Diagnosis
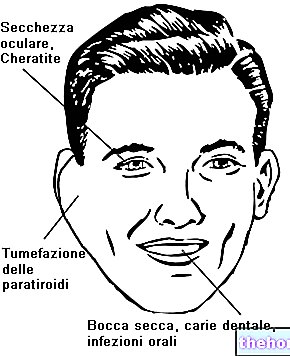
As seen in the introductory article, the symptoms of Sjögren's syndrome are numerous and affect several organs and tissues. Therefore, the diagnosis of the syndrome is based on several investigations. The main ones are:
- Ophthalmological tests
- Blood tests
- Lip biopsy
- Scintigraphy and sialography
- Scialometry
OPHTHALMOLOGICAL TESTS

BLOOD TESTS
They are essential for making a count and for evaluating the appearance of white blood cells in the bloodstream. A higher than normal number and an abnormal shape indicate the presence of lymphoma.
In addition, they are used to detect the presence of auto-antibodies, that is, the abnormal antibodies directed against the tissues of the organism. Among these, the anti-nuclear antibody, anti-phospholipid, anti-gastric mucosa, anti-thyroid, anti-Ro , anti-La and, finally, rheumatoid factors.
LABIAL BIOPSY
Lip biopsy is the most convenient histological examination to know the health of the glandular cells. It is performed on the inner lip.
SCINTIGRAPHY AND SCIALOGRAPHY
They are two diagnostic techniques that provide radiological images of the salivary glands. They both use a contrast agent to visualize the anatomy of the glandular tissue. These are two minimally invasive tests.
SCIALOMETRY
It is used to measure the amount of saliva produced in a given period of time.
OTHER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
There are, then, other methods of investigation, less practiced, but equally revealing of the disease. By means of some laboratory tests, it is possible to measure the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and the quantities of lysozyme, in tears and saliva. In patients with the syndrome of Sjögren, the ESR is increased, while the lysozyme content is lower than normal.
Another possible diagnostic test is the renal clearance of creatinine. In about half of patients with Sjögren's syndrome it is increased.
Finally, to evaluate or not the presence of a lymphoma, a CT scan can be used. The CT scan uses ionizing radiation, so it is an invasive test.
Treatment
There is currently no specific cure for Sjögren's syndrome. Therapy, therefore, aims to relieve:
- Local symptoms, such as xerostomia, xerophthalmia, or vaginal dryness.
- Systemic manifestations, typical of autoimmune diseases (the adjective systemic indicates that more organs and tissues are affected by the disease).
LOCAL THERAPY FOR XEROSTOMY
Patients are advised, first of all, to always keep their mouth hydrated, both through the intake of liquids and through the application of a special moisturizing gel.
To stimulate saliva production, pilocarpine 5 mg tablets should be taken, 4 times a day. Pilocarpine is only effective if the salivary glands have retained some of their functions; in case of complete glandular atrophy, in fact, the treatment does not give results.
Oral hygiene and dental health are also very important. In fact, the use of antifungals is required as protection from oral candidiasis, while avoiding sugars and periodic dental checks are used to prevent the formation of dental caries.
LOCAL THERAPY FOR XEROPHTHALMIA
To treat keratoconjunctivitis sicca, the patient must take artificial tears and eye drops based on methylcellulose or polyvinyl alcohol. In this way, the sensation of sand in the eyes, burning and dry eyes are relieved. The number of applications depends on the degree of dryness.
Oral pilocarpine can be used to stimulate glandular secretion. The effectiveness of this treatment depends, also in this case, on the state of atrophy of the lacrimal glands. Finally, the patient is advised periodic ophthalmological checks, to prevent a possible infection of the eye and damage to the cornea.
LOCAL THERAPY FOR VAGINAL DRYNESS
The remedy, in these cases, involves the use of lubricating gels, based on propionic acid. Also in this case, hygiene is important, to ward off the danger of an infection (vaginal candida).
SYSTEMIC THERAPY
The systemic therapy of Sjögren's syndrome aims to alleviate the extraglandular manifestations.
As mentioned, the cause of these disorders are auto-antibodies and other cells of the immune system, which rebel against the organism and attack it.
Therefore, different drugs are administered, such as:
- Corticosteroids
- Preparations with immunosuppressive action (immunosuppressants)
- NSAIDs
Low-dose corticosteroids are indicated in the primary forms of Sjögren's syndrome. They are used to relieve pain due to arthralgia and asthenia. Higher doses, on the other hand, are taken in the most serious cases, when vasculitis and renal deficits appear.
Immunosuppressive drugs include cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine and cyclosporine A. Their main action is to reduce the number of auto-antibodies in the blood. But they can also be useful in the treatment of vasculitis and interstitial nephritis, due to to the lymphocyte infiltrate. Immunosuppressive drugs are particularly indicated when Sjögren's syndrome is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus.
NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and are used to relieve pain due to joint and muscle disorders.
Prognosis
Patients with Sjögren's syndrome have a different prognosis from case to case. Some patients show only the main symptoms: xerostomia and xerophthalmia. For these, the prognosis is good, as long as they undergo periodic medical checks and follow strict hygiene rules, both oral and ocular. Otherwise, the quality of life can be affected.
The case of patients with secondary forms of the syndrome is quite different. For them, the prognosis becomes worse, as other organs and tissues of the body are affected more easily. Among the most dangerous consequences of Sjögren's syndrome, the possibility of developing lymphomas should be noted.
Other articles on "Sjogren's Syndrome - Diagnosis and Treatment"
- Sjogren's Syndrome - Causes and Symptoms
- Scarlet fever - Drugs for the treatment of scarlet fever