Pasta food
Pasta is a TYPICAL ITALIAN product; it is a food made up of cereal-based flours, water and possibly other ingredients (eggs, fillings, etc.); the production of pasta is carried out through: mixing and processing, fragmentation and shaping, possible drying. Its nutritional composition is characterized by:
- High energy intake
- High intake of complex carbohydrates

Pasta industrial (contrary to the artisanal one) is composed exclusively of DURUM wheat mixed with water, while the addition of other ingredients requires the classification in the category of special pastes (with egg [further regulated], with cuttlefish ink, pasta dietetic etc).
Diabetics
All people with diabetes are diabetic mellitus type 1, type 2 and gestational.
The type 1 diabetic has a scarce or absent production of insulin which requires exogenous injection at the end of each meal; it is a disease with autoimmune or idiopathic etiology, or caused by severe pancreatitis, but still IRREVERSIBLE. The insulin dose is estimated. based on the quantity and quality of the meal: the higher the glycemic load (quantity and quality of carbohydrates in the meal) corresponds to the need for higher doses of insulin.
The type 2 diabetic, on the other hand, suffers from chronic hyperglycemia caused by poor peripheral sensitivity to insulin (with hyperinsulinemia = overweight), consequently (in the long term) develops a reduction in pancreatic secretion up to definitive insufficiency; it is a disease with multiple etiology, which recognizes risk factors such as genetic predispositions, nutritional imbalance with excess sugars, overweight or obesity, sedentary lifestyle, etc. The type 2 diabetic is treated pharmacologically with hypoglycemic agents and more rarely requires postprandial insulin injection.
The gestational diabetic (pregnant female) presents a picture similar to the type 2 diabetic; if left untreated, diabetes gravidarum can compromise the development of the unborn child (see macrosomal child) and persist even after childbirth.
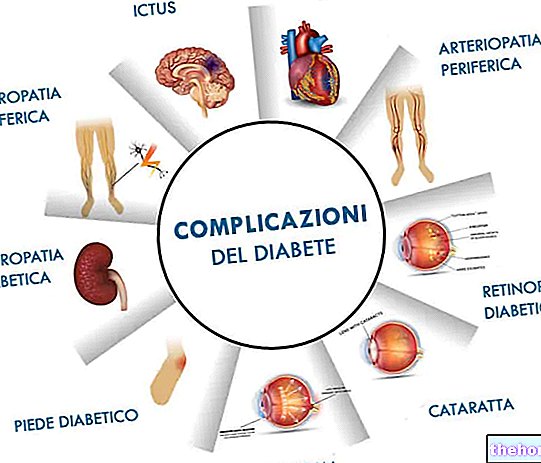
The diabetic, whatever he is, MUST keep his blood sugar and insulin levels under control. Certainly, nutrition plays an essential role, especially in disorders characterized by peripheral resistance (type 2 and gestational); in this case, an excess of calories and especially carbohydrates, associated with overweight or obesity, as well as representing an etiological cause of diabetes it can cause their worsening predisposing the subject to: neuropathies, complications of the micro and macrocirculation, cataracts, dyslipidemias ... atherogenesis, metabolic syndrome, myocardial infarction, cerebral stroke and death.
Essential lifestyle interventions for diabetics (especially those at risk of complications) are:
- Increased physical and sporting activity
- Caloric moderation
- Reduction of overweight
- Reduction of carbohydrates, especially simple ones
- Reduction of sodium, cholesterol and saturated fat
- Increase PERCENTAGE (and not quantitative!) of unsaturated fats and carbohydrates with a LOW glycemic index
- Increase in dietary fiber, essential fats, antioxidants, lecithins, phytosterols and other useful molecules present in food.
What is pasta for diabetics?
There pasta for diabetics is a special pasta and specifically a diet food.
Pasta for diabetics was born with the aim of compensating for the two negative characteristics that make pasta (as well as bread, polenta and all refined cereals) a product NOT RECOMMENDED in case of Diabetes Mellitus:
- HIGH glycemic load
- HIGH glycemic index
NB. It should be emphasized that, more than just use, the diabetic frequently manifests a real abuse of pasta, which is why (often) - although the consumption of food is allowed with due moderation - it is easier to ELIMINATE it from diet rather than reduce it.
Pasta for diabetics differs from traditional pasta for:
- LOWER glycemic load - 58g VS 82.8g of traditional pasta
- MINOR Glycemic Index - 23 GI VS> 50 GI of traditional pasta
- LOWER energy intake - 283 kcal VS 356 kcal of traditional pasta
- MORE "dietary fiber - 15g VS 2.6g of traditional pasta
In theory, in addition to guaranteeing a best metabolic impact, diabetic pasta should allow the optimization slimming therapy ... provided that it is inserted in a balanced / low-calorie nutritional context associated with constant and regular physical exercise; in light of these beneficial properties, pasta for diabetics has obtained a Decree of the Ministry of Health for Diabetics Nutrition (n.600.12 / 8114 of 10/12/2001).
How does diabetic pasta work?
Pasta for diabetics, compared to traditional pasta and if well used, has effects of glycemic moderation and weight loss.
How is it possible?
It is actually very simple; being a special pasta, pasta for diabetics can make use of the addition of one or more ingredients which, if they are able to counteract a specific pathology, they attribute to the food dietary properties (see diet foods). In short, the MAGIC ingredient is one and only one ... FIBER.
The reader might also reiterate ... even wholemeal pasta contains more fiber than normal, does this mean that it has the same therapeutic effects? ... Unfortunately not!
Dietary fiber added in pasta for diabetics is INULIN, a soluble compound (and not INSOLUBLE like wheat bran) which, in addition to being quantitatively superior 50% compared to the integral one and 600% compared to the white one, modulates intestinal transit in a decidedly effective way.
Pasta for diabetics is nothing more than: pasta with the addition of INULIN, a dietary fiber typically found in vegetables e in fruit.
And here is the video recipe to prepare homemade pasta for diabetics, with inulin, wholemeal flour and soy lecithin.
Pasta for Diabetics - Wholemeal Pasta with Zucchini and Ricotta Sauce
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to the Video Recipes Section
- Watch the video on youtube