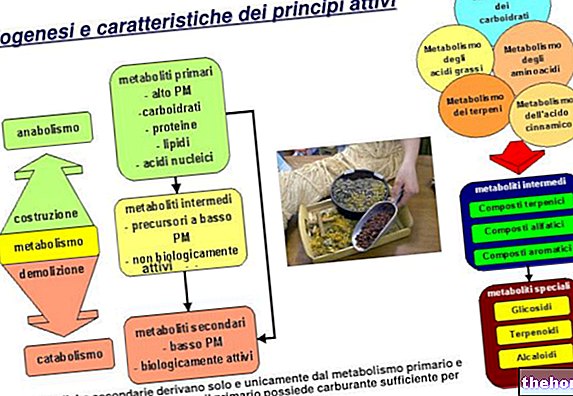
The juice poured from the fresh leaves was then cooked over high heat, to remove all the water, until it reached a solid consistency and a brown-red color, with glass fracture after breaking (therefore with clear margins).
Update: New European Regulation of 18 March 2021
On April 8, 2021, the ban on marketing foods and food supplements containing hydroxyanthracenes and their derivatives, a family of molecules contained in various plants, such as aloe, cassia, rhubarb and senna, came into force.
More in detail, the new European Regulation of March 18, 2021 - which came into force, precisely, April 8, 2021 - modifies Annex III of Regulation (EC) No. 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council to as regards the botanical species containing hydroxyanthracene derivatives.
The full text can be consulted by clicking here. However, we can summarize the main points as follows:
- The following are added to the list of substances whose use in food is prohibited (Annex III part A of the aforementioned regulation):
- Aloe-emodin and all preparations in which this substance is present;
- Emodin and all preparations in which this substance is present;
- Preparations based on leaves of Aloe species containing hydroxyanthracene derivatives;
- Dantrone and all preparations in which this substance is present.
- The following are added to the list of substances whose use in food is subject to Community surveillance (Annex III part C):
- Preparations based on the root or rhizome of Rheum palmatum L., Rheum officinale Baillon and their hybrids containing hydroxyanthracene derivatives;
- Preparations based on leaves or fruits of Cassia senna L. containing derivatives of hydroxyanthracene;
- Preparations based on bark of Rhamnus frangula L. o Rhamnus purshiana A.D. containing derivatives of hydroxyanthracene.
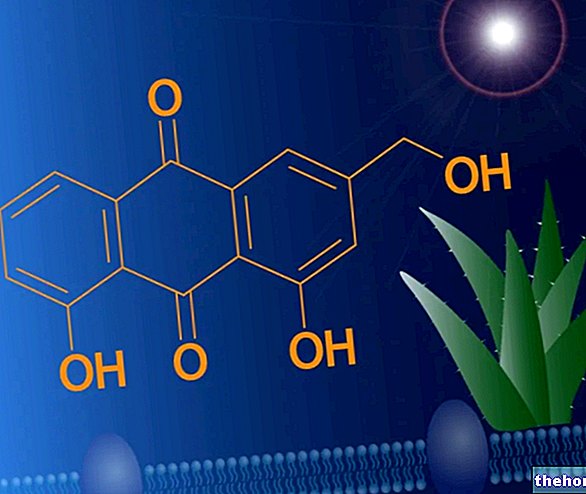
The gel (Aloe vera gel) is also obtained from the aloe leaves, which should be free of anthracenic derivatives (anthraquinones), or in any case contain very low percentages.
The leaves used to obtain the gel can be those already used to extract the juice, therefore free of anthraquinones, or derive from genetically selected species to break down the anthraquinone content and thus make them compatible with only one type of drug: the gel.
To obtain the gel, the fresh leaves of Aloe are squeezed and from this their squeezing a gel is obtained, a whitish colloidal liquid, which according to the different types of use, external or internal, is treated to be deprived of most of the content in water. The Aloe gel is also suitably worked to block the oxidation of some compounds that characterize it, both chemically and functionally; in general, preservatives, citric acid for example, are added to the aloe gel.
induced by the anthraquinones contained in the juice of the plant is of an irritative type and is decidedly drastic. For this reason, when its use was possible, the advice was to limit its use to sporadic cases.At the same weight, aloe juice - compared to senna fruit, cascara bark and rhubarb rhizome (other anthraquinone plants) - boasts the greatest laxative effects, while the minor ones are borne by rhubarb. Likewise, the side effects are greatest in aloe juice.
Aloe Vera Gel
From the compositional point of view, aloe gel is characterized by heteropolysaccharides, therefore carbohydrates, organic acids, vitamins, water.
For external use it has healing, vulnerary and humectant properties. It is used in the presence of bedsores, but above all burns, skin lesions or irritations in general; it is also an important soothing agent, like all mucilage drugs.
Usually, if the use is external, the aloe gel is treated to evaporate most of the water present, then stabilized and added with preservatives, to avoid the aggression of unwanted microorganisms and the oxidation of the main functional components, or treated with UV rays.
For internal use, however, much of the water is kept and the objectives for which it is used are different. Aloe gel for internal use is often contained within food supplements or drinks.
Other articles on "Aloe"
- Aloe in Herbalist: properties of Aloe
- Aloe: properties of Aloe
- Aloe gel
- Aloe juice
- Aloe juice: side effects
- Aloe Vera - Botanical Description, Chemical Composition
- Aloe vera - Therapeutic indications
- Aloe vera, Contraindications and Anthrichinones
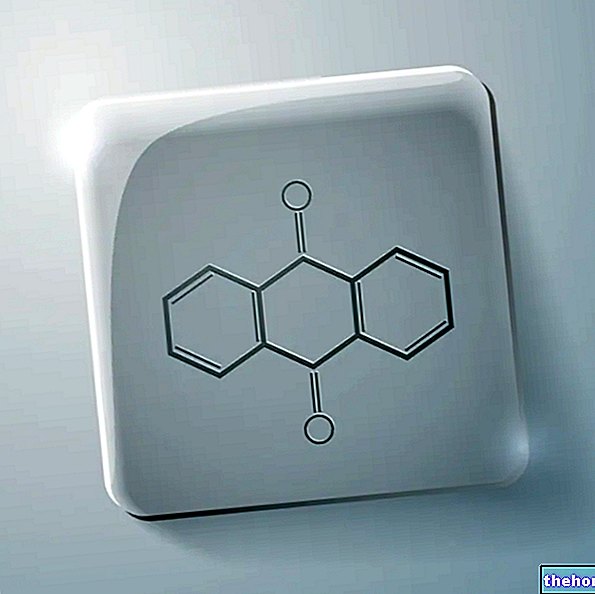
- Anthraquinones
- Pharmacognosy