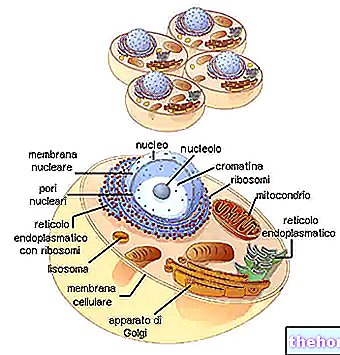
THE LYSOSOMES
Lysosomes are vesicles of about one micron in diameter filled with lytic enzymes for various organic substances (lysozyme, ribonuclease, protease, etc.). Lysosomes have the function of isolating these enzymes from the rest of the cell, which, otherwise, would be attacked and demolished.
Lysosomes then serve the cell to digest foreign particles. Depending on the nature and size of the substances incorporated by the cell, the process is called pinocytosis (when it comes to droplets), or phagocytosis (when it comes to more or less large particles). After the usable fractions have been reabsorbed by the cell, the residue to be eliminated is transported to the surface outside the cell. Lysosomes can be thought of as the internal digestive system of the cell, and can have two main modes of action. First, in single-celled organisms such as paramecia, they digest bacteria and other food particles taken up by the cell. In specialized cells. of the human body, as in certain white blood cells, the digestion of bacteria and other organisms that cause disease, represent the body's first line of defense against infection.
Second, lysosomes are involved in breaking down worn-out cell organelles in a process known as autophagy. In plant cells, lysosomes may be involved in the breakdown of protoplasm, which occurs in certain cell types as they mature. The products of lysosomal digestion are small molecules (amino acids, sugars, nucleotides, etc.) which from the place where digestion took place diffuse into the cytoplasm where they are reused. Defects in lysosomal function are believed to be responsible for many degenerative diseases, particularly those of the heart and brain.
THE ENDOPLASMATIC OR ERGASTOPLASMATIC RETICLE (R.E.)
Another membranous formation in the cell is that of the endoplasmic or ergastoplasmic reticulum. The membranes of the R.E. they resume the three-dimensional structure of the cytoplasmic membrane; they are always double, so as to determine more or less large cavities (cisterns, tubules).
The ergastoplasmic reticulum can be covered by ribosomes (and then it is called rough or granular), or smooth (or agranular). In the first case, the lattice is mainly linked to protein synthesis.

Click on the names of the various organelles to read the in-depth study
Image taken from www.progettogea.com

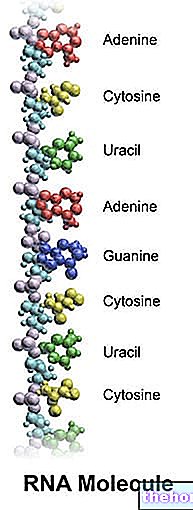
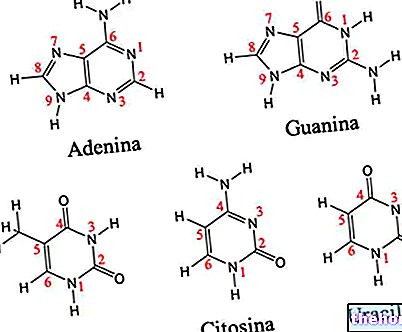
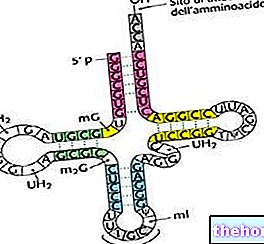
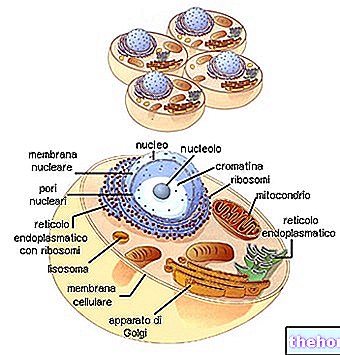


.jpg)


















