Favored by conditions such as the misuse of antibiotics, pregnancy, immunosuppression, diabetes and poor intimate hygiene, vaginal candida is typically responsible for pain and itching in the vulva, pain during sexual intercourse and pain or burning. during urination.
A physical examination and anamnesis are generally sufficient for the diagnosis of vaginal candida; however, in some situations, more in-depth diagnostic tests are also needed, such as vaginal swabs, blood tests or urinalysis.
The treatment of vaginal candida revolves around the use of antifungal drugs available in cream or in the form of tablets for oral or vaginal use.
Did you know that ...
Candida albicans it can also infect the man, giving rise to the so-called male candida.
For information on male candida, we recommend the article at this link.
What is Candida and the role of Candida Albicans: a brief review
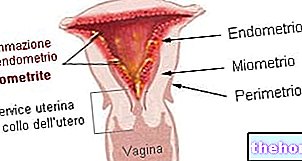
Candida (or candidiasis) is a "fungal infection (or mycosis) caused by the fungus Candida albicans. This fungus is naturally present in the human body; in particular, it loves to live in humid and warm environments, such as the mouth, the throat, the esophagus, the gastrointestinal tract and the genitals (vagina, in women, and glans, in men).
Like Candida Albicans causes Candida
Candida albicans it is, in fact, a fungus that is generally harmless to humans, as the so-called "good bacteria" constituting the bacterial flora and the immune system prevent its pathological proliferation.
However, when these two control systems fail, Candida albicans begins to multiply intensively, giving rise to the condition known as candida or candidiasis.
Mushrooms that behave like Candida albicans - that is, who take advantage of a difficult situation on the part of the host - are called opportunistic mushrooms.
For further information: CandidaScientific classification of Candida albicans
Candida albicans it is a saprophytic fungus (that is, it feeds on decaying material), belonging to the saccharomycetes family. Saccharomycetes are particular unicellular organisms, which live in colonies and which fall into the category of so-called yeasts (exactly as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the yeast used for bread).
Vaginal Candida and other forms of Candida in Women
Vaginal candida is, without a doubt, the best known and most widespread form of purely female candida.
However, it should not be forgotten that women can also develop candida in the breast while breastfeeding.
Generally, immunosuppression is a typical problem of: people with diseases such as AIDS (which undermine the integrity of the immune system), those who take immunosuppressive drugs (ie drugs that lower the immune defenses) and the elderly (for reasons physiological);

Shutterstock
- Pregnancy. The characteristic increase in estrogen observed during pregnancy predisposes pregnant women to infection with Candida albicans.
- Sexual intercourse with an infected person. A woman who has sexual intercourse with a man with candida can develop the same infection, as she is exposed to a "major colony of Candida albicans;
- Sharing the use of towels, underwear or soaps with an infected person (mixed use of infected objects). In these circumstances, what is reported on the occasion of sexual intercourse with people with candida is repeated.
Is Vaginal Candida a Sexually Transmitted Disease?
According to the medical community, although it can arise from sexual intercourse with affected people, vaginal candida is not to be considered a sexually transmitted disease (such as syphilis or genital herpes).
Epidemiology
Vaginal candida is a "very common infection; in this regard, statistics say that:
- Vaginal candida figures, along with bacterial vaginosis and vaginitis from Trichomonas, in the list of the top 3 most common vaginal infections in the female population;
- Annually, vaginal candida is a problem for about 20% of the female population;
- Vaginal candida affects approximately 75% of women at least once in their lifetime.
Vaginal candida is more common among women on antibiotic therapy, women with diabetes mellitus or AIDS, and women taking cancer chemotherapy.
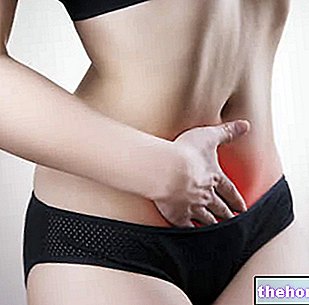
of vaginal candida are:- Pain and itching at the vulva (entrance to the vagina)
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia);
- Stinging or burning pain when urinating (dysuria)
- Leaking fluid from the vagina. Typically, this liquid is odorless, white and sometimes watery, sometimes thick.
