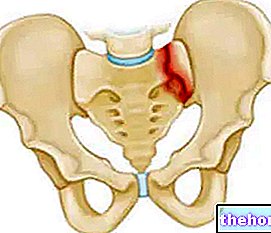
As a result of the herniation in the lumbar or lumbosacral tract of the spine, a protrusion of the intervertebral disc is created which compresses the nerve roots directed to the spinal cord and / or the lower limbs.
The lumbar hernia can be the direct consequence of trauma that the spine undergoes during physical activity, following a lifting of weights or, again, for the habit of assuming and maintaining incorrect positions. spine, loss of elasticity of the intervertebral discs, lumbar spondylosis and the deterioration of the osteoarticular structures associated with aging increase the chances of developing a lumbar disc herniation.
The main symptom is lower back pain (low back pain) which tends to radiate down the lower limbs and can occur in combination with weakness, tingling and spinal cord impairment (myelopathy).
In addition to a medical examination, to confirm the presence of a "lumbar hernia and evaluate its" entity, radiographs and magnetic resonance imaging, CT scans of the spine, electromyography and other diagnostic investigations are required.
In most cases, it is sufficient to resort to conservative treatment (rest, physiotherapy and drugs). However, if the hernia is responsible for increasingly serious neurological and motor disorders and such as to compromise the performance of daily activities, surgery may be indicated.
(fibrous ring). The role of the latter is to keep the intervertebral disc anchored to its two vertebrae. The nucleus pulposus therefore comes into contact with the nerve structures contained in the vertebral canal (spinal cord and nerve roots).
The fibrous ring can deform under the elastic thrust of the nucleus pulposus (contained hernia) or break, causing it to come out (expelled hernia) and invading an irrelevant space in the vertebral canal (migrated hernia).
of the back and the ligaments of the vertebral column play a certain importance in the appearance of the problem: the weakening and thinning to which they may be subject hinder the task of containing the nucleus pulposus in its natural seat.