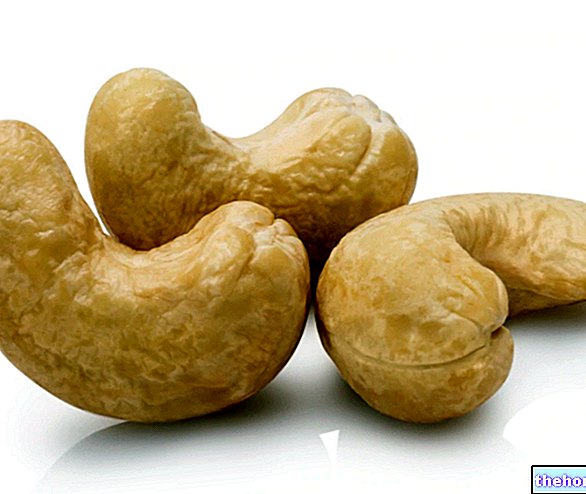
They appear as small nuts similar to "beans" (reniform), about 2-4 cm long. The seed, closed inside the shell, is yellowish-white in color and is characterized by a sweet and oily taste.
Cashews are not well placed in the VII fundamental food groups. This is because, despite being fruit in all respects, they have "promiscuous" nutritional characteristics. Unlike the VI and VII groups (fruit and vegetables rich in vitamin A and vitamin C, water, potassium and fructose), cashews contain high percentages of fat (with a higher concentration of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), different minerals (such as zinc and selenium). ) and vitamin E (tocopherol). The only common feature is the high fiber content. Compared to acidulous fleshy fruits, cashews contain starch and much more protein (not low, but medium biological value).
Note: The chemical content of raw cashews is different from roasted cashews.
In the Mediterranean diet, cashews play a marginal role. This is because the percentage of fats is covered not only by those naturally contained in fish, meat, milk and cheeses, but also by extra virgin olive oil. Let's say that, preferring lean foods of animal origin, and using little EVO oil , it would be possible to eat 7-15 g of cashews per day.