Male cystitis produces a number of characteristic symptoms, including: an urgent and persistent urge to urinate, burning when urinating, pollakiuria (frequent urination, but with the passing of small amounts of urine) and dysuria (difficulty urinating).
Usually, the diagnosis of male cystitis and its causes is based on information from: physical examination, medical history and some more specific tests, such as urinalysis, cystoscopy and ultrasound of the lower abdomen.
Male cystitis therapy varies according to the triggering cause; this explains why, in the course of diagnosis, doctors try to understand the precise causal factor.
, from the presence of a foreign body in the bladder or, finally, from unrecognizable causes (the so-called interstitial cystitis).
Cystitis is more common in women; this is due to the characteristics of the "female urethra: the latter, in fact, is shorter and closer to the anus than the male urethra (which is a possible source of infecting bacteria).
Brief anatomical recall of the Bladder

Also known as the urinary bladder, the bladder is a hollow, musculomembranous and odd organ, which is used to collect the urine produced in the kidneys and ready to be eliminated by the mechanism of urination.
The bladder is located in the anterior region of the pelvis, resting on the pelvic floor, behind the abdominal wall and the pubic symphysis, in front of the rectum and above the prostate in men, in front of the uterus and vagina in women.
In men and women, infecting bacteria reach the bladder through the urethra, which has an "opening towards the outside" (the urinary meatus) aimed at expelling the urine.
Male cystitis following a "bacterial infection" is an example of a urinary infection (or urinary tract infection).
Specifically, drugs with these characteristics are mainly chemotherapeutic agents, such as cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide.

Shutterstock
- Prolonged use of the bladder catheter (foreign body cystitis). Long-term use of the bladder catheter can damage the inner wall of the bladder, irritating and inflaming it.
- Exposure to certain chemicals (chemical cystitis). For some individuals, the substances that make up certain intimate cleansers and bubble baths represent a kind of allergen, capable of irritating and inflaming the bladder.
- Unknown causes (interstitial cystitis).
The potential causes of cystitis in men are the same as in cystitis in women.
Risk Factors of Male Cystitis
Factors such as:
- Poor or excessive intimate hygiene;
- The use of the bladder catheter for long periods of time;
- Pelvic radiotherapy;
- The intake of chemotherapy drugs (in particular cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide);
- The weakening of the immune system;
- The presence of urethral stricture;
- The presence of benign prostatic hypertrophy;
- Diabetes mellitus (the high blood sugar typical of this condition favors the proliferation of those bacteria such as E. Coli, which are normally present in the human body).
In addition, male cystitis is more common in sexually active men and the elderly.
most common of male cystitis are:
- Urgent need to urinate, even if you have recently done so;
- Burning when urinating;
- Frequent urination, but with the emission of small amounts of urine (pollakiuria);
- Difficulty urinating (dysuria).
If male cystitis is particularly severe, the aforementioned disorders are joined by:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pus in the urine (pyuria)
- Cloudy, foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain
- Sense of pressure in the lower abdomen;
- Mild fever.
Did you know that ...
Only the infectious (bacterial) forms of cystitis cause the symptom of fever; this means that, when cystitis is not of an infectious nature, it is generally not a reason for alterations in body temperature.
Complications of Male Cystitis
In the absence of timely and appropriate treatment, in male cystitis of bacterial origin, the pathogens responsible for the infection can reach the kidneys and infect them in turn, resulting in a condition known as pyelonephritis.
Pyelonephritis is kidney infection; this disorder represents an important danger to kidney health, as, if not treated properly, it can permanently damage the kidneys, permanently compromising their functions.
If the treatments are timely and adequate, it is rare for male cystitis of bacterial origin to result in complications.
Conditions Associated with Male Cystitis
When caused by bacteria, male cystitis is very often associated with bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate due to bacteria.
To justify this frequent association is the proximity between the bladder and the prostate, proximity that facilitates the movement of bacteria from one organ to another.
When to see a doctor?
Male cystitis experts recommend seeking medical attention if symptoms such as:
- Hematuria (i.e. blood in the urine);
- Pain in the hips or back (a typical manifestation of pyelonephritis, kidney infection);
- Fever associated with chills
- Nausea and vomiting (these are two other manifestations of pyelonephritis);
- Frequent, urgent and / or painful urination, lasting for several hours.
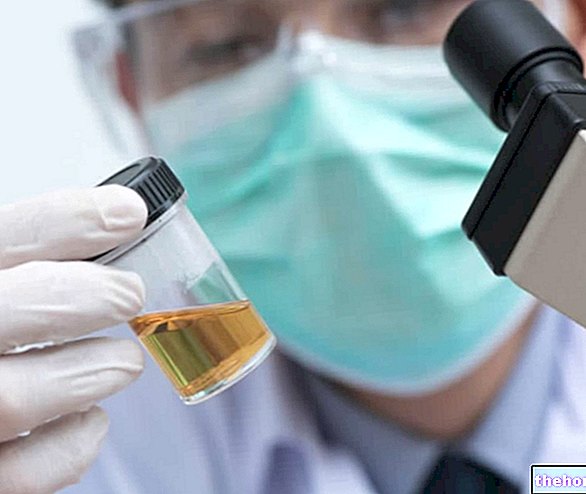
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the laboratory test for looking for bacteria or other pathogens in a urine sample.
In a context of male cystitis, urinalysis allows us to establish whether or not the inflammation is due to a bacterial infection and, in the case of inflammation of infectious origin, what is the precise infecting pathogen.
Any negative response to the search for bacteria in the urine is the reason for diagnostic investigations, which include the aforementioned cystoscopy or ultrasound of the lower abdomen.
Cystoscopy

