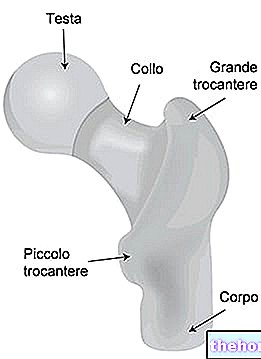
It is a "generalized osteoarthritis of the spinal column, in which the progressive, albeit slow, deformation of the posterior vertebral joints and the disc is expected.
Spondylosis should not be confused with spondylitis, despite the fact that the two terms are mistaken for synonyms.
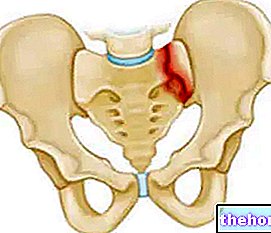
Spondylosis can compromise the spinal column in all its length, or concentrate only in some parts: in this case, the term spondylosis is refined in spondylarthrosis. When joint pain involves the lumbar spine, it is referred to as lumbar spondylosis.
, heavy work, strain, degenerative diseases affecting the spine, and surgical interventions such as, for example, the removal of herniated discs (discectomy).
One very important factor must not be overlooked: the physiological increase in collagen with respect to the gelatinous component of the disc, correlated to the progressive fibro-cartilage dehydration of the same; both of these factors weigh heavily on the symptoms derived from spondylosis.
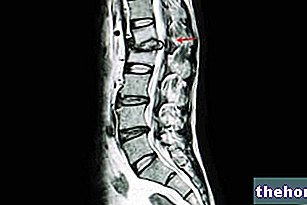
With the evolution of spondylosis, we are witnessing a possible Hard disc herniation (also called disco-osteophytic bar), responsible for the progressive narrowing of the vertebral canal. [adapted from Handbook of orthopedics and traumatology, by Federico Grassi, Ugo Pazzaglia, Giorgio Pilato].
: in these cases, the pain is generally bearable and scarcely mentioned.
In other situations, however, spondylosis could cause pains localized in a precise point, or generalized to the entire spine, causing more intense suffering: this is the case of slipping of the vertebrae, which could also generate a pseudo-invalidity.
Patients with spondylosis often complain "diffuse stiffness and intermittent pain, which is accentuated in the morning”: Pain and stiffness tend to lessen over the course of the day, with rest and with heat applications.
; however, the patient with spondylosis should rest, avoid exertion, follow a proper diet, undergo targeted physiotherapy massages, and practice stretching or swimming.
For patients suffering from severe spondylosis, surgery could represent the only solution.
For further information: Drugs for the Treatment of Spondylosis compared to the gelatinous component in the disc
- Onset of spondylosis: degenerative process of the intervertebral disc
- Evolution of the disease: sclerosis and irregularity of the bone tissue, flattening of the intervertebral discs, wear at the level of the cartilages between the joints, osteophytes, hard disc herniation
Pain of varying intensity
Perception of generalized tension
Pain accentuated in the morning
Pseudo invalidity (severe cases)
In some people, spondylosis is asymptomatic
Anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory drugs
Rest, swimming, stretching
Physiotherapy
Follow a proper diet
Surgical intervention


















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