Furthermore, if vaginal candida also involves "inflammation of the genital area", the symptomatological picture is enriched with further manifestations, such as:
- Redness of the vulva and vagina;
- Vaginal fissures;
- Local swelling
- Very painful skin sores (very rarely seen).
Did you know that ...
In women, skin sores in the genital area are a typical sign of genital herpes.
Complications of Vaginal Candida
For some women, vaginal candida is a relapsing / recurring condition, that is, it recurs from time to time; this situation is not serious from a clinical point of view, but it can have significant repercussions on the quality of the patient's sexual life.
Furthermore, if it affects women in a state of immunosuppression or with particular diseases (eg diabetes), vaginal candida can degenerate into a systemic condition, known as invasive candidiasis (or invasive candida).
Invasive candida is the infection resulting from the fungus passing through the blood Candida albicans (fungemia or funghemia) and its spread to important organs, such as the heart (endocarditis), the brain (encephalitis), the eyes (endophthalmitis) or the bones (osteomyelitis).
Invasive candida can be fatal for the patient, therefore it represents a "medical emergency, which needs immediate help.
Who is most at risk for Invasive Candidiasis?
Among women with vaginal candida, they are most at risk for invasive candidiasis:
- People with AIDS. As the reader will recall, AIDS affects the efficiency of the immune defenses;
- Those taking immunosuppressive drugs. This is the case, for example, of women who have undergone an organ transplant;
- Those who are undergoing chemotherapy to treat a tumor. Chemotherapeutics have the side effect of reducing the efficiency of the immune system;
- People with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes promotes the proliferation of Candida albicans;
- Subjects who have to periodically resort to dialysis (the so-called dialysis). This is the case for women with renal insufficiency;
- Those who, thanks to a certain health condition, must undergo the insertion of a central venous catheter. The central venous catheter is a medical device used in long-term therapies, to administer liquids, drugs and other substances that the body needs human under certain conditions.
Did you know that ...
For people with diabetes or kidney failure who develop candida, doctors recommend hospitalization so that they can receive all the most effective treatments against the fungal infection and associated complications.
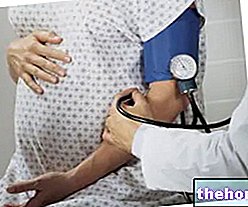
Consequences of Vaginal Candidiasis in Pregnancy
In the absence of adequate treatment, vaginal candida in pregnant women is a risk factor for premature birth (or preterm delivery).
In addition, in a very small percentage of pregnant women with vaginal candida, the infection can be passed on to the baby at delivery, resulting in a condition known as congenital neonatal candida (or neonatal candida).
Vaginal Candida: when to worry?
The appearance of suspicious symptoms, such as pain and itching in the genitals and pain during urination and during sexual intercourse, should prompt you to contact your general practitioner immediately, who will most likely prescribe a specialist visit to a gynecologist.
Main situations in which, in case of vaginal candida, it is good to contact the doctor:
- When is the first time you suffer from vaginal candida;
- When the patient is under 16 or over 60;
- When the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding;
- When the symptomatology includes loss of foul-smelling fluid and / or blood loss;
- When the patient has been the victim of at least two episodes of vaginal candida in the past 6 months.
In particular situations, however, it may happen that it is also necessary to resort to the execution of laboratory tests, such as blood analysis, urinalysis and vaginal swab.
When are laboratory tests needed?
- When doubts persist about the nature of the present infection;
- When the symptoms of vaginal candida are severe or persist despite treatment;
- When vaginal candida is, for no clear reason, a recurring condition.
What to do in case of Recurrent Vaginal Candida
Generally, women who repeatedly suffer from vaginal candida are people at risk (eg patients with diabetes), aware of the reason behind the recurrence of the infection.
When this is not the case, however, they should undergo diagnostic tests, to find out the reason for the repeated episodes of vaginal candida; the diagnostic tests indicated include: blood analysis, urinalysis and vaginal swab.
What to do when you get Vaginal Candida for the first time
Women who develop vaginal candida for the first time must undergo a thorough medical examination, which includes, in addition to the observation of symptoms, also the evaluation of the clinical history.
