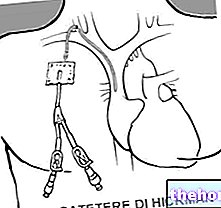
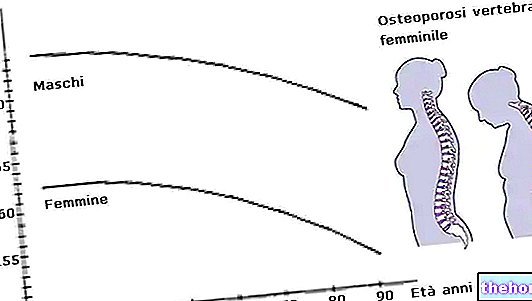
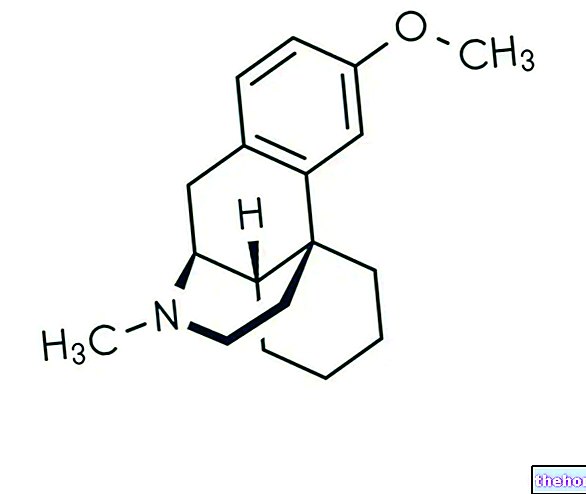
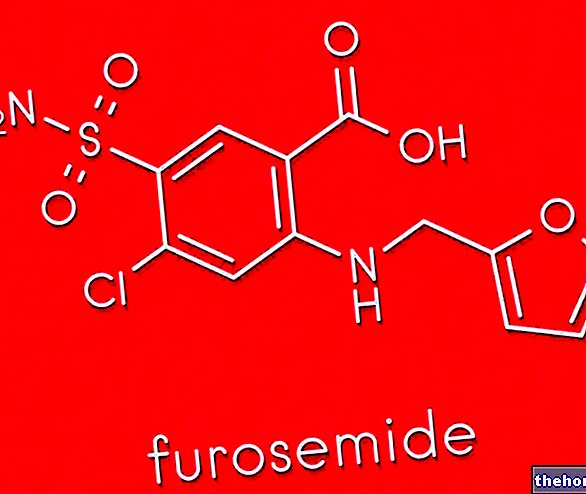
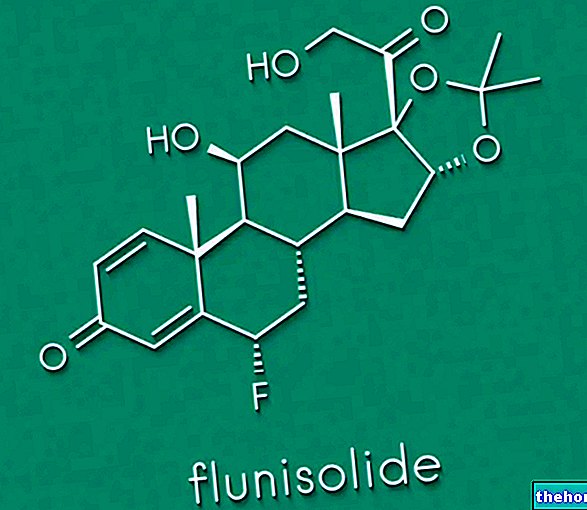
Aetiopathogenesis is defined as the analysis of the causes and development of a pathology or an abnormal condition. The term derives from the "union of" etiology "and" pathogenesis ", which in the medical field indicate, respectively, the causal factors (etiology) and the mechanism of onset, and consequent development, of a pathological process (pathogenesis).
.jpg)