- The amniotic sac and the placenta have formed;
- Organogenesis began, that is the process of generating organs (heart, stomach, organs of the nervous system, pancreas, blood vessels, nerves, etc.);
- The limbs appeared and began to lengthen.
- The fetus has gone from "being a very small fertilized egg-cell to" being an organism measuring 6.5 centimeters and weighing 73 grams, and in which a head, the sketches of the eyes, etc. are recognizable.
During the second trimester, exactly in the time window between the 20th and 22nd week, a "particular prenatal ultrasound, called morphological ultrasound (or second trimester ultrasound), is planned, which is used to verify the size of the fetus and its normal anatomy.
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the development of the fetus is characterized by:
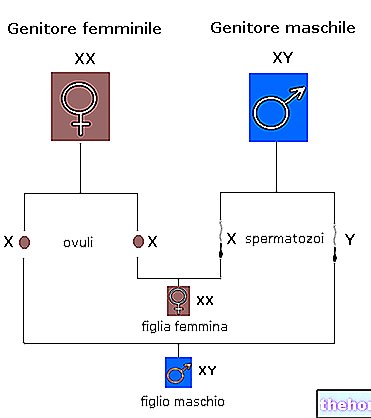
- The definition of sex, including ultrasound images;
- The continuation of organogenesis;
- The entry into function of the nervous system;
- The strengthening and improvement of the muscles, which is reason for the child to move;
- The growth of hair and, on some areas of the body (eg shoulders), of a particular down called fluff;
- The development of hearing ability
In the span of the second three months, the future unborn child passes from a length of 7.9 centimeters and a weight of about 93 grams, in the fourth month, to a length of 36.5 centimeters and a weight of just over 1,000 grams, at the end of the sixth month.
Here, however, is what happens in more detail month by month and week by week, during the second quarter.
4th MONTH
The 4th month of fetal development and pregnancy is from the 14th week to the middle of the 18th.
Between the 14th and 15th week, there is a "further definition of the neck and lower limbs; the spleen becomes a functional organ, which produces red blood cells; the sexual organs develop further; the bones continue to strengthen.
At the end of the 15th week, on average, the fetus measures 16.4 centimeters and weighs 117 grams.
At the 16th week, the head becomes erect; the eyes begin to make slow movements, however they are still closed as the eyelids have not yet separated; the ear is reaching its final position; the muscles are defining and strengthening.
Also at the 16th week, thanks to the strengthening of its musculature, the fetus begins to make its first movements; the latter, however, are still too slow and not very vigorous for the mother to warn them (they are observable through an "ultrasound").
At the end of the 16th week, the fetus measures just over 18 centimeters and weighs 145-150 grams.
Between the 17th and 18th week, toenails appear; the heart is getting bigger; the auditory system is formed, which means that the fetus begins to hear; the ears are now well defined and the eyes are assuming their final position; the digestive system is developed and functioning; the cerebellar vermis (a particular anatomical element of the cerebellum) becomes visible on ultrasound examination.
Also in these weeks, the future unborn becomes even more active and inclined to movement.
At the end of the 4th month, the fetus measures 22 centimeters and weighs around 220 grams.
5th MONTH
The 5th month of fetal development and pregnancy ranges from mid 18th week to near 22nd week.
At the 19th weekthanks to the activity of some specific glands, the fetus becomes covered with an oily substance, called vernix, which serves to protect the skin from amniotic fluid.
Also in this week, the nose, lips and ears are now well defined; in female individuals, the formation of the uterus and vaginal canal begins.
At the 20th week, the fetus becomes even more active and the mother finally begins to perceive its movements.
It should be noted that, starting this week, thanks to the definitive development of the ears, the future unborn child begins to be sensitive to noises.
At the 20th week, the fetus measures 25.5 centimeters and weighs approximately 330 grams.
At the 21th week, the first hair appears and on the body (especially on the shoulders, back and face) a down begins to form, called fluff, which tends to persist for some time even after birth; the fluff serves to retain vernix on the skin.
Also at the 21st week, the fetus begins to develop the sucking reflex, which sometimes leads to thumb sucking; in addition, he can suffer from hiccups.
From the 21st week, pregnant women may experience the first Braxton-Hicks contractions.
At the 22th week, the hair now grows evenly over the entire scalp; eyebrows have appeared; the production of the so-called brown fat begins, which has the function of producing heat; in males, the testicles begin to descend into the scrotum.
At the end of the 5th month, the fetus measures about 29 centimeters and weighs around 480 grams.
6th MONTH
The 6th month of fetal development and pregnancy is from week 23 to week 27 inclusive.

