How many grams of this flavonoid should be taken daily? On average, people get 5 to 40 milligrams of quercetin per day by consuming certain foods. By eating a lot of fruit and vegetables, however, the daily intake could increase up to 200-500 milligrams. There is no definite and clear number for the amount of quercetin to be taken every day, but most nutritionists recommend dosages between 500 and 1,000 milligrams per day, the same dosage also mentioned by many studies conducted on the benefits of quercetin.
There are many quercetin supplements, but the best plan of attack to increase quercetin intake is to include a variety of foods rich in quercetin, such as capers, red onions, organic cabbage and tomatoes, in your diet. Before taking a supplement. quercetin, medical advice is recommended.
, which causes oxidative damage, and can help protect against a variety of health problems, including cancer, heart disease and Alzheimer's disease, to name a few.
Scientific research has also linked the intake of quercetin to allergy relief and rather effective immune support: all thanks to its action similar to that of a prebiotic and its work of nourishing the good bacteria of the gut. It also increases the effects of vitamin C, helping synergistically to prevent the excessive activation of mast cells, which secrete histamine when the body is inflamed. This compound of the flavonoid family is also able to transport zinc, a natural antiviral, into the cells, where can help mitigate viral replication.
, which also provide additional phytochemicals, vitamins and minerals that work synergistically to deliver bonus benefits.
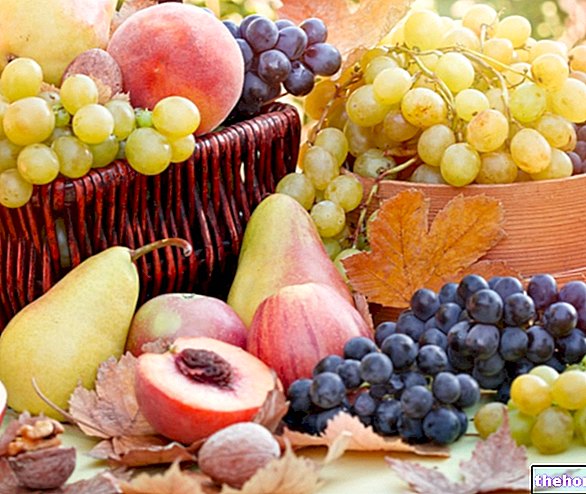
To raise the quercetin level, daily intake of a variety of these foods is recommended:
- capers: food with the highest content of quercetin. It contains 181 mg / 100 g. Rich in flavonoids, they are beneficial for the metabolism of cholesterol, as they lower the levels in the blood, perform an anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic action;
- red onion: contains vitamin C, iron, vitamin E, selenium, iodine, zinc and magnesium. Diuretic and purifying. Red onion contains 20 mg / 100 g of quercetin;
- red apples: rich in vitamins, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, zinc, magnesium and copper. Quercetin content: 4.4 mg / 100 g;
- grapes: the fruit with the highest contribution of flavonoids, with berries, especially blueberries (18 mg / 100 g) and black currants (6 mg / 100 g);
- cherries: rich in vitamins C and A, they contribute to the proper functioning of the immune defenses. They also contain folic acid, calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus and flavonoids such as quercetin;
- shallot: contains iodine and antioxidants, useful for the health of the thyroid and brain, and against cholesterol;
- cabbage, broccoli and Brussels sprouts: they contain sulfur, calcium, selenium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, copper, sodium, B vitamins, including folic acid, and vitamin C, which also makes vitamin E easily absorbable. They have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which slow down cellular aging. Broccoli, for example, contains 3.2 mg / 100 g of quercetin;
- tomatoes: organically grown tomatoes have up to 79% more quercetin than conventional fruit. They contain potassium, phosphorus, vitamin C, vitamin K and folate. The red color of tomatoes is due to an antioxidant, lycopene;
- citrus fruits: rich in calcium, potassium, iron and phosphorus, vitamins A, B and C, flavonoids, antioxidants, terpenes and pectins.
- green and yellow peppers: rich in quercetin, solanine, potassium, beta-carotene, fiber. They have purifying and diuretic power;
- walnuts, almonds and pistachios: also rich in Omega3 fatty acids. Beware of Omega 3 deficiency and how it can be handled.
- asparagus: cooked asapragi have a higher concentration of quercetin than raw ones;
- buckwheat: the cereal that has the highest quantity of quercetin. It also has a low glycemic index and many fibers, characteristics that make it suitable for the diet of diabetics, and stimulate regular intestinal transit.
- black and green tea: they contain tannins and polyphenolic compounds with astringent properties - responsible for the sensation of dry mouth after drinking a cup of tea - antiseptics and disinfectants;
- elderberry infusion: elderberry contains flavonoids (sambucina), fatty acids, tannins and polyphenols. It is indicated to counteract cold symptoms and respiratory tract infections.
Apples and citrus fruits also help preserve tooth health.