The information that emerges from the clinical history is of fundamental importance for the understanding of the precise triggers of vaginal candidiasis and for the planning of the most appropriate treatment plan.
If the doctor has doubts or considers it possible the presence of a serious disease that has not yet been diagnosed (such as diabetes), he will most likely resort to the diagnostic tests already mentioned several times, namely blood tests, urine and vaginal swab.
, that is medicines with specific anti-fungal power; secondly, it provides for "particular attention to personal hygiene and temporary abstention from sexual activity."
Vaginal Candida: Antifungal Drugs

Currently, on the market, antifungal drugs that can be used in the presence of vaginal candida are present in three formulations:
- In cream (topical antifungals);
- In tablet for vaginal use (antifungals for vaginal use);
- In tablet for oral use (oral antifungals).
Topical Antifungals
Topical antifungals for the treatment of vaginal candida are drugs in the form of a cream to spread on the genital areas affected by the infection (vulva and vagina).
Among the topical antifungals used in the presence of vaginal candida, clotrimazole, econazole, fenticonazole nitrate, miconazole and nystatin are reported.
With the exception of nystatin (which is an antibiotic with an antifungal action), clotrimazole, econazole, fenticonazole nitrate and miconazole belong to the category of so-called imidazole derivatives (or imidazole derivatives); imidazole derivatives are antifungal drugs that exert their power by destroying the cell membrane of fungi.
Vaginal antifungals
Vaginal antifungals for the treatment of vaginal candida are drugs in the form of tablets to be inserted into the vagina.
Among the antifungals for vaginal use used in the presence of vaginal candida are the aforementioned clotrimazole, econazole, fenticonazole nitrate, miconazole and nystatin (they are the tablet version for vaginal use of those in cream mentioned above).
Possible side effects of clotrimazole, econazole and fenticonazole nitrate (both for topical and vaginal use): local burning and skin irritation.
Oral Antifungals
Oral antifungals for the treatment of vaginal candida are drugs in tablet form to be swallowed by mouth.
Among the oral antifungals used in the presence of vaginal candida, fluconazole and itraconazole stand out.
Fluconazole and itraconazole belong to the category of triazoles; characterized by a stronger anti-fungal power than imidazole derivatives, triazoles act against some enzymes that fungi such as Candida albicans they use to reproduce and survive (in simpler words, they destroy molecules essential for the reproduction of fungi).
Possible side effects of fluconazole and itraconazole: nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea and flatulence.
Attention to Personal Hygiene

Paying attention to personal hygiene is a fundamental part of the treatment of vaginal candida.
In this sense, the rules to be followed include:
- Use of good quality intimate cleansers, so as not to irritate the already suffering genital area;
- Be careful, after each shower, to dry the genital areas.
Did you know that ...
In the case of vaginal candida, to keep the intimate parts dry as much as possible, doctors recommend the use of wide, non-compressing panties.
Temporary abstention from sexual activity
Although the use of condoms prevents the transmission of vaginal candida, doctors advise to avoid sexual intercourse with the partner for the duration of the treatment and to resume only after recovery.
It should be noted that the condom and the contraceptive diaphragm are sensitive to topical antifungals and to vaginal antimitotics, where by sensitive we mean that they could be damaged; any damage to these methods of contraception could be not only a cause of transmission of vaginal candida, but also of an unsolicited pregnancy.
Treatment of Vaginal Candida in Pregnancy
Before taking any medication, pregnant women who develop vaginal candida should consult their doctor and their gynecologist, in order to know which medication is best for them.
Generally, for pregnant women suffering from vaginal candida, an antifungal therapy based on clotrimazole or nystatin in the form of tablets for vaginal use is provided.
vaginal are:- Do not abuse antibiotics (follow the methods of administration indicated by the attending physician);
- In the presence of conditions favoring candida (eg: diabetes, AIDS, immunosuppression from chemotherapy, pregnancy, etc.), take maximum care of personal hygiene and avoid sexual relations with people infected with Candida albicans;
- Wash the private parts with quality detergents;
- Thoroughly dry your private parts after each shower.