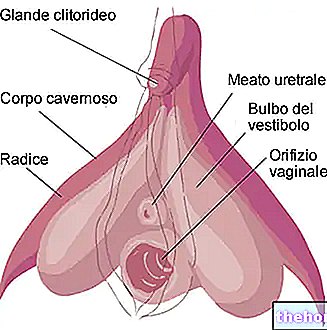
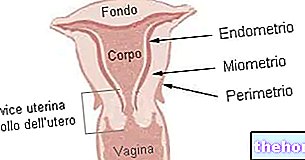
, that is, of the external part of the female genitalia.
The causes that can determine the onset of vulvitis are different: given its anatomical position, the vulva can be involved in inflammatory processes that originate from the genital tract, urinary tract and skin.
Vulvitis predisposing and triggering factors include infections, allergic reactions and traumatic injuries.Furthermore, the mucous membrane and skin of the vulva are particularly vulnerable to irritation, due to humidity and local heat.
The symptomatology of vulvitis is essentially represented by redness, itching, edema, burning and tenderness. Vulvar irritation can worsen with sexual intercourse and the habit of excessive intimate hygiene. Furthermore, vulvitis can coexist with vaginitis of various kinds (inflammation of the vagina), in which case we speak of vulvovaginitis.
Inflammation is diagnosed by physical examination and identification of any microorganisms responsible for the altered physiology of the vulvo-vaginal environment.
The treatment is directed to the triggering cause, to the elimination of irritating factors and to the correction of hygienic habits.
Tags:
Cosmetic Surgery workout-for-weight-loss skin-health
The causes that can determine the onset of vulvitis are different: given its anatomical position, the vulva can be involved in inflammatory processes that originate from the genital tract, urinary tract and skin.
Vulvitis predisposing and triggering factors include infections, allergic reactions and traumatic injuries.Furthermore, the mucous membrane and skin of the vulva are particularly vulnerable to irritation, due to humidity and local heat.
The symptomatology of vulvitis is essentially represented by redness, itching, edema, burning and tenderness. Vulvar irritation can worsen with sexual intercourse and the habit of excessive intimate hygiene. Furthermore, vulvitis can coexist with vaginitis of various kinds (inflammation of the vagina), in which case we speak of vulvovaginitis.
Inflammation is diagnosed by physical examination and identification of any microorganisms responsible for the altered physiology of the vulvo-vaginal environment.
The treatment is directed to the triggering cause, to the elimination of irritating factors and to the correction of hygienic habits.