An irregular period is defined as a menstrual cycle that occurs at a different time than the normal range (24-35 days; the most common interval is 28 days).

Another sign of irregularity is the “cycle jump”, even if up to 3 times a year it can be considered physiological. The absence of relapsing menstruation is logically included among the irregularities.
From a statistical and diagnostic point of view, it is considered “cycle irregularity” when the duration exceeds 15% of the standard deviation. Put simply, a range of 18-40 days is still considered "borderline".
Another form of irregular menstruation is the amount of bleeding: too little (oligomenorrhea) or profuse (polymenorrhea). Usually, the change of 3-7 sanitary pads per day (approximate average term) is defined as “normal”.
NB. When the irregular menstrual cycle is heavy (menorrhagia), it is often also very painful.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of the Irregular Menstrual Cycle; such indications must in no way substitute the opinion of the attending physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
What to do
If in doubt that the menstrual cycle is irregular, it is advisable to:
- Investigate whether it may be a genetic tendency (e.g. from the mother or grandmothers).
- Carefully evaluate the level of psychological stress (it can greatly affect).
- Make sure that any excess bleeding is not due to the introduction of foreign bodies into the vagina; for example, intrauterine contraceptive devices.
- Make sure your lifestyle is adequate:
- Sleep-wake rhythms.
- Timing of meals.
- Habits of dubious health (abuse of drugs, alcohol, nerve substances, etc.).
- Consider any defects in nutritional status; your period can be very irregular or sometimes absent in case of:
- Avoid underweight (BMI eating disorders.
- Maintain a normal percentage of fat (fat deficiency does not always fall under underweight; women who practice bodybuilding are a prime example).
- Preventing generalized malnutrition.
- Practicing motor and sports physical activity with reasonable volume and intensity.
- Discontinue any unnecessary drug or dietary supplement, especially based on hormonal precursors, stimulants, etc.
- Consult your doctor (preferably a gynecologist) who will carefully evaluate the diagnostic investigations to be undertaken to search for any:
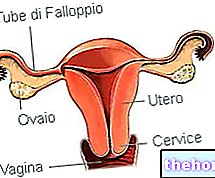
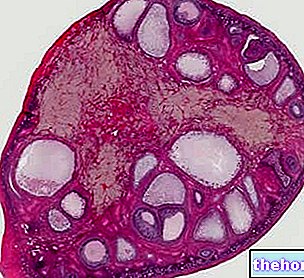
- Uterine developmental abnormalities (for example, polycystic ovary).
- Hormonal dysfunctions of the brain.
- Hormonal dysfunctions of other peripheral glands.
- Anemia and changes in the blood corpuscle.
- Miscarriage; it can go unnoticed in the first few days and cause irregular menstruation. Invasive medical treatment is needed.
- Premature menopause.
- Endometrial cancer or other neoplasms.
- Pregnancy complications (e.g. extra uterine pregnancy)
- Infections of the uterus.
- Endometriosis.
What NOT to do
- Do not consult the gynecologist and ignore the condition for a long time or, even worse, permanently; sometimes an early diagnosis is essential.
- Using intrauterine contraceptives or overly invasive sex toys.
- Follow a very stressful lifestyle without worrying about the repercussions it could have on the nervous (therefore hormonal) balance.
- Sleeping little or not respecting the breaks in work shifts.
- Skip meals or eat only once a day.
- Abusing alcohol or using drugs
- Not taking care of your nutritional status:
- Remain underweight.
- Conceal the onset of an eating disorder (especially anorexia nervosa).
- Achieve or maintain a lower than normal body fat percentage.
- Follow unbalanced or extreme diets.
- Practicing motor-sporting physical activity with volume and intensity beyond the threshold of reasonableness for long periods.
- Taking medications or dietary supplements that could affect your menstrual cycle (including some contraceptive pills).
What to eat
Diet plays a fundamental role only when the irregular cycle has a "nutritional etiology. In this case it is necessary to rely on a dietician or nutritionist.