Cystoscopy is the endoscopic examination that allows to evaluate the state of health of the bladder, through the observation of the latter from the inside and, sometimes, the collection of a sample of the bladder wall to be subjected to subsequent laboratory analysis.
In a context of male cystitis, cystoscopy is a useful test for identifying the signs of the inflammatory process in progress and for recognizing the cystitis that have been negative for urine control.
Did you know that ...
To perform the cystoscopy, House introduces a long flexible tube with a camera and a light source into the urethra and then takes it into the bladder.
Ultrasound of the Lower Abdomen
Ultrasound of the lower abdomen is an examination of imaging which allows you to observe the organs and soft tissues of the pelvic region.
In a context of male cystitis, ultrasound of the lower abdomen allows an analysis of the organs and tissues surrounding the bladder, in order to understand if these have any role in the ongoing inflammatory process.
It should be noted that this examination, in the diagnostic path that leads to the identification of male cystitis (as well as cystitis in women), represents an uncommon practice.
Diagnosis of Male Cystitis: Importance of the Causes
Recognizing the precise causes of male cystitis is essential for planning the most appropriate treatment plan.
Indeed, without information on the nature of the ongoing inflammation, it is impossible to establish an effective cure.
The cornerstone of this therapeutic path is, without doubt, the antibiotic treatment: without it, in fact, the patient's immune system would find it very difficult to eliminate the bacteria responsible for the inflammation.
Treatment of Non-Infectious Male Cystitis
- There male interstitial type cystitis it is a condition for which there are no specific treatments, but only symptomatic treatments (ie with the sole ability to alleviate the symptoms); the reason for this is to be found in the lack of knowledge of the factors triggering this particular form of inflammation of the bladder.
Among the symptomatic treatments of male interstitial cystitis, there are: painkilling and anti-inflammatory drugs (eg: ibuprofen, paracetamol and amitriptyline), drugs against urinary incontinence (eg: tolterodine), antihistamine drugs (eg: loratadine), drugs capable of stimulate the repair of the internal bladder wall (eg: sodium pentosan polysulphate), the nerve stimulation technique known by the acronym TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nervous Stimulation), physiotherapy for relaxation of the pelvic muscles and a series of surgical techniques more or less invasive (they are indicated only when all the treatments mentioned above have proved ineffective). - There male cystitis of the radioactive type and the male chemotherapy cystitis they recover with the interruption of radiotherapy, in the first case, and of the intake of chemotherapy, in the second circumstance.
To speed healing and relieve pain symptoms, those with either of these two variants of male cystitis can take an over-the-counter pain reliever and anti-inflammatory drug (e.g. acetaminophen or an NSAID). - There male cystitis of a chemical type and the male foreign body cystitis they heal, respectively, by avoiding the use of those personal hygiene products that promote inflammation of the bladder and by stopping the use of the bladder catheter.
As in the previous case, to promote healing and ease pain, those suffering from one of these two types of male cystitis can take an over-the-counter pain reliever and anti-inflammatory drug.
- Drink a lot and often. The consumption of water helps to prevent cystitis, as it avoids the stagnation of urine inside the bladder;
- Avoid holding back the urge to urinate for too long.Voluntarily withholding the urge to urinate seems to facilitate bacterial multiplication;
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet, avoid stress by taking relaxing breaks and exercising regularly. These behaviors are essential for the well-being of the immune system;
- Take care of personal hygiene. It is particularly important to clean the private parts after defecation;
- As soon as possible, urinate after sexual intercourse and wash the private parts;
- Avoid the common use of towels and underwear, at home, in the hotel or in any other condition;
- Prefer a shower to a bath in the tub. Bathing in the tub is a contributing factor to cystitis, especially in people at risk of chemical cystitis.






.jpg)


















