Generality
Tinea versicolor (or pityriasis versicolor) is a "fungal infection that affects the skin surface.

Tinea versicolor is often associated with increased sebum and sweat production. This skin infection is favored by the combination of heat and humidity, by ineffective personal hygiene and by immunosuppression secondary to certain drug therapies, malnutrition, diabetes and other systemic diseases.
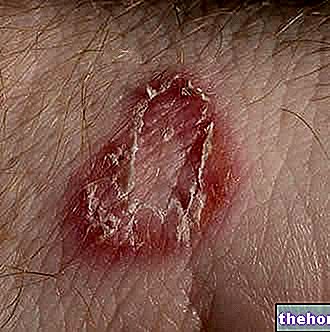
Tinea versicolor manifests itself with the appearance of small flat and discolored spots, often well demarcated. The lesions preferably appear on the upper body (neck and back) and may flow together into a larger patch.
Generally, tinea versicolor causes no other symptoms; only in some cases, the rash may cause mild itching and peeling.
Diagnosis is based on the clinical appearance of the lesions and examination of skin scarifications under a microscope.
The treatment of tinea versicolor involves the use of antifungal drugs to be applied locally on the skin (in the presence of a localized infection) or to be taken orally (in the case of extensive disease or frequent relapses).
Pityriasis versicolor is generally chronic and persistent; therefore, the doctor can also prescribe an adequate therapeutic regimen to prevent relapses. For this purpose, it is important to observe a "careful personal hygiene, choose natural fabrics (not synthetic) and wash the garments at a high temperature (at least 60 ° C).