- If menstruation remains compromised by the malnutrition of vitamins, minerals, amino acids and essential fatty acids, it becomes necessary:
- Follow a normal calorie diet that meets all compromised needs.
- If your period has worsened due to being underweight and lacking fatty tissue:
- Respect a high-calorie nutritional scheme (+ 10% of the energy) in order to restore a suitable weight and body composition.
- If the losses are such as to create anemia or vice versa, the latter worsens the irregularity of menstruation (sometimes both):
- Increase the consumption of foods rich in: heme iron (meat, offal, fish, eggs), folic acid (fresh vegetables and fruits), cobalamin (foods of animal origin) and vitamin C (sour fruit and many vegetables).
- If menstruation is complicated by a generalized "alteration of the" hormonal axis, take care of the intake of mineral salts that could be involved in the endocrine deficit (copper, zinc, manganese, iodine, etc.).
What NOT to Eat
There are no foods that worsen the regularity of the cycle.
It is logical to think that preferring some nutritionally poorer ones (vitamins and mineral salts) or altering the nutritional balance could aggravate the situation.
It becomes necessary to avoid:
- Diet exclusively consisting of foods of plant origin.
- Diet exclusively consisting of foods of animal origin.
- Single-issue diets.
- Diets mainly based on cooked and preserved foods.
- Nutritional plans based on meal replacements or supplements.
- Alcohol abuse.
Natural Cures and Remedies
For many causes of irregular periods, there are no natural remedies.
- If the reason is not known and the alteration is minor:
- Salvia officinalis: in the form of an extract it can be taken in 15-20 drops twice a day or as an infusion of flowers or leaves for 1-2 cups a day.
- Parsley: it is part of folk medicine; using it in all recipes many women admit to having found an improvement in regularity. It is recommended to be careful as it has a not very high toxic dose.
- If the cause is a defect in estrogen secretion, the following may prove useful:
- Soya phytoestrogens or isoflavones: 1-2 tablets per day (up to 3-4 months).
- Red clover phytoestrogens or isoflavones: 1-2 tablets per day (up to 3-4 months).
- If the cause is a "slight but generalized alteration of the hormonal axes, it is advisable to take food supplements based on: copper, zinc and manganese.
- If the cause is of a global food type, it is necessary to regularize the diet and start a complete dietary supplementation process.
- If the cause is an anemic form, dietary supplementation of iron, folic acid and cobalamin (vit B12) can be very useful.
- If the cause is stress, it is recommended to undertake activities dedicated to reducing the levels of discomfort: yoga, advanced relaxation, mental training, psychotherapy etc.
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment is closely related to the triggering agent; on the other hand, when the intent is to regularize the cycle in the absence of pathologies, doctors can choose to administer:
- Progestin and estrogenic drugs: when the irregular menstrual cycle is caused by a defect in the specific hormonal axis.
- Coagulants and reinforcing the uterine wall: used especially in case of hypermenorrhea.
- Antidepressants and antipsychotics: used especially when the irregular menstrual cycle is due to very intense mental pathologies or symptoms; also applies to eating disorders.
- Painkillers: when your period is very painful.
Prevention
The prevention of irregular periods is based solely on common sense:
- In the event of a hereditary defect, undertake gynecological treatment or establish a well-organized follow-up with close checks.
- Eat properly.
- In the case of competitive sports, pay close attention to the body mass index and the balance between the masses (lean and adipose).
- Prevent excessive stress loads, organize life properly and get enough sleep.
- Avoid abuse and the use of harmful products (drugs, medications, particular supplements, etc.).
Medical Treatments
Among the medical remedies for the irregular menstrual cycle we also recognize the specific diagnostic investigations:
- Endoscopic gynecological visit and possible biopsy.
- Blood test: to evaluate hormone levels, blood corpuscle consistency, hemoglobin, ferritin, etc.
- Uterine curettage: it is necessary in case of miscarriage.
- Surgery: it becomes essential for diseases such as endometriosis, severe polycystic ovary, tumors, etc.