How it is produced, how it works, how to control its secretion
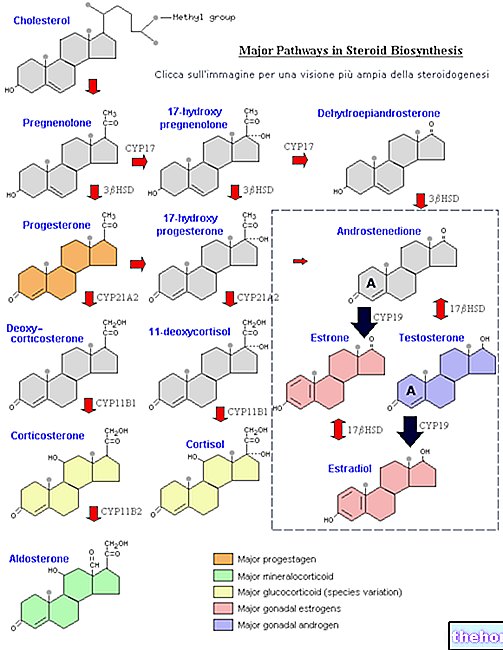
in response to the pituitary hormone ACTH. ACTH is therefore the precursor of cortisol.
Cortisol is often referred to as the "stress hormone" because its production increases, in fact, in conditions of severe psycho-physical stress, for example after extremely intense and prolonged physical exercises or surgery.
An increase in circulating cortisol also occurs in the case of prolonged fasting or incorrect eating habits. Skipping breakfast and / or eating a lot in a single daily meal favors hypercortisolism (ie the increase in the production of cortisol).

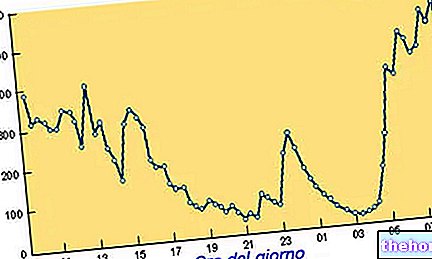
Daily variation in plasma hormone levels. Note the main nocturnal wave; before awakening, 50% of the total daily cortisol is secreted.
AVERAGE VALUE * OF CORTISOL IN BLOOD:
- adult (at 8:00 am) 100-200 micrograms / l or 250-550 nmol / l;
- adult (at 20:00) 100 micrograms / l;
- child under 10 years of age: 50-100 micrograms / l
About 77% of circulating cortisol is bound to transcortin or CBG (Cortisol binding protein), 15% albumin and 3-10% are free.* reference values may vary slightly depending on the analytical laboratory

Cushing's disease: pathology due to an overproduction of cortisol. It causes characteristic redistribution of body fat, loss of muscle mass, hypertension, capillary fragility, thinning of the skin, difficulty in wound healing, osteoporosis, immunosuppression, secondary diabetes and psychosis.
which causes a consistent increase in cortisol secretion is approximately 60% of VO2max.
Its secretion is related to the duration and intensity of physical exercise, the more these factors increase and the greater the amount of cortisol secreted. Note the "increase in" ACTH already in the pre-competition period, caused by the psychological stress of competition.

N.B: the adrenocortical response to sports activity is enhanced by fasting and psychological stress, while it is reduced by the ingestion of food.
We also remember that glucocorticoids:
- stimulate protein catabolism, accelerating the degradation of muscle myofibrils (effects more evident in resistant or type II fibers, present in a high percentage in the muscle masses of the lower limbs)
- increase the activity of glycogen synthetase (accumulation of glycogen)
- stimulate the feeling of hunger
- promote the storage of fat in the abdominal region
To keep cortisol levels under control, it is good to eat small meals in terms of calories, but frequent (5 or more a day). It is also advisable to start the day with a hearty breakfast and to favor the intake of complex carbohydrates such as oats, sugar-free cereals, wholemeal flours and their derivatives. In training, then, it is important to allow yourself the right rest periods, since the parameters "intensity" and "volume" are generally not expendable, being - if well calibrated - the basis for the phenomena of adaptation and improvement of athletic performance . In other words, cortisol must not become an expedient to train us less in fear of its catabolic effects that become concrete and preponderant in the "overall homeostasis of the body" only when the stresses are multiple and / or particularly intense and / or perpetuated over time. .
Elevated cortisol and difficulty losing weight
Cortisol and prolactin
High cortisol and low cortisol accumulated from similar negative effects