It is a fairly common and not necessarily pathological condition, which can be supported by numerous causes.
The doctor can notice an excessively enlarged liver already from the clinical examination, carrying out specific and precise palpatory maneuvers; the ultrasound and various blood tests will subsequently investigate the real causes of the phenomenon.
Often an asymptomatic increase in liver size is due to the accumulation of fat (steatosis).
This condition typically appears towards middle age when the diet is chronically high in lipids and high in calories (cheeses, fried foods, etc.) and when alcohol (wine and beer) and spirits are abused.
Consult the article dedicated to the relationship between diet and liver to find out which foods promote the good health of this very important organ.
As for symptoms, an enlarged liver often does not show any particular signs of itself; only when the volumetric increase is rather rapid and / or conspicuous can the patient experience a pain localized in the right upper abdominal region (often it is a simple discomfort, which among other things not rarely has extrahepatic origin). However, hepatic pain may worsen or manifest itself only during palpation of the organ and / or be accompanied by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
, of alcoholics, type II diabetics and those who love overeating (in particular fried foods and foods rich in fat), fatty liver causes hepatomegaly with a soft, smooth and generally painless liver.
Alcoholism
liver diseases are typical of alcoholics.
Hepatitis
inflammatory pictures of the liver often of viral origin (as in hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, hepatitis E); they are accompanied by an enlarged liver which appears soft, smooth and generally painful in the acute forms, while in the chronic ones the pain occurs only in an advanced stage and the organ takes on a hard and gnarled consistency.

Liver cancer
in an advanced stage, the tumor mass can increase the size of the organ until it causes pain, making it quite hard to touch. This disease is typically associated with jaundice, rapid and substantial weight loss, anorexia (lack of appetite), fatigue, nausea and He retched.
Cirrhosis
chronic and degenerative liver disease, in which normal liver tissue is replaced by a network of scar tissue, between the meshes of which regenerating hepatocyte nuclei are recognized. Cirrhosis is the natural evolution of many forms of hepatitis not adequately treated, it is typical of alcoholics and some dysmetabolic diseases (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, glycogenosis, hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease). The liver is generally enlarged and in any case hard and nodular. it is accompanied by edema (swelling due to accumulations of diffuse liquids), especially in the abdominal area (ascites, with a swollen and globular abdomen).
Mononucleosis
this infectious disease (kissing disease) is typically accompanied by an enlarged liver and spleen; it is generally associated with a strong sense of weakness, fever and pharyngitis (sore throat).
Hemochromatosis
often hereditary disease characterized by excessive accumulation of iron in the body; the deposit of the mineral in the liver, in particular, causes an excessive enlargement of the organ; in an advanced phase the skin takes on a bronze / grayish color.
congestive heart failure
if the heart is unable to pump adequate amounts of blood, the liver may increase in volume due to insufficient blood supply.
OTHER POSSIBLE CAUSES
An enlarged liver can also be caused by:
- other infectious diseases, such as abdominal typhus, infectious brucellosis, rickettsiosis, leishmaniasis, leucetic hepatitis or spirochetal hepatitis;
- other metabolic diseases, such as amyloidosis, type II and type IV glycogenosis, lysosomal storage diseases;
- haemopathies and lymphomas: chronic myeloid and lymphatic leukemia, haemolytic anemias, Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin type lymphomas;
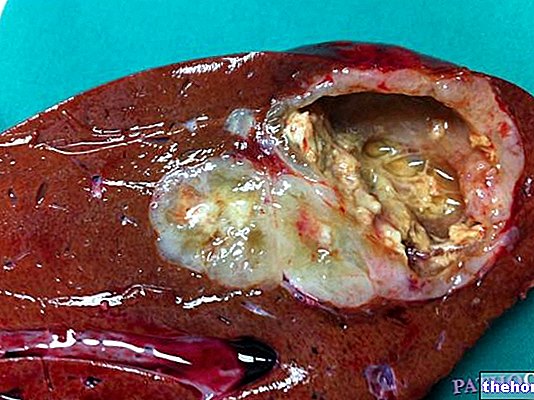
- biliary diseases: sclerosing cholangitis; biliary stasis;
- abuse of certain drugs, such as paracetamol (widely used as an analgesic and antipyretic), statins (against high cholesterol), macrolides (antibiotics), amiodarone (anti-arrhythmic drug).
Other articles on "Enlarged Liver"
- Fat liver
- Fatty Liver - Drugs for the Treatment of Fatty Liver
- Fatty liver - Herbal medicine
- Diet and Fatty Liver Disease - Fatty liver