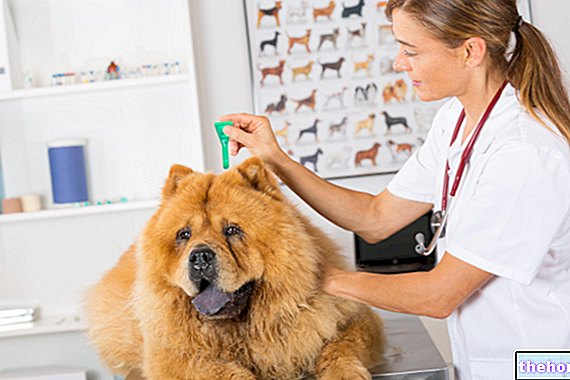
They are the most common cause of dermatological symptoms in dogs and cats and must always be excluded at the beginning of a therapeutic protocol. The presence on the skin and on the coat of mange mites or fleas can cause lesions related to the direct feeding of the parasite on the skin. "animal and, in the case of pulicosis, lead to allergic symptoms by activation of the immune system with components of the saliva of the parasites. This last situation is called flea allergy dermatitis or DAP and affects animals of any age or breed, even suddenly. However, it has been seen that DAP is mostly diagnosed in subjects who are not used to being in contact with fleas and who therefore respond more to their bite.
- Malassezia dermatitis
Malassezia is a yeast normally present on the skin and ears of dogs and cats. In healthy subjects the quantity of yeast is not high, but in predisposing situations this can proliferate and cause a specific dermatitis. Alterations of the skin system, alterations of the immune system, prolonged antibiotic treatments or concomitant diseases can favor the growth of Malassezia. In addition to the manifestation of dermatitis, there is also a very frequent form of otitis caused by the same yeast and more evident in dogs with pendulous ears or subjects with allergies.
- Fungal infections
Fungal infections in dogs and cats are sustained by dermatophytes, fungi that draw their energy to develop by digesting the keratin of the host's skin. Fungal infections can be contracted with contact with sick subjects or carriers of the fungus, or by contact with objects and environment in which the spores have been deposited. It must be remembered that dermatophytes can also infect humans, causing skin symptoms also in this case.
- Bacterial infections
The bacteria present at the environmental level can infect the skin of the animal and cause inflammation. Depending on the location, pyoderma is classified as superficial or deep, but in both cases the most commonly found bacteria is Staphylococcus.
- Atopic dermatitis
The term atopy indicates allergies to substances present in the environment in the veterinarian. These substances can be many, including pollen, plants, dust, mold, animal or human dandruff, and can cause allergies in dogs and cats with a predisposition The first symptoms are usually manifested by the animal between 6 months and 3 years of age.
Being atopic also increases the likelihood of developing other types of dermatitis, bacterial or yeast infections, and ear infections.
- Food allergy
Among the allergies that cause skin symptoms we also find those caused by animal (chicken, bovine, fish) or vegetable (soy, wheat, corn) food proteins. Generally this allergy manifests itself as early as the third or sixth month of life and develops after administration of the food for at least a few weeks or months.
- Endocrine pathologies
Some endocrinopathies, such as hypothyroidism and Cushing's syndrome or hyperadrenocorticism, have a manifestation also at the cutaneous level due to the relapse of the pathogenesis also on the skin and hair turnover. The subjects presenting pathologies of this type are also those more predisposed to infections secondary and require additional care in addition to the treatment of endocrine disease.
- Autoimmune Diseases
These are pathologies that affect the animal's immune system and cause an exaggerated response to the very components of the organism. The autoimmune skin diseases that are most commonly diagnosed in dogs and cats are pemphigus foliaceus and lupus erythematosus and can affect individuals of any age, sex and race. The mechanism of development is not yet well known for these pathologies.
- The eosinophilic granuloma complex
This type of pathology affects the cat and can manifest itself in the form of eosinophilic plaque, indolent ulcer or linear granuloma. It is also in this case an anomalous response of the organism towards different allergens and infecting agents. The similarity of these manifestations is grouped in the denomination of the eosinophilic granuloma complex, but each being differs in localization and appearance.
- Contact dermatitis
They are skin inflammations that can be caused by direct contact with chemical or natural histologic agents. They therefore affect the most exposed parts of the animal and can cause superficial or deep lesions, being conditioned by contact time, the quantity of the substance and the reaction of the organism itself.
- Skin neoplasms
Tumors in the skin are also found in dogs and cats. These can be benign or malignant in nature with different localizations.The most commonly diagnosed tumors in dogs are hemangiomas, melanomas, mast cell tumors, lymphomas; in cats, in addition to cutaneous lymphoma, the most common is squamous carcinoma, detectable above all in subjects with white coat and hairless areas. There are well-researched breed predispositions in both dogs and cats.
To learn more: Fleas how to recognize and eliminate them , papules, itching, hair loss with areas of alopecia, scabs or scales, ulcers. In some cases it is possible to detect a thinning of the skin, in others an increase in the thickness of the skin and a progressive darkening of the affected areas. The onset of lesions can be acute or chronic depending on the underlying cause.
Although the symptoms can be shared by various underlying pathologies, the veterinarian, with a clinical examination, the collection of anamnestic information and the help of diagnostic investigations (cytological, parasitological or laboratory tests), will be able to formulate an etiological diagnosis by putting together the information received. .
For further information: Sphynx cats: the most frequent diseases and mites throughout the year.- The treatments that can be proposed by the veterinarian see the use of antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungals for fungal infections and antiparasitics in case of parasitosis. Often it is necessary to add the action of anti-inflammatories to reduce the inflammatory response of the organism or drugs in able to stop the itch cascade. Furthermore, the pharmacological action can be both systemic and topical with specific formulations. There are also a series of nutraceuticals that help the action of the drugs administered and are able to support the skin in its return to normal.
- Finally, the role of nutrition assumes great importance in allergic diseases, which itself becomes part of the prescribed therapy. In subjects who may have abnormal reactions to proteins present in foods, specific diets called hypoallergenic or hypoallergenic can be administered. so-called protein hydrolysates, ie proteins made much smaller that do not activate the body's allergy response. Allergic dogs and cats must therefore undergo a controlled diet, without being able to afford continuous and extra modifications.