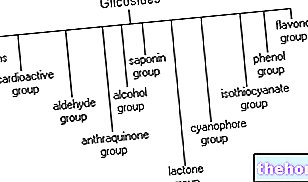
The aromatic amino acids originate from the scichimic acid, which being primary metabolites possess a greater productive urgency in the metabolic processes. If the cell does not need aromatic aa, the scichimic acid pathway gives rise to secondary metabolites: phenylalanine undergoes the " catabolic action of the phenylalanine-ammonium-lyase enzyme, which removes an amino group from the amino acid; the deaminated phenylalanine is a precursor of all secondary metabolites that originate from the metabolic pathway of scichimic acid (secondary metabolism exclusive to plant cells).
The direct product of phenylalanine deamination is cinnamic acid, identified by the name C6-C3: a 6-membered ring to which an aliphatic chain with 3 carbon atoms is linked.
Simple phenylpropanoids.
Cinnamic acid is a molecule that has in itself all the structural characteristics of simple phenylpropanoids, the first secondary metabolites that are formed in the scichimic acid pathway. Phenylpropanoid compounds are C6-C3 compounds, from which coumarins, phenols and flavonoids originate.
Among the drugs that are characterized by phenylpropanoid active principles there is the "echinacea.
Echinacea
Phenols

Simple phenols are C6-C1 compounds, or at least C6 bonded to a hydroxyl group. Phenolic compounds have retained the C6 ring of cinnamic acid and in some cases are C6-C1 compounds.
Phenols originate from the decarboxylation of cinnamic acid; their functional properties are generally disinfectant or antimicrobial. These properties are attributable to all phenols and can be extended depending on the drug that contains them. Examples of phenol drugs are:
Bearberry
Salicine
Vegetable tar
Other articles on "Drugs characterized by the presence of active ingredients deriving from the" scichimic acid pathway "
- Grinding of oils
- Pharmacognosy
- Echinacea: properties