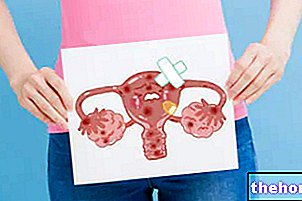
In most cases, the simple inflammation of the Bartholin's glands is transient and resolves within 3-5 days. In other cases, however, the pathological process can result in the formation of a cyst or abscess.
The diagnostic classification of Bartholinitis includes a gynecological examination.
The therapeutic intervention consists in the use of anti-inflammatories to counteract the acute inflammatory process in progress, possibly associated with hot-moist compresses or sitz baths to favor the spontaneous drainage of the gland. The doctor can prescribe antibiotics, to be taken both orally and through the use of ointments to be used locally.
The abscess formations that result from Bartholinitis are incised and drained. If the inflammation recurs two or three times over the course of a year, surgical removal of the involved Bartholin glands (Bartholinectomy) may be indicated.