Nausea is a very uncomfortable and sometimes disabling symptomatic manifestation.
Marked by a more or less intense malaise, it is often accompanied by the desire or need to vomit.
The symptom of nausea compromises the act of eating and sometimes drinking, creating a considerable discomfort both to the sight, to the smell and to the taste of food and drink.
Nausea can lead to vomiting. However, the two symptoms are not necessarily related.

Causes of nausea can be of various types:
- Intestinal gastrointestinal tract.
- Cerebral and vestibular system (brain and inner ear).
- Metabolic (functional insufficiency of certain regulatory organs and diabetes).
- Tumor.
- Emotional and / or psychological (anxiety, panic, visual or olfactory stimuli, etc.).
- Infectious (gastrointestinal or systemic).
- Pharmacological (chemotherapy drugs, anesthetics, oral contraceptives and antibiotics).
- For food intolerances.
- For poisoning.
- For intoxication (from ethyl alcohol, THC, iron).
- Gravidic.
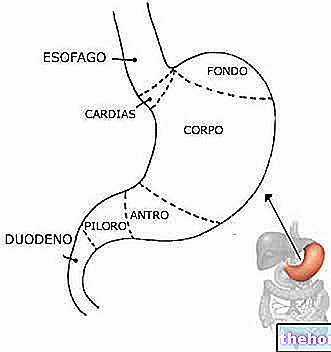
In gastrointestinal conditions, nausea can be caused by: gastrointestinal diseases, severe gastroesophageal reflux, hepatitis, swallowing air, too large meals, frugal eating, etc.
Causes of nausea that primarily affect the central nervous system and inner ear are: head trauma, brain haemorrhages, labyrinthitis, migraines and motion sickness (motion sickness, such as seasickness, etc.).
Among the various pathologies and metabolic conditions that can trigger nausea we mention: ketoacidosis (diabetic or not), hypoglycemia, low blood pressure, liver failure (accumulation of ammonium), renal failure (excess or defect of various molecules and ions), advanced neoplasms, severe and / or widespread.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Nausea; such indications must in no way substitute the opinion of the attending physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
, gastritis (or other serious pathological evolutions, including of the duodenum), hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux, esophagitis (or other serious pathological evolutions) etc.
- Adequate diet.
- Appropriate lifestyle.
- Reduction of nervous stress.
- Dedicated medical care.
- Specific drugs for the disease in question.
- Reduce the total volume of foods, portions and individual bites.
- Establish a chewing rhythm.
- To impose a minimum time within which to consume food.
- The most suitable foods are those that are highly digestible and do not over-engage the stomach.
In some cases, postprandial nausea from swallowing air is due to a disorder called dysphagia. In this case it is necessary to differentiate the diagnosis (to identify the type of dysphagia) and follow the appropriate guidelines.
Post-prandial nausea can also occur as a result of loss of control over food (compulsive eating). This happens in some eating disorders such as bulimia nervosa and Binge Eating Disorder. It has nothing to do with self-induced vomiting.
When Nausea Depends on Other Causes
- When nausea occurs after a head injury or "cerebral haemorrhage, the medical priority is the treatment of nerve injuries. The symptom vanishes with the resolution of the problem."
- Migraine nausea is difficult to treat. The priority should be to cure the headache; nevertheless, this disorder does not always respond effectively to therapy. Sometimes it is necessary to use drug therapy for nausea while waiting for the migraine to subside.
- Motion sickness and labyrinthitis are responsible for dizziness such as to trigger both nausea and vomiting. In case of labyrinthitis it is sufficient for the subject to remain immobile in bed; the body autonomously takes care of the recovery. For motion sickness, on the other hand, useful measures can be adopted; these are not able to cure the disorder but help to control nausea:
- Avoid drinking liquid food or drinks.
- Prefer dry foods.
- Try to focus on the road, horizon, or stationary object.
- Anticipating the movements of the means of transport or driving it etc.
- Hepatic and renal insufficiency are characterized by a reduction in organ function. The compromised liver and kidneys, not being able to carry out their metabolic functions correctly, are responsible for very serious metabolic imbalances which favor the onset of nausea. The medical objective is to compensate for the functional deficit by restoring homeostasis. the remission of nausea and all other related complications.
