Definition
In medical terms, liver cancer is called hepatocarcinoma: we are talking about a cancer in the vast majority of cases, unfortunately difficult to resolve. Liver cancer, although quite rare in Italy, occurs in a very virulent way, so much so that the disease gives a bad outcome in almost all patients.
Causes
Hepatocarcinoma is closely related to cirrhosis and some forms of hepatitis; it follows that limiting alcohol intake and avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse (risk factors for cirrhosis and viral hepatitis) are important guidelines for the prophylaxis of cirrhosis, therefore also of liver cancer.
Symptoms
One of the heaviest limits for the treatment of liver cancer is represented by its diagnosis: in fact, the cancer does not begin with any particular symptom, therefore the individual does not realize that he is sick. The liver cancer can still be accompanied by : ascites, asthenia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, edema, hepatomegaly, fever, loss of appetite, jaundice, nausea, itching, intense thirst, dark urine, vomiting. of colic and can cause peritonitis.
Information on Liver Cancer - Liver Cancer Treatment Medicines is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Liver Cancer - Liver Cancer Treatment Medications.
Medicines
As we have seen, the biggest obstacle to treating liver cancer is diagnosis: in fact, due to symptomatic non-specificity, liver cancer is usually diagnosed when it is too advanced. Consequently, the life expectancy of the affected patient is very low: in most cases, the liver, at the time of the tumor detection, is heavily compromised.
Surgical excision of the tumor is the most immediate therapeutic option; Unfortunately, however, it is estimated that only a quarter of sick patients can be operated on.
Alternative techniques for treating liver cancer:
- Intravenous chemotherapy: ineffective
- Local chemotherapy: the anticancer drug is injected into the hepatic artery (direct transport of the active ingredient into the diseased liver)
- Ligation of the hepatic artery: in this way the supply of nutrients to the liver is denied, consequently the tumor is induced to death
- Chemoembolization: this practice makes use of radioactive drug contrast substances that highlight the site of the tumor; the intervention aims to keep the drugs in the liver for as long as possible, blocking the hepatic circulation either permanently or temporarily.
- Radioembolization: radioactive substances are used injected through a catheter directly into the hepatic artery and from there into the area affected by the tumor.
- Radiotherapy
- Percutaneous alcoholization: ethanol is injected on site (into the tumor), using an ultrasound scan (to identify the tumor mass) and a needle to inject ethyl alcohol
- Laser ablation (pending transplant)
- Organ transplant: liver transplant is a valid therapeutic alternative for the treatment of cancer; however, it is not always possible, given that the expansion of cancer often constitutes a limit.
Liver cancer: drugs
Let us concentrate on the therapeutic use of drugs for the treatment of liver cancer: we have analyzed that the classic systemic administration (intravenous / oral) of anticancer drugs does not fully carry out the hoped-for therapeutic effect. Local applications of chemotherapy drugs, directly into the hepatic artery, appear to be more effective.
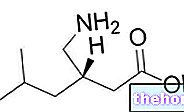
- Sorafenib (eg Nexavar) is the drug of choice in the treatment of liver cancer and is administered at the starting dose of 400 mg twice a day, one or two hours after meals. patient draws marked benefits, without serious side effects.The administration of this new chemotherapy molecule seems to increase the survival hopes of patients by three months, compared to patients who do not take any drugs.
In any case, it must be emphasized that this active ingredient is used in therapy to improve the patient's symptomatological conditions: chemotherapy - especially systemic - plays a completely marginal role in the context of liver cancer, since efficacy is not guaranteed. on the prognosis.
Other less commonly used chemotherapy molecules in liver cancer therapy include:
- Gemcitabine (eg. Gembin, tabin, gemzar)
- Oxaliplatin (eg. Eloxatin, oxaliplatin tev)
- Doxorubicin (eg Adriblastin, Caelyx, Myocet)
The dosage, method of administration and duration of therapy of the drugs described above must be established by the physician on the basis of the stage of advancement of the tumor and the patient's response to treatment.
Other articles on "Liver Cancer - Liver Cancer Medication"
- Secondary liver tumors
- Tumors of the liver
- Types of liver tumors
- Liver cancer symptoms
- Liver cancer diagnosis
- Liver cancer: survival and treatment




















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




