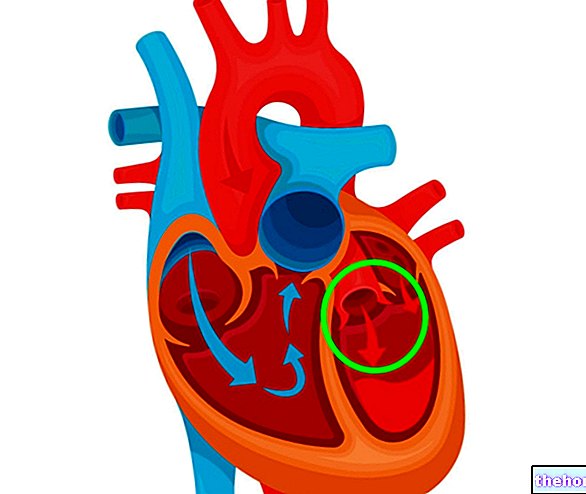
he is called to a super job. To cope with heat waves, it activates a series of mechanisms. In detail, it stimulates the sweat glands to increase the production of sweat: in fact, it cools the body by evaporating. Furthermore, it causes vasodilation, that is, it increases the caliber of the blood vessels, so the blood reaches the peripheral tissues more easily, to which it transfers heat; these, in turn, release heat to the surrounding environment. In addition, it increases the frequency of breathing: the heat is thus eliminated also through breathing. Finally, appetite, motor activity and the secretion of some hormones decrease, in order to slow down the metabolism and, therefore, the internal production of heat.
Under certain conditions and in certain subjects, the thermoregulation system can go haywire. For example, this happens when there is a prolonged period of extreme weather conditions with above average temperatures, often associated with high humidity, strong sunlight and lack of ventilation. This is why ailments such as cramps, fatigue, fainting, swelling, difficulty breathing, dehydration, headache, dizziness, tachycardia, palpitations, tingling in the legs can occur.
and an increase in heart rate. This is why even healthy people can be prone to tachycardia. Obviously, for those who already suffer from cardiovascular disorders, the dangers increase.
In addition to high temperatures and excessive heat, attention must be paid to sudden thermal variations, those that occur for example when passing from very hot outdoor environments to cold indoor environments due to air conditioning and vice versa. In these situations, in fact, the thermoregulation system is called to a demanding and quick job. Well, this stress can also have a negative effect on the heart. It is the same reason why it is not recommended to jump into the sea or into the pool after being exposed to the sun for a long time: if you are very hot and the water is cold, a dangerous thermal shock can occur. The dangers increase if you have eaten. and, therefore, a lot of blood is present in the stomach: if it suddenly cools, congestion can arise.
Also pay attention to physical exertion. When exercising on hot and humid days, the dehydration process tends to accelerate. If the lost fluids are not replenished, therefore, various ailments can appear. The heart can also tire.
must pay even more attention. It is important that you check the values more frequently than usual. And don't go to the mountains without first asking your doctor for advice. In fact, at high altitudes the air is less rich in oxygen: the heart tends to compensate for this condition with an increase in the heart rate (tachycardia) and with an increase in pressure, working harder. .