Generality
The human body is the physical structure of the human organism, made up of about 37.2 trillion cells and organized into a head, a neck, a trunk, two upper limbs and two lower limbs.

The organs, cooperating with each other, take part in the formation of the so-called systems or apparatuses.
The human body has a specific chemical composition. The latter mainly includes: water, lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and inorganic minerals.
Due to aging, the human body undergoes numerous changes, some of which are very profound.
What is the human body?
The human body is the physical structure of the human organism, resulting from the synergy of an enormous number of different cells; this structure is organized in a head, a neck, a trunk, two upper limbs (each including an arm, a forearm and one hand) and two lower limbs (each including a thigh, leg and foot).
Cells represent the basic units of life. In fact, they make up the tissues → tissues of different types make up the organs → sets of different organs form the systems (or apparatuses).
Structure
From birth to adulthood, the human body undergoes some physical changes, which however do not alter its general organization (that which includes a head, a neck, a trunk, etc.).
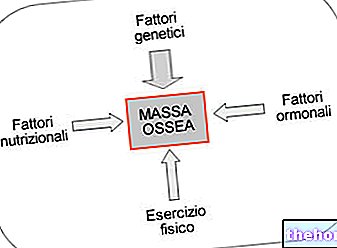
These changes mainly concern body height, body weight and the distribution of muscles and fat, and depend on various factors, including diet (understood as a diet), physical exercise, sex and genetics.
THE CAVITIES OF THE HUMAN BODY
Observing it from the inside, the human body has several cavities.
The two most important cavities, in terms of width, are the abdominal-pelvic cavity (the largest) and the thoracic cavity.
The abdominal-pelvic cavity takes place in the lower part of the trunk and contains numerous vital organs, including the liver, kidneys and intestines.
The thoracic cavity occupies the upper part of the thorax and houses, inside it, the heart, the lungs and a part of the aorta, all fundamental organs for life.
Minor cavities, which deserve a special mention, are the paranasal sinuses. Formed by some bones of the skull, the paranasal sinuses are spaces through which air passes and which serve to improve the perception of smells and to amplify sounds and voice.
WHAT IS THE AVERAGE STATURE OF THE HUMAN BODY?
The average height of the human body of an adult man is about 1.7-1.8 meters.
The average height of the human body of an adult woman, on the other hand, is about 1.6-1.7 meters.
In Italy, according to some studies, the average height of the male population is about 1.74 meters, while that of the female population is about 1.62 meters.
HOW MANY BONES DOES THE HUMAN BODY INCLUDE?
The human skeleton, with its bones, is the scaffolding that guarantees stability and support to the human body.
Without the skeleton, the human being would not be able to keep upright and would lack a protective element of the internal organs of fundamental importance.
In the human body, the bones that make up the skeleton are 206.
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of the human body includes: water, elements of an organic nature and inorganic minerals.
WATER
Water is by far the most conspicuous chemical component. In fact, in the human body of a young adult, the water content represents about 60-65% of the total weight.
The water is distributed both in the so-called extracellular fluids (blood plasma, lymph and interstitial fluids), and inside the cells (here, it constitutes the so-called intracellular fluid).
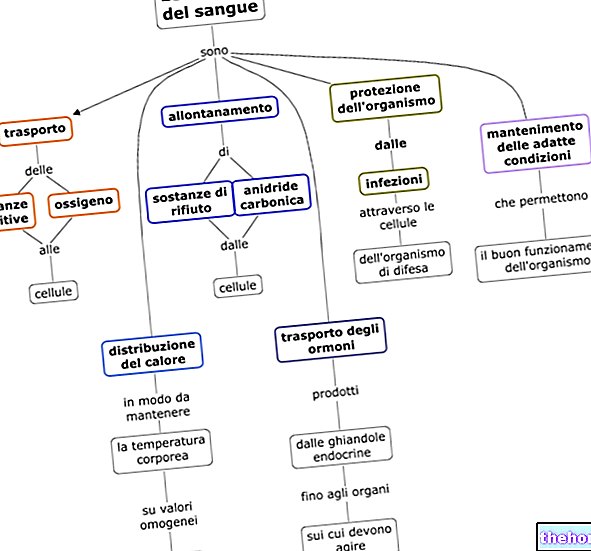
Water is a solvent and, as such, acts as a transport vehicle for the substances that keep the individual cells alive. Furthermore, it contributes to the digestive process, guarantees thermoregulation (think of sweating) and favors the elimination of waste , accumulated in the organism.