Generality
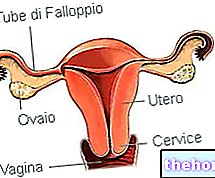
Vulvar vestibulitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the access to the vagina (vestibule).

At the origin of vulvar vestibulitis there is often an overactivity of some cells of the immune system, called mast cells, which induce a prolonged inflammatory state. The reflex contraction of the pelvic muscles and the hyperstimulation of the nerve endings responsible for pain perception can also contribute to the disorder. The factors that aggravate or maintain the manifestations also include chronic or recurrent infections, microtraumas associated with vaginal dryness and the use of inappropriate intimate hygiene products.
Vulvar vestibulitis typically manifests itself with redness of the mucous membrane of the vulvar vestibule, pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) and severe localized burning. This involves a series of more or less limiting hassles; if not managed promptly, this problem can persist for years and, in general, the manifestations tend to extend to the perianal region or to other genital areas not initially involved.
The treatment allows to alleviate the manifestations related to vulvar vestibulitis and can include measures on the medical, rehabilitative and psychosexual level.