inserting a needle-cannula, which in turn is connected to a "special oxygen bag.
Did you know that ...
In tracheostomy, the use of the cannula is essential to avoid the collapse of the soft tissues
The operation is performed under local anesthesia (injection of local anesthetic through the cricothyroid membrane), since general analgesia would require excessively long times.
ELECTIVE TRACHEOTOMY
It is performed in the operating room in a longer time than in the previous case. After light general anesthesia (usually) and / or local (less frequently), the surgeon makes an "incision on the patient's skin, at the level of the lower part of the neck (in the area between the Adam's apple and the upper part of the sternum).

Curiosity
The incision of the tracheal rings can be performed in different ways. The incision methods can in fact be: vertical, horizontal, H, inverted H or "lower hinge".
An oxygen bag or ventilator can be attached to the cannula to facilitate the transport of oxygen to the lungs. To keep the tube in the correct position, sutures are performed.
Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
Percutaneous tracheostomy
This is a relatively recent variant of tracheostomy that involves the use of dilating instruments to widen the tissue bundles of the trachea rather than dissect them.
Percutaneous tracheostomy, which creates a temporary airway, is indicated for patients requiring prolonged artificial respiratory assistance. It is a very quick surgical maneuver, therefore very used in emergency situations.
There are numerous variations of percutaneous tracheostomy. Most of the time, a special connecting cannula is used, which is introduced between the cricoid cartilage and the first tracheal ring; often, the cannula is inserted directly into the trachea, therefore further down, between the tracheal rings.
Compared to the classic tracheostomy, percutaneous involves fewer risks and complications after surgery, both in infectious and traumatic terms.
In any case, the choice of the operative modality (standard or percutaneous tracheostomy) is exclusively of medical competence.
Healing of the tracheostoma (hole)
We have seen that the cannula used in "tracheostomy surgery is indispensable both to avoid the collapse of the soft tissues (which connect the various cartilaginous rings of the trachea), and to facilitate / facilitate the patient's breathing. Having said this, we understand how the" extraction of the aforementioned connecting tube from the trachea results in the closure of the skin-trachea passage (called stoma or tracheostoma). The stoma healing (closing) times are strongly influenced by the time in which the cannula has been positioned: the longer the tube remains in place, the longer the healing time will be. While, in a dated tracheotomy, the skin-tracheal passage tends to remain open for quite a long time, in a recent tracheotomy the collapse of the connective tissue is almost immediate.
Curiosity
In addition to the period of stationing of the tracheal cannula, the closing times of the stoma are influenced by several factors:
- Respiratory pressure changes
- Thickening of connective tissue (induced by the inflammation produced during the operation)
If, after the collapse of the stoma, natural breathing is completely restored, there is a physiological reparative process that favors the total healing and scarring of the incision: in such circumstances, the stoma closes definitively.
When you want to restore natural breathing, it is therefore sufficient to extract the tracheal cannula and immediately dress the skin hole created during the tracheotomy with a medicated sterile gauze, essential to speed up healing times and minimize the risk of infections.
The surgical re-stitching of the stoma following a tracheotomy must not be considered a first choice method to promote healing: in such situations, in fact, the patient may encounter complications and post-surgery problems of various kinds and entities, such as in particular tracheal stenosis (narrowing).
Other articles on "Surgery and Types of Tracheostomy"
- Tracheotomy
- Tracheotomy: risks after surgery and convalescence