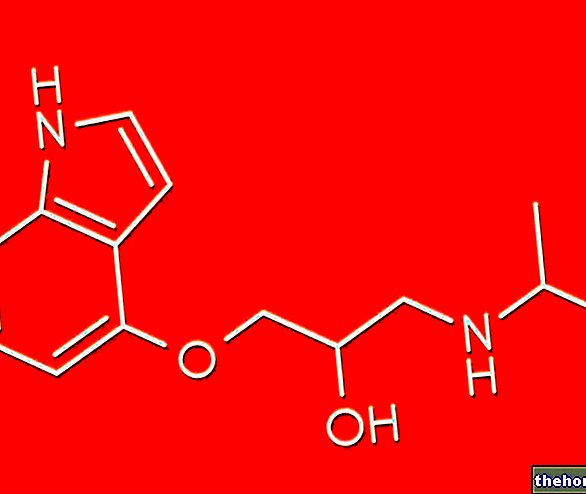
Also known as glyceryl guaiacolate, guaifenesin is able to thin, thus facilitating the expulsion of excess mucus (phlegm) produced in the course of diseases - both acute and chronic - of the respiratory system.
Guaifenesin - which chemically is an ether of guaiacol - is available in pharmaceutical formulations suitable for oral administration (syrup, oral solution, tablets to be dissolved in the mouth). The active ingredient can be found in medicines both alone and in association with active ingredients with a sedative action of cough (generally, dextromethorphan); products of this type are useful if the patient has both a fat cough and a dry cough.
Examples of Specialty Medicines Containing Guaifenesin
- Actigrip Cough Mucolitico®
- Bronchenolo Sedative and Fluidifying®
- Vicks Cough Fluidifying®
Curiosity
Guaifenesin is also used in the veterinary field by parenteral route. However, in this context it is not used as a centrally acting muscle relaxant.
whose cause could lie in asthma;- Fever;
- Persistent headache;
- Skin rashes.
Furthermore, we remind you that guaifenesin intake could interfere with the results of laboratory urine tests.
Please Note
The intake of guaifenesin-based medicinal products that contain ethyl alcohol may result in positive doping tests in relation to the alcohol concentration limits imposed.
such as dextromethorphan - the expectorant active ingredient mentioned above must never be taken in combination with cough suppressants.
In any case, before taking guaifenesin, it is advisable to inform your doctor if you are taking - or have recently taken - medicines of any kind, including over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, medicines without prescription (SOP ), natural products and herbal remedies.
Interactions with Food and Drinks
Alcoholic beverages should be avoided during guaifenesin therapy.
;Allergic reactions
Guaifenesin can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Such reactions can manifest themselves with:
- Skin reactions;
- Itching;
- Redness;
- Urticaria;
- Erythema;
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
Overdose
The accidental intake of excessive doses of guaifenesin can cause the appearance of various symptoms whose severity varies according to the amount of drug ingested:
- A mild overdose can cause gastrointestinal upset, dizziness and mental confusion.
- A severe overdose can give rise to more severe symptoms consisting of:
- Confusion;
- Excitement;
- Nausea and / or vomiting;
- Respiratory depression.
In addition, taking excessive amounts of guaifenesin medicines for long periods of time can lead to kidney stones manifesting with symptoms such as nausea, abdominal pain and changes in the normal urine characteristics.
Treatment of guaifenesin overdose is symptomatic and possibly includes gastric lavage.
Therefore, in case of suspected intake of excessive doses of guaifenesin, it is necessary to contact your doctor immediately and / or go to the nearest emergency room.
of the medicine containing guaifenesin that you want to use.Tablets to dissolve in the mouth
The guaifenesin-based tablets to be dissolved in the mouth contain lower concentrations of active ingredient (approximately 50-55 mg per tablet) than the syrup and the oral solution, therefore, they can also be used in children under the age of 12 years. The recommended doses are as follows:
- Adults and children over 12 years of age: three to six tablets a day, to be slowly dissolved in the mouth.
- Children aged between 6 and 12: two to three tablets per day.
Guaifenesin should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless your doctor deems it absolutely necessary. Therefore, although most guaifenesin-based medicines are freely available without a prescription, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should not use it without first seeking medical advice.
On the other hand, for this category of patients, before taking any drug or product, the consultation of the doctor and / or gynecologist is always required.