- Ketoacidosis (excess of ketone bodies) and hypoglycemia (lack of glucose in the blood) can trigger nausea. Both can arise in physiological conditions (due to a diet lacking in carbohydrates and an "excessive motor activity) or pathological conditions (diabetes mellitus). To reduce related nausea, it is necessary to maintain normal blood levels of glucose and insulin (hormone deficient in type 1 diabetics).
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) can cause dizziness and nausea. In that case, it may be helpful to:
- Reduce the ambient temperature.
- Increase the intake of fluids, mineral salts and glucose.
- In the case of severe or widespread neoplasms, nausea is treated pharmacologically.
- Nausea from poisoning, intoxication and food intolerances require the exclusion / elimination of poisonous principles from the diet, from the atmosphere or from the organism (vomiting, gastric lavage, intestinal practices, etc.).
- Infections that can cause nausea primarily affect the gastrointestinal tract. Characterized by the ingestion of bacteria and / or their toxins, food poisoning can also cause vomiting and diarrhea. In other cases, nausea is associated with systemic viral infections. It is necessary to wait for the organism to eliminate the pathogen or adopt medical practices to speed up the process (drugs).
- Nausea of pharmacological origin can be fought:
- Excluding the responsible drug.
- Replacing it.
- Compensating for discomfort by taking other specific nausea medications.
- Emotional nausea can be fought with:
- Mental training systems.
- Psychotherapy.
- With the help of anxiolytic drugs.
- Pregnancy is a special physiological condition that almost always determines the onset of mild or more intense nausea (especially in the first 12 weeks). Often accompanied by vomiting, this discomfort can be fought similarly to motion sickness.
- Moving too much (working, playing sports, heavy housework, etc.).
- Engage intellectually.
- Engage emotionally.
- Staying in closed, crowded and noisy places for a long time.
NB. In case of unconsciousness it is necessary to put the body on its side to prevent choking in case of vomiting.
- Exposure to high temperatures. The perception of heat tends to make nausea worse. Also for this reason, it is sometimes recommended to apply a wet cloth on the forehead.
- Drink large quantities of water, beverages or liquid foods. The fluid tends to "toss" in the stomach making the feeling of nausea worse. It is recommended to drink frequently and in small sips.
- Eat large quantities of food quickly, chewing little, preferring poorly digestible foods. As we have already specified, these behaviors can worsen or even cause nausea.
- Fast. Fasting should be avoided, as it promotes some negative reactions such as: hypoglycemia, blood hypotension and a feeling of gastric vacuum. It is aggravated by intense motor physical activity.
- Take medicines that are potentially responsible or that can aggravate nausea. It is advisable to abolish: contraceptives and (if possible) painkillers. In agreement with the doctor, it could be useful to try to replace the drugs in use that could be responsible for the symptom.
- Expose yourself to smog or toxic fumes. The inhalation of combustion products is harmful to the central nervous system. In case of nausea, a hypersensitivity to any unwanted molecule occurs. It is advisable to avoid potentially contaminated places such as: mechanical workshops, kitchens in operation, ovens, city traffic, etc. .
- Smoking, using drugs (even light drugs) and drinking alcohol. These are all habits that lead to an increase in the blood concentration of principles favoring nausea.
- Reduce the hours of sleep. The brain needs to recharge periodically and systematically. This does not happen simply by resting but it is essential to sleep. When the brain does not recharge sufficiently, nausea can appear or worsen.
- Movements with means of transport led by other people. It is advisable to travel as little as possible and especially when it is not possible to drive the vehicle.
The most suitable foods are: lean crusty bread, rice, pasta, bananas, potatoes, carrots, shelled legumes, crackers, wasa bread, unsalted lean crackers, etc.
The preferred cooking methods are: affogatura (boiling in water), steam and pressure cooker. Heat treatment in a pan (moderate flame) and baked in the oven are also allowed.
Functional foods that can reduce nausea include: ginger, licorice root, coca-cola (the reason is not clear, but it seems to reduce the feeling of nausea) and ginger ale (it is a ginger-based drink).
Some suggest the use of mint, even though it is one of the foods not recommended for gastroesophageal reflux.
, raw or cooked for a long time.
The least suitable foods are: fatty meat broth, whole milk, cured meats, fatty cheeses, fatty and / or stewed or fried meats and fish, more than two eggs at a time (especially in omelettes), fried vegetables, creamy or fatty desserts, snacks, foods that are too salty, rich in chilli and pepper, chocolate, mint, coffee and alcoholic beverages.
of ginger (up to 1 gram per day)