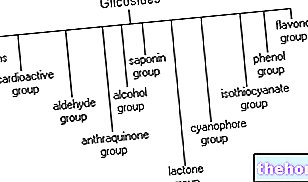
-flavonoid: the ring is in position C2 and in C3 it has bound a hydroxyl group;
-isoflavonoid: the ring is in position C3;
-flavone: the ring is in position C2.
Flavonoids are generally pigmented compounds and accumulate in vacuoles and plastids, giving the typical color to flowers and fruits. The main properties ascribed to flavonoids are the following: antioxidants, antiallergic, antiviral and antihepatotoxic.
Milk thistle
Artichoke
Blueberry
Other articles on "Flavonoid glycosides and anthocyanins"
- Arnica
- Pharmacognosy
- Milk thistle - Silybum marianum