Bronchitis without fever never has an infectious origin; in fact, it can depend on conditions such as: sporadic or continuous exposure to irritating substances for the bronchial tree, chronic pulmonary diseases (eg: asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ) and gastroesophageal reflux.
Bronchitis without fever can cause several symptoms, including: coughing, chest discomfort, wheezing, and wheezing or wheezing.
The diagnosis of bronchitis without fever always starts with a physical examination and anamnesis.
Bronchitis without fever requires causal therapy, where possible, and symptomatic therapy.
Brief review of the Bronchial Tree
Following the trachea and preceding the pulmonary alveoli, the bronchial tree is the complex section of the lower airways (or lower respiratory tracts), which includes, in order, the primary bronchi, the secondary bronchi, the tertiary bronchi, the bronchioles, the terminal bronchioles and respiratory bronchioles.
According to the most common anatomical view relating to the "bronchial tree," the latter can be divided into two sections: the extrapulmonary tract (ie external to the lungs), to which only the primary bronchi belong, and the intrapulmonary tract (ie internal to the lungs), which include the secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles and respiratory bronchioles.
Bronchitis Without Fever: Acute Type and Chronic Type
Bronchitis without fever can have the characteristics of an acute condition (therefore intense in symptoms, but of limited duration) and be an example of acute bronchitis, or it can have the characteristics of a chronic condition (therefore mild-moderate in symptoms, but of long-lasting) and being an example of chronic bronchitis.
, cigar, pipe etc. (in other words, tobacco smoke), the substances that constitute the so-called environmental pollution, some chemical fumes and some toxic dusts.
In addition to attacking the bronchial tree and causing fever-free bronchitis, the aforementioned irritants could also inflame the trachea, resulting in a condition known as tracheitis.
Chronic Lung Diseases that Cause Bronchitis Without Fever
In the list of chronic lung diseases potentially capable of causing bronchitis without fever, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) stand out in particular.
Typically, fever-free bronchitis resulting from chronic lung disease is a form of chronic bronchitis.
Chronic fever-free bronchitis is a persistent, difficult-to-treat condition.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory lung disease, which usually causes respiratory infections, medicines (eg NSAIDs), physical exertion, excessive emotions, stress and smoking, usually due to the effect of allergens (eg pollen and animal hair), the temporary narrowing of intrapulmonary bronchi and bronchioles, thus resulting in an obstacle to the passage of inspired air.
According to the most reliable hypotheses, "asthma has a" genetic origin.
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (or COPD) is an inflammatory lung disease, which determines a permanent narrowing (which is why it is called chronic and obstructive) of the bronchial tree inside the lungs.
COPD is a very serious condition, which recognizes as main causal factors: smoking (ie the habit of tobacco smoke), passive smoking and constant exposure to certain dusts or toxic substances.
COPD has a sneaky behavior; in fact, it begins as an asymptomatic condition and becomes responsible for severe symptoms (such as dyspnea, cough with phlegm, fatigue, etc.) only in the most advanced stages (when the patient's health is already irremediably compromised).
COPD permanently affects the health of the lungs and the bronchial tree.
Other Conditions That Cause Bronchitis Without Fever
Among the causes of bronchitis without fever labeled "other special conditions", gastroesophageal reflux disease deserves a special mention.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is the medical condition characterized by the continuous repetition of the anomalous phenomenon of ascent towards the esophagus of the gastric contents, whose acidic nature makes it irritating to any other organ other than the stomach.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease can take the role of cause of bronchitis without fever in the most serious situations, that is when the ascent of the gastric contents goes beyond the esophagus, first reaching the larynx and then the airways.
Who is Most at Risk of Bronchitis Without Fever
Those most at risk of bronchitis without fever are:
- Smokers. Smoking is the main cause of bronchitis without fever;
- Those who live in particularly polluted urban centers;
- Who practices a job that exposes daily to irritants for the bronchial tree;
- People with asthma or COPD
Is fever-free bronchitis contagious?
Bronchitis without fever is not a contagious condition, as it does not possess any infectious nature.
without fever are:
- Cough. Depending on the severity of the cause, the cough can be either a temporary phenomenon (lasting a few weeks) or chronic (therefore a constant) and may or may not be accompanied by expectoration (ie production of phlegm);
- Difficulty in breathing (dyspnoea). In the milder forms of bronchitis without fever, dyspnea appears only on the occasion of physical exertion; in the most severe forms of bronchitis without fever, however, dyspnea is also present at rest (dyspnea at rest);

- Breathing with wheezing or rattles;
- Sense of discomfort in the chest, in less severe cases, and real chest pain, in more severe cases.
Other Symptoms of Bronchitis Without Fever
Depending on the underlying cause, symptoms of cough, wheezing and chest pain, bronchitis without fever could accompany ailments, such as:
- Feeling of recurrent exhaustion;
- Swollen ankles
- Loss of appetite and consequent weight loss.
Did you know that ...
The presence of exhaustion, swollen ankles and decreased appetite associated with cough, wheezing and chest discomfort is typical of bronchitis without fever due to COPD.
When to see a doctor?
Among the reasons that should prompt an individual with bronchitis without fever to immediately contact the attending physician or go to the nearest hospital center as soon as possible are:
- The addition to the classic symptoms (cough, dyspnea and chest pain) of a sudden drop in body weight;
- A worsening of the cough
- The appearance of severe breathing problems (dyspnea at rest);
- The presence of real chest pain;
- The permanence of the cough.
Complications
In its most severe forms, bronchitis without fever can profoundly impair respiratory function.
In addition, when it depends on a very serious cause such as COPD, it can give rise to serious complications, including: acute forms of pneumonia, heart problems (e.g. heart attack), lung cancer, pulmonary hypertension and depression (consequent to need of continuous care and assistance).
During the physical examination for a person with presumed bronchitis without fever, the evaluation of the breath (which, in case of positive test, will present wheezing or rattles) and cough (which, in case of positive test, it will result catarrhal).
Did you know that ...
In a person with a disease of the bronchial tree or lungs (such as bronchitis without fever), the assessment of the breath is done by so-called auscultation.
Anamnesis
The anamnesis is the particular study of the symptomatology with a view to identifying its triggering / favoring factors; the anamnesis, in fact, consists of an examination of the symptoms, combined with an investigation into elements such as the age of the patient, his clinical history, his working activity, his habits, his family history, etc.
In a context of presumed bronchitis without fever, the anamnesis allows to identify the possible causal factors of the current condition (eg: cigarette smoking, in a smoker patient; exposure to irritants, in a patient with a job at risk; etc. .).
In-depth exams
To trace the precise causal factor and outline the characteristics of a fever-free bronchitis, the doctor can follow the physical examination and the medical history:
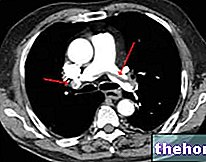
- A chest x-ray (or chest x-ray) and / or a chest CT scan. These radiological tests provide detailed images of the lungs and bronchial tree, so that the diagnostic physician can thoroughly assess their state of health;
- Oximetry is the measurement of oxygen saturation in the blood. As simple and immediate as spirometry, for its execution you need an instrument called an oximeter, which is applied to a finger or to one of the two earlobes;
- Spirometry. It is used to measure the inspiratory and expiratory capacity of the lungs; in addition, it provides information on the patency (or opening) of the pulmonary airways;
- The stress test. It consists in recording how heart rhythm, blood pressure and breathing of an individual vary, while the latter is practicing a more or less intense physical activity.
The exercise test is especially useful when bronchitis without fever is due (or appears to be due) to COPD; - The blood gas analysis. It allows to measure three important parameters of the blood of an individual: the circulating oxygen levels, the circulating carbon dioxide levels and the pH;
- Cardiac tests (echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, etc.). They are among the useful tests, when heart problems emerged from a previous stress test.
Why is it important to investigate the underlying causes?
The diagnosis of the causes of bronchitis without fever is important, because it is on the basis of the triggers that any therapeutic choice is based.
if the cause is tobacco smoke;This is why fever-free bronchitis due to COPD is a chronic condition.
- Ad hoc diet (abolition of fried foods, fatty foods, drinks that promote production in the stomach, etc.);
- Drugs (prokinetics, proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists);
- Surgery aimed at restoring the functionality of the gastroesophageal sphincter.
For two conditions such as COPD and asthma (for which there is no causal therapy), symptomatic therapy is essential.
Symptomatic therapy
Fundamental to relieve the patient's suffering, the symptomatic therapy of bronchitis without fever varies in relation to the clinical severity of the triggering cause and the repercussions of this on the health of the lungs and the bronchial tree.
Indeed:
- Bronchitis without fever due to a clinically irrelevant and resolvable cause (eg: sporadic inhalation of irritants) could involve very simple symptomatic treatments, such as taking an NSAID against chest pain, taking a drug against cough and / or humidification of the air in the home (to improve breathing);
- Bronchitis without fever due to COPD or asthma provides a series of important symptomatic treatments, to be adopted either permanently or in the presence of an exacerbation of the disorders.
In the case of COPD, these treatments include: oxygen therapy, respiratory rehabilitation, bronchodilator medication, mucolytic medication, and corticosteroid medication.
In the case of asthma, however, the aforementioned symptomatic treatments include all those drugs which, taken by inhalation or orally, mitigate or prevent the consequences of the so-called asthma crisis (eg: long-lasting beta-agonists, corticosteroids, leukotrienes etc.).
Some advices

Anyone who suffers from a form of bronchitis without fever benefits from certain behaviors such as:
- Not smoking. Not smoking is good behavior both when it is the cause of bronchitis without fever and when it is not directly responsible;
- Eat in a healthy and balanced way;
- Exercise regularly.






















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