At the 23th week, the fetus begins to have rapid eye movements while sleeping; furthermore, fingerprints begin to form on his fingers and toes.
The out-of-womb survival rate for a baby at the 23rd week of fetal development is 33%.
At the 24th week, the skin becomes wrinkled and translucent, and takes on a pink-red color, due to the blood flowing into the subcutaneous capillaries.
At the end of this week, the fetus measures approximately 32 centimeters and weighs 670 grams.
The out-of-womb survival rate for a baby at the 24th week of fetal development is approximately 65%..
At the 25th week, the fetus begins the last phase of the formation of the lungs; moreover, it becomes capable of recognizing familiar sounds, in particular the mother's voice, to which it responds with a movement.
The out-of-womb survival rate for a baby at the 25th week of fetal development is approximately 81%.
At the 26th week, the lungs are now able to produce a substance essential for their proper functioning and maintenance of health: surfactant; the eyelids begin to become openable and reclosable structures.
As of this week, the fetus measures about 35 centimeters and weighs around 910 grams.
The out-of-womb survival rate for a baby at the 25th week of fetal development is approximately 87%.
At the 27th week, the nervous system further matures; the skin begins to accumulate fat, therefore it thickens and becomes smoother.
The out-of-womb survival rate for a baby at the 25th week of fetal development is approximately 94%.
At the end of the 6th month, the fetus measures 36-37 centimeters and weighs around 1,050 grams.
;Over the last three months, the future unborn child goes from a length of almost 38 centimeters and a weight of over 1,100 grams, at the beginning of the seventh month, to a length of 52 centimeters and a weight of 3,500-3,600 grams, at the end of the ninth month.
Here, however, is what happens in more detail month by month and week by week during the third quarter.
7th MONTH
The 7th month of fetal development and pregnancy is from the 28th week to the first half of the 31st week.
At the 28th week, eyelashes appear on the eyelids, which are increasingly functional; the nervous system reaches such a maturation that it is able to regulate breathing and body temperature.
At the end of this week, the fetus measures nearly 38 centimeters and weighs around 1,100-1,200 grams.
At the 29th week, the muscles and joints have reached such a development that the fetus, with increasing frequency, kicks, stretches and moves the fingers of the hands as if to grasp something.
At the 30th week, the fetus can now open its eyes wide, as the lids are now fully mature; moreover, it could have a considerable crown.
Also this week, the now formed bone marrow begins to produce red blood cells (in the first months of fetal development, the liver produces red blood cells).
At the end of the 30th week, the fetus measures just over 40 centimeters and weighs around 1,500 grams.
From the 31st week, the fetus begins to gain weight rapidly, as the internal organs are now almost all developed and mature (lungs are still missing).
At the end of the 7th month, the fetus measures almost 42 centimeters and weighs around 1,700 grams.
8th MONTH
The 8th month of fetal development and pregnancy runs from the second half of the 31st started week to the 35th week inclusive.
At the 32nd week, the fluff begins to disappear; the accumulation of adipose tissue continues and, indirectly, weight gain; the brain enlarges further and, consequently, the head also becomes larger; in the kidney, the nephron begins to form.
At the end of the 32nd week, the fetus measures just over 43 centimeters and weighs over 1,900 grams.
Between the 33rd and 34th week, the ocular pupils become sensitive to light, therefore they change size in response to a light stimulus; the bones harden considerably, except those of the skull which remain "softer" and "flexible" in anticipation of childbirth; the fingernails have grown to the fingertips.
At the end of the 34th week, the fetus measures 45.5 centimeters and weighs just over 2,300 grams.
At the 35th week, the now pink skin is less and less wrinkled and more and more thick and smooth, thanks to the accumulation of adipose tissue (the limbs have begun to take on a plump appearance).
At the end of the 8th month, the fetus measures 46-47 centimeters and weighs almost 2,600 grams.
9th MONTH
The 9th month of fetal development and pregnancy is from the 36th week started to the 40th week.
At the 36th week, the fetus begins to have difficulty moving inside the uterus, as its size is now such as to hinder its movements.
Furthermore, this week, the formation of the renal nephron ends.
At the 37th week, the fetus begins to prepare for birth, turning the head towards the neck of the uterus and descending towards the latter.
If she does not turn her head towards the neck of the uterus, the natural birth could be problematic, therefore the gynecologist could propose other solutions to the mother (eg: caesarean section).
At the 38th week, the toenails have reached the fingertips; head and abdomen have now reached the circumference that they will also have at birth; the fluff has now almost completely disappeared; the skin continues to thicken.
Starting this week, a possible birth is considered to have already been completed.
At the end of the 38th week, the fetus measures almost 50 centimeters and weighs around 3,200 grams.
According to obstetric medicine, a possible birth before the 25th week is to be considered a case of extreme premature birth; a possible birth between the 25th week and the 33rd week is a case of severe premature birth; a possible birth between the 34th week and the 37th week is a case of late premature birth.
At the 39th week, the chest becomes more prominent; in males, the testicles continue to descend into the scrotum; adipose tissue is increasing more and more, especially along the arms, shoulders and legs.
At the end of the 39th week, the fetus measures almost 51 centimeters and weighs just over 3,400 grams.
At the 40th week, the development of the fetus is now complete and the baby is ready to be born.
At the end of the 9th month, the fetus measures 52 centimeters and weighs around 3,600 grams.

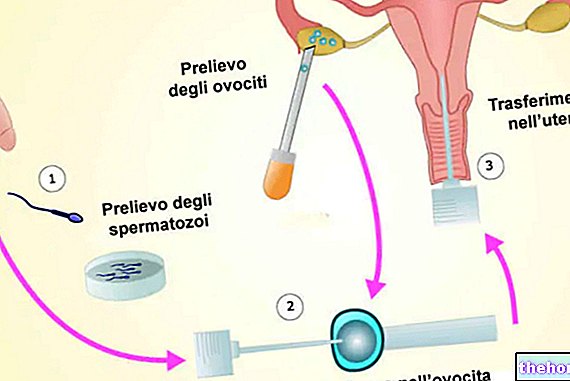




.jpg)


















