More important than simple food: the Mediterranean diet is truly a style of food made up of rules and habits inspired by the Mediterranean tradition in which foods, due to natural and epidemiological characteristics, are common in Italy, Greece and Spain.
But these nations, in addition to sharing food, also share the processes involved in obtaining, cooking and consuming food, as well as other lifestyle factors, such as moderate alcohol consumption, not smoking and being physically active. Numerous clinical studies have shown that blood glucose and insulin levels rise much more on a low-fat diet than on a reduced-carbohydrate diet.
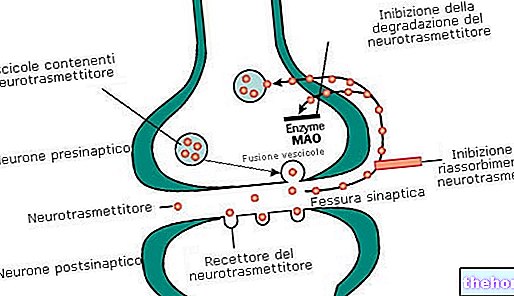
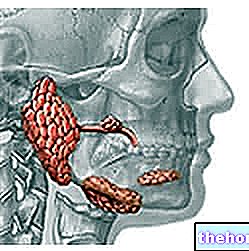
The insulin reaction to a Mediterranean-type diet shows how the insulin response in the hours following lunch is better, favored by an increase in the secretion of incretins.
The advantages of the Mediterranean diet for women do not only concern a more effective glycemic control, but also a beneficial effect on weight, lipid profile and therefore on cardiovascular risk.
, approximately 2500 are consumed daily by an adult, divided between the three macronutrients: 55-65% from carbohydrates, 20-30% from lipids and 10-15% from proteins. The Mediterranean diet is characterized by:
- Greater consumption of vegetable proteins than animal ones
- Reduction of animal fats such as butter, lard, in favor of unsaturated vegetable fats such as olive oil
- Increase of complex carbohydrates and strong moderation of simple ones
- High fiber intake
- Reduction of cholesterol intake
- Reduced consumption of red meat (limited to a maximum of once a week), and greater consumption of fish and legumes
- Consumption of eggs and dairy products no more than twice a week
- Few sweets
- Reduction in the consumption of: sausages, spirits, white sugar, butter, fatty cheeses, sauces, salt, margarine, pork
- Water is the main daily drink, but moderate consumption of wine is permitted during meals
These biomarkers, such as cholesterol levels and the amount of inflammation, can be influenced by diet and lifestyle. Whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits and vegetables are the most viable ways to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes.
Within the category of whole grains / starchy vegetables, it will certainly be useful to take into account the glycemic index of some foods, particularly suitable for the treatment of diabetes or to reduce the risk of its onset, such as sweet potatoes, barley, quinoa and oats. .
Adding more plant fiber to your diet is particularly beneficial: there is a special type of plant fiber, known as psyllium, which is particularly useful for regulating both blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Low-GI foods help in blood sugar management largely due to their soluble fiber content.
Soluble fiber has a slowing effect on the movement of food through the digestive system and thus leads to a more modest insulin response.
, sugar and salt, and is therefore the most suitable nutritional profile to come and fight: arteriosclerosis, heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, tumors (especially affecting the digestive system, see: diet and cancer) and intestinal motility disorders (or irritable colon ).
and fruit
When to eat.
Eat three main meals a day: breakfast, lunch and dinner, remembering to break with two snacks, useful to avoid sitting at the table hungry and eating too abundant meals, excessively caloric, and therefore cause of overweight. As for the post-prandial metabolism, it is necessary to consider the levels of sugars and insulin: if they are too high, the reduction in the activity of the beta cells of the pancreas is more marked and the risk of cardiovascular disease is higher.