Definition
Female androgenetic alopecia is a condition characterized by hair loss that occurs, in fact, in female individuals.
Causes
Female androgenetic alopecia is related to the levels of androgens and occurs in women who have a certain genetic predisposition for the development of this same disorder.
In particular, women suffering from hyperandrogenism are exposed to a greater risk of experiencing the onset of alopecia. The main cause of hyperandrogenism is attributable to polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS).
Symptoms
Obviously, the characteristic symptom of female androgenetic alopecia is hair loss.
Generally, scalp thinning occurs in women from 30-40 years of age, but in some cases it can also occur later, during menopause.
In women, hair loss occurs more slowly than in men, but affects a larger area. In particular, the thinning includes the vertex and the areas behind the frontal-temporal line.
The information on Female Androgenetic Alopecia - Drugs and Treatment is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Female Androgenetic Alopecia - Drugs and Treatment.
Medicines
Although alopecia is not considered a real pathology, hair loss can have significant psychological repercussions in women who are affected by this disorder.
Fortunately, if diagnosed early, alopecia can be treated before scalp thinning becomes an irreversible process.
The therapeutic approaches normally undertaken to defeat female androgenetic alopecia include the administration of drugs topically (such as minoxidil and estrone sulfate) and systemically. This last route of administration is particularly indicated in women with hyperandrogenism associated with the syndrome of " polycystic ovary. In these cases, the active principle mostly used is ethinylestradiol in association with cyproterone acetate.

The following are the drugs most used to combat female androgenetic alopecia and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the active ingredient and dosage most suitable for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient. patient and his response to treatment.
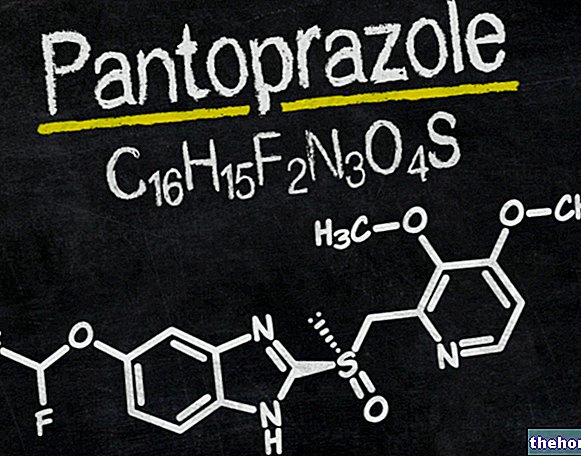
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a drug initially created as an antihypertensive to be administered orally, but - due to the side effects it causes (among which hypertrichosis stands out) - it is no longer used to treat this type of disorder.
Currently, minoxidil (Regaine ®, Aloxidil ®, Carexidil ®) is available in the form of pharmaceutical formulations for cutaneous use with specific therapeutic indications for the symptomatic treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
In fact, when administered topically, this active ingredient is able to promote hair and hair growth, even if the exact mechanism by which this occurs has not yet been fully understood.
Usually, the minoxidil-based product is applied directly to the affected area twice a day, for a period of at least 3-4 months.
In any case, it is always good to follow the instructions provided by the doctor, both as regards the frequency of administration and the duration of treatment.
It should also be remembered that minoxidil treatment should not be stopped abruptly, as there is a risk of nullifying the progress made and returning to the pre-treatment situation within a few months.
Estrone sulfate
Estrone is a female sex hormone normally produced by the body of women, especially after menopause.
It has been shown that the topical administration of this hormone in the form of estrone sulfate can be very useful in combating female androgenetic alopecia. In fact, this active principle - when applied directly on the scalp - is able to prolong the duration of the hair growth phase and to activate the production of growth factors that favor cell multiplication at the level of the hair itself.
Cyproterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol
Cyproterone acetate and ethinylestradiol (Visofid ®) can be administered in combination to treat female androgenetic alopecia in patients with hyperandrogenism.
These active substances are available for oral administration in the form of tablets containing 2 mg of cyproterone acetate and 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol.
Treatment with ethinylestradiol and cyproterone acetate should commence on the first day of menstrual bleeding and requires one tablet per day. Treatment should be discontinued 3-4 cycles after resolution of scalp thinning.
In any case, while being treated with these drugs, it is essential that you follow all the instructions given by your doctor.
Finally, it is good to remember that - although these active ingredients also have contraceptive effects - their use in the prevention of pregnancy is absolutely not recommended.