Arthrosis (osteoarthritis) is a degenerative arthropathy.
It is a joint disease that causes the progressive loss of the typical anatomical parts of the joints.
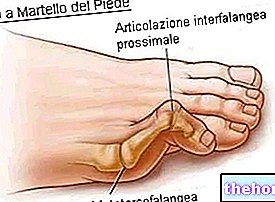
It can affect the spine, hips, upper and lower limbs.
Osteoarthritis causes wear on the articular cartilage and the replacement of chondroid tissue with bone. It causes pain and limitation in movement.
The onset of osteoarthritis and the onset of symptoms increase with age. It is identifiable (at least in one district) in most of the forties and almost all of the seventies. The greatest incidence is found between the ages of 75-79.
It is the most important cause of joint pain and disability among Italians (over 4 million). Males suffer most by age 45 and females beyond. The prevalence of osteoarthritis progresses with old age.
Many risk factors for osteoarthritis are the same as for osteoporosis.
- It will analyze the presence or absence of the pathology.
- It will carry out a differential diagnosis.
- He will prescribe a cure.
- Mild motor activity: it serves to maintain articular excursion, lubrication, muscular and even bone trophism (preventive for osteoporosis).
- When needed, use of mild anti-inflammatories.
- Taking cartilage supplements.
- Application of medical treatments with heat, ultrasound and mud.
- Infiltration of chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid.
- Preventive-conservative physiotherapy activity: involves mobilization and some motor exercises necessary to preserve muscle tone.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs by mouth or rarely by injection.
- Cartilage surgery or transplant.
- Physiotherapy and functional motor rehabilitation.
- Consume an adequate amount of calories, which is 70% of normal calories.
- Choose foods with a suitable metabolic impact (whole foods and foods without refined carbohydrates) by preventing spikes in blood sugar and insulin.
- Get a good amount of dietary fiber. It helps to keep blood sugar under control, modulates fat absorption and positively affects estrogen levels.
- Keep the fraction of simple carbohydrates no more than 10-16% of total calories (it is sufficient to eliminate all sweet foods by keeping 4-6 servings of fruit and vegetables, as well as 1-3 servings of milk and yogurt).
- Keep the fat fraction no more than 25-30% of total calories, preferring the "good" ones (raw vegetable oils and medium-fat blue fish) over the "bad" ones (saturated, hydrogenated, bi-fractionated, etc.).
- Omega 3: they are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic (DHA) and alpha linolenic (ALA). They have an anti-inflammatory role. The first two are biologically very active and are found mainly in: sardines, mackerel, bonito, sardinella, herring , alletterato, tuna belly, garfish, seaweed, krill etc. The third is less active but constitutes a precursor of EPA; it is mainly contained in the fat fraction of certain foods of vegetable origin or in the oils of: soy, linseed, seeds of kiwi, grape seeds etc.
- Vitamins: the antioxidant vitamins are carotenoids (provitamin A), vitamin C and vitamin E. Carotenoids are contained in vegetables and red or orange fruits (apricots, peppers, melons, peaches, carrots, squash, tomatoes, etc.); they are also present in crustaceans and milk. Vitamin C is typical of sour fruit and some vegetables (lemons, oranges, mandarins, grapefruits, kiwis, peppers, parsley, chicory, lettuce, tomatoes, cabbage, etc.). Vitamin E can be found in the lipid portion of many seeds and related oils (wheat germ, corn germ, sesame, kiwi, grape seeds, etc.).
- Minerals: zinc and selenium. The first is mainly contained in: liver, meat, milk and derivatives, some bivalve molluscs (especially oysters). The second is mainly contained in: meat, fish products, egg yolk, milk and derivatives, enriched foods (potatoes, etc.).
- Polyphenols: simple phenols, flavonoids, tannins. They are very rich: vegetables (onion, garlic, citrus fruits, cherries, etc.), fruit and relative seeds (pomegranate, grapes, berries, etc.), wine, oil seeds, coffee, tea, cocoa, legumes and whole grains, etc.
- It is advisable to eliminate junk foods and drinks, especially fast food and sweet or savory snacks.
- It is also necessary to reduce the frequency of consumption and the portions of: pasta, bread, pizza, potatoes, derivatives, fatty cheeses, fatty meats and fish, cured meats, sausages, sweets, etc.
- Opiates (e.g. morphine): have a very powerful pain reliever effect but are addictive.
- NSAIDs or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: systemic to be taken orally. They reduce pain and facilitate joint mobility; fairly short courses of therapy are recommended due to potential side effects (stomach and liver compromises). They are most used:
- Paracetamol or acetaminophen: for example Acetamol, Tachipirina, Efferalga.
- Ibuprofen: for example Brufen, Moment and Subitene.
- Naproxen: for example Aleve, Naprosyn, Prexan and Naprius.
- Indomethacin: for example Difmetre, Indom and Liometacen.
- Nabumetone: for example Nabuser, Artaxan and Relifex.
- Piroxicam: for example Feldene, Piroxicam EG and Artroxicam.
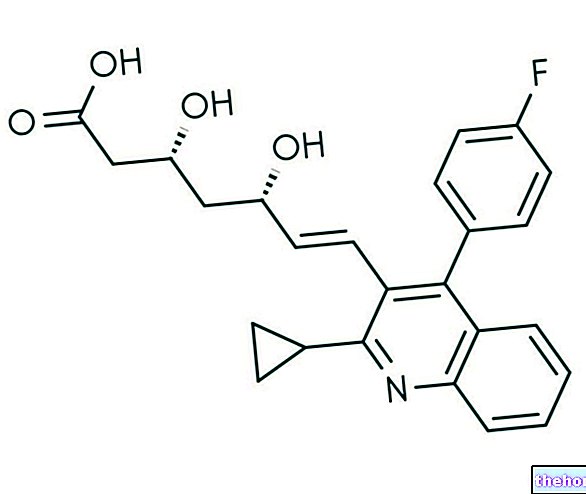
- Celecoxib: for example Aleve, Naprosyn, Prexan and Naprius.
- Topical or local infiltration pain control drugs:
- Capsaicin: for example Qutenza.
- Methylprednisolone acetate: for example Medrol, Urbason and Solu-Medrol.
- Sodium hyaluronate: for example Artz injectable.
- Cortisones: systemic to be taken orally or locally by injection. Generally not recommended because they increase the osteoarthritis process, they are used ONLY in the case in which the inflammation from bone rubbing (depleted cartilage) is at very high levels.
- Hyaluronic acid and chondroprotectors: injection rooms. They will also be described in the paragraph on medical treatments.
- Perichondrium or periosteum implant: these are membranes that cover the cartilage.
- Mosaicoplasty or osteochondral graft: uses cylinders of osteochondral tissue taken from the joint of the same patient and inserted under pressure into the cartilage defect.
- Autologous chondrocyte transplant: cartilage cells are taken from the patient and cultured in the laboratory for 2-4 weeks using biotechnological techniques. At this point the lesion is cleaned and covered with the periosteum leaving a small hole through which the cultured cells will then be